热门问题
时间线
聊天
视角
命令模式
来自维基百科,自由的百科全书
Remove ads
在面向对象编程的作用域中,命令模式(英语:Command pattern),是一种行为型设计模式,它是用来封装以后某个时间进行的一个动作或触发一个事件的所有信息的一个对象。这些信息包括方法名字,拥有这个方法的对象和给这个方法诸参数的诸值[1]。

概述
使用命令对象,可以更容易的构造以通用构件,用来在其选定的时间,委托、序列或执行方法调用,而不需要知道这个方法的类或者这个方法的诸参数。使用调用者(invoker)对象,允许方便进行对命令执行的簿记,还有为命令实现不同的模态(mode),这是由调用者对象管理的,不需要让客户知晓簿记或模态的存在。
这个设计模式的中心想法,是紧密镜像函数式编程语言中的头等函数和高阶函数的语义。尤其调用者对象是高阶函数,而命令对象是其头等实际参数。
结构
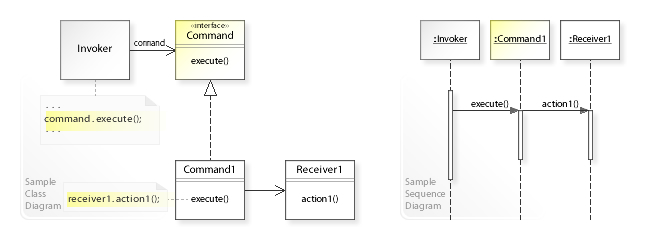
在上面的UML类图中,Invoker类不直接实现一个请求。Invoker转而提及到Command接口,通过它来办理一个请求(command.execute()),这使得Invoker独立于这些请求的办理者。Command1类实现了Command接口,它在一个接收者(receiver1.action1())上施行一个动作。此外,客户Client创建具体命令类比如Command1的对象并设置它的接收者。
UML序列图展示了运行时交互:Invoker对象调用execute()于Command1对象之上。Command1调用action1()在一个Receiver1对象之上,它办理这个请求。
示例
下面是Java例子:
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/* The Command interface */
public interface Command {
void execute();
}
/* The Invoker class */
public class Switch {
private List<Command> history = new ArrayList<Command>();
public Switch() {
}
public void storeAndExecute(Command cmd) {
this.history.add(cmd); // optional
cmd.execute();
}
}
/* The Receiver class */
public class Light {
public Light() {
}
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("The light is on");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("The light is off");
}
}
/* The Command for turning on the light - ConcreteCommand #1 */
public class FlipUpCommand implements Command {
private Light theLight;
public FlipUpCommand(Light light) {
this.theLight = light;
}
public void execute(){
theLight.turnOn();
}
}
/* The Command for turning off the light - ConcreteCommand #2 */
public class FlipDownCommand implements Command {
private Light theLight;
public FlipDownCommand(Light light) {
this.theLight = light;
}
public void execute() {
theLight.turnOff();
}
}
/* The test class or client */
public class PressSwitch {
public static void main(String[] args){
Light lamp = new Light();
Command switchUp = new FlipUpCommand(lamp);
Command switchDown = new FlipDownCommand(lamp);
Switch mySwitch = new Switch();
try {
if ("ON".equalsIgnoreCase(args[0])) {
mySwitch.storeAndExecute(switchUp);
}
else if ("OFF".equalsIgnoreCase(args[0])) {
mySwitch.storeAndExecute(switchDown);
}
else {
System.out.println("Argument \"ON\" or \"OFF\" is required.");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Arguments required.");
}
}
}
Remove ads
下面是C#例子:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace CommandPattern {
public interface ICommand {
void Execute();
}
/* The Invoker class */
public class Switch {
private List<ICommand> _commands = new List<ICommand>();
public void StoreAndExecute(ICommand command) {
_commands.Add(command);
command.Execute();
}
}
/* The Receiver class */
public class Light {
public void TurnOn() {
Console.WriteLine("The light is on");
}
public void TurnOff() {
Console.WriteLine("The light is off");
}
}
/* The Command for turning on the light - ConcreteCommand #1 */
public class FlipUpCommand : ICommand {
private Light _light;
public FlipUpCommand(Light light) {
_light = light;
}
public void Execute() {
_light.TurnOn();
}
}
/* The Command for turning off the light - ConcreteCommand #2 */
public class FlipDownCommand : ICommand {
private Light _light;
public FlipDownCommand(Light light) {
_light = light;
}
public void Execute() {
_light.TurnOff();
}
}
/* The test class or client */
internal class Program {
public static void Main(string[] args) {
Light lamp = new Light();
ICommand switchUp = new FlipUpCommand(lamp);
ICommand switchDown = new FlipDownCommand(lamp);
Switch s = new Switch();
string arg = args.Length > 0 ? args[0].ToUpper() : null;
if (arg == "ON") {
s.StoreAndExecute(switchUp);
