ബാന്റ് ഗ്യാപ്
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
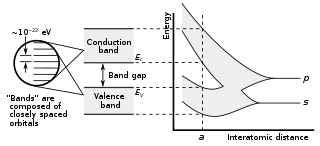
സോളിഡ് സ്റ്റേറ്റ് ഫിസിക്സിൽ ബാന്റ് ഗ്യാപ് (band gap, energy gap, അല്ലെങ്കിൽ bandgap) എന്നെല്ലാം അറിയപ്പെടുന്നത് ഒരു ഖരത്തിൽ ഇലക്ടോണുകൾക്ക് സ്ഥിതി ചെയ്യാൻ സാധ്യമല്ലാത്ത ഒരു ഊർജ്ജ മേഖലയെയാണ്.
Remove ads
സെമികണ്ടക്ടർ ഫിസിക്സിൽ

ബാന്റ് ഗ്യാപ്പുകളുടെ പട്ടിക
Remove ads
പദാർത്ഥങ്ങൾ
- Aluminium gallium arsenide
- Boron nitride
- Indium gallium arsenide
- Indium arsenide
- Gallium arsenide
- Gallium nitride
- Germanium
- Metallic hydrogen
ഇലക്ട്രോണിൿ വിഷയങ്ങളുടെ പട്ടിക
- Electronics
- Bandgap voltage reference
- Condensed matter physics
- Direct and indirect bandgaps
- Electrical conduction
- Electron hole
- Field-effect transistor
- Light-emitting diode
- Photodiode
- Photoresistor
- Photovoltaics
- Solar cell
- Solid state physics
- Semiconductor
- Semiconductor devices
- Strongly correlated material
- Valence band
Remove ads
ഇവയും കാണുക
- Wide bandgap semiconductors
- Band bending
- Spectral density
- Pseudogap
അവലംബം
പുറത്തേക്കുള്ള കണ്ണികൾ
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