}
else if (arg == "OFF") {
s.StoreAndExecute(switchDown);
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("Argument \"ON\" or \"OFF\" is required.");
}
}
}
}
Remove ads
下面是Python例子:
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Light():
def turn_on(self):
print("The light is on")
def turn_off(self):
print("The light is off")
class Command(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def __call__(self): pass
class FlipUpCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, light):
self.__light = light
def __call__(self):
self.__light.turn_on()
class FlipDownCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, light):
self.__light = light
def __call__(self):
self.__light.turn_off()
class Switch():
def __init__(self):
self.history = []
def __call__(self, cmd):
assert isinstance(cmd, Command)
self.history += [type(cmd).__name__]
cmd()
class PressSwitch():
def __init__(self):
lamp = Light()
self.__switch_up = FlipUpCommand(lamp)
self.__switch_down = FlipDownCommand(lamp)
self.__switch = Switch()
def __call__(self, cmd):
cmd = cmd.strip().upper()
if cmd == "ON":
self.__switch(self.__switch_up)
elif cmd == "OFF":
self.__switch(self.__switch_down)
else:
print("Argument 'On' or 'Off' is required.")
其执行:
>>> press_switch = PressSwitch()
>>> press_switch("On")
The light is on
>>> press_switch("Off")
The light is off
>>> press_switch("ThirdState")
Argument 'On' or 'Off' is required.
Remove ads
下面是Javascript例子:
/* The Invoker function */
var Switch = function(){
var _commands = [];
this.storeAndExecute = function(command){
_commands.push(command);
command.execute();
}
}
/* The Receiver function */
var Light = function(){
this.turnOn = function(){ console.log ('turn on')};
this.turnOff = function(){ console.log ('turn off') };
}
/* The Command for turning on the light - ConcreteCommand #1 */
var FlipUpCommand = function(light){
this.execute = light.turnOn;
}
/* The Command for turning off the light - ConcreteCommand #2 */
var FlipDownCommand = function(light){
this.execute = light.turnOff;
}
var light = new Light();
var switchUp = new FlipUpCommand(light);
var switchDown = new FlipDownCommand(light);
var s = new Switch();
s.storeAndExecute(switchUp);
s.storeAndExecute(switchDown);
Remove ads
下面是基于《设计模式》书中前C++98实现的C++23实现例子:
import std;
using std::shared_ptr;
using std::unique_ptr;
// Abstract command
class Command {
protected:
Command() = default;
public:
// declares an interface for executing an operation.
virtual void execute() = 0;
virtual ~Command() = default;
};
// Concrete command
template <typename Receiver>
class SimpleCommand : public Command {
private:
Receiver* receiver;
Action action;
public:
using Action = void (Receiver::*)();
// defines a binding between a Receiver object and an action.
SimpleCommand(shared_ptr<Receiver> receiver, Action action):
receiver{receiver.get()}, action{action} {}
SimpleCommand(const SimpleCommand&) = delete;
const SimpleCommand& operator=(const SimpleCommand&) = delete;
// implements execute by invoking the corresponding operation(s) on Receiver.
virtual void execute() {
(receiver->*action)();
}
};
// Receiver
class MyClass {
public:
// knows how to perform the operations associated with carrying out a request. Any class may serve as a Receiver.
void action() {
std::println("MyClass::action called");
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
shared_ptr<MyClass> receiver = std::make_shared<MyClass>();
// ...
unique_ptr<Command> command = std::make_unique<SimpleCommand<MyClass>>(receiver, &MyClass::action);
// ...
command->execute();
}
程序输出为:
MyClass::action called
Remove ads
引用
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
