热门问题
时间线
聊天
视角
桥接模式
来自维基百科,自由的百科全书
Remove ads
桥接模式(英语:bridge pattern),是一种软件设计模式, 它将针对事物的抽象与其实现进行解耦,使它们可以各自独立的变化。桥接使用了封装、聚集和继承来将诸多责任分离进入不同的类之中。
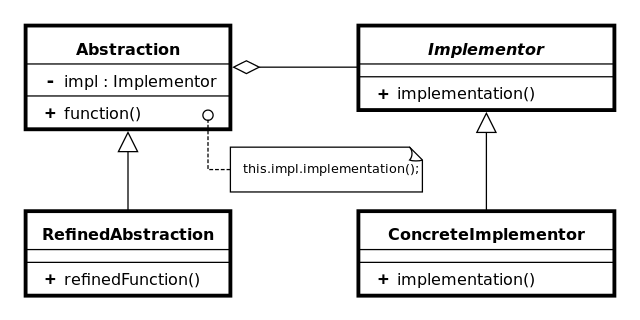
结构

、
在上面的UML类图中,抽象类(Abstraction)不实现为平常的单一继承层级。这里转而有个层级用于抽象类(Abstraction),另一个独立的层级用于它的实现者(Implementor),这使得二者相互独立。Abstraction接口(operation())的实现依据了(委托于)Implementor接口(imp.operationImp())。
UML序列图展示了运行时交互:Abstraction1对象委托实现于Implementor1对象(通过调用operationImp()在Implementor1之上),它进行运算并返回到Abstraction1。
- Abstraction:定义抽象的界面。该界面包含实现具体行为、具体特征的Implementor界面。
- Refined Abstraction:抽象界面Abstraction的子类,依旧是一个抽象的事物名。
- Implementor:定义具体行为、具体特征的应用界面。
- ConcreteImplementor:实现Implementor界面。
示例
桥接模式将事物对象的抽象概念与其具体行为和特征分离开来,如“圆形”、“三角形”归于抽象的“形状”之下,而“画圆”、“画三角”归于实现行为的“画图”类之下,然后将事物对象的抽象概念与其行为桥接起来,即由“形状”调用“画图”,例如:“圆形”调用“画圆”,而“三角形”调用“画三角”。下列各语言的代码都用于写出两个不同的圆的坐标和半径。
下面是C++的例子:
import std;
using std::string;
using std::vector;
class DrawingAPI {
public:
virtual ~DrawingAPI() = default;
virtual string drawCircle(float x, float y, float radius) const = 0;
};
class DrawingAPI01: public DrawingAPI {
public:
[[nodiscard]]
string drawCircle(float x, float y, float radius) const override {
return std::format("API01.circle at {}:{} - radius: {}", x, y, radius);
}
};
class DrawingAPI02: public DrawingAPI {
public:
[[nodiscard]]
string drawCircle(float x, float y, float radius) const override {
return std::format("API02.circle at {}:{} - radius: {}", x, y, radius);
}
};
class Shape {
protected:
const DrawingAPI& drawingApi;
public:
Shape(const DrawingAPI& api):
drawingApi{api} {}
virtual ~Shape() = default;
virtual string draw() const = 0;
virtual float resizeByPercentage(const float percent) noexcept = 0;
};
class CircleShape: public Shape {
private:
float x;
float y;
float radius;
public:
CircleShape(const DrawingAPI& api, float x, float y, float radius):
Shape(api), x{x}, y{y}, radius{radius} {}
[[nodiscard]]
string draw() const override {
return api.drawCircle(x, y, radius);
}
[[nodiscard]]
float resizeByPercentage(float percent) noexcept override {
return radius *= (1.0f + percent / 100.0f);
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
const DrawingAPI01 api1;
const DrawingAPI02 api2;
vector<CircleShape> shapes {
CircleShape{1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, api1},
CircleShape{5.0f, 7.0f, 11.0f, api2}
};
for (CircleShape& shape: shapes) {
shape.resizeByPercentage(2.5);
std::println("{}", shape.draw());
}
return 0;
}
输出为:
API01.circle at 1.000000:2.000000 - radius: 3.075000
API02.circle at 5.000000:7.000000 - radius: 11.275000
Remove ads
下面是Java的例子:
/** "Implementor" */
interface DrawingAPI {
public void drawCircle(double x, double y, double radius);
}
/** "ConcreteImplementor" 1/2 */
class DrawingAPI1 implements DrawingAPI {
public void drawCircle(double x, double y, double radius) {
System.out.printf("API1.circle at %f:%f radius %f\n", x, y, radius);
}
}
/** "ConcreteImplementor" 2/2 */
class DrawingAPI2 implements DrawingAPI {
public void drawCircle(double x, double y, double radius) {
System.out.printf("API2.circle at %f:%f radius %f\n", x, y, radius);
}
}
/** "Abstraction" */
interface Shape {
public void draw(); // low-level
public void resizeByPercentage(double pct); // high-level
}
/** "Refined Abstraction" */
class CircleShape implements Shape {
private double x, y, radius;
private DrawingAPI drawingAPI;
public CircleShape(double x, double y, double radius, DrawingAPI drawingAPI) {
this.x = x; this.y = y; this.radius = radius;
this.drawingAPI = drawingAPI;
}
// low-level i.e. Implementation specific
public void draw() {
drawingAPI.drawCircle(x, y, radius);
}
// high-level i.e. Abstraction specific
public void resizeByPercentage(double pct) {
radius *= pct;
}
}
/** "Client" */
class BridgePattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[2];
shapes[0] = new CircleShape(1, 2, 3, new DrawingAPI1());
shapes[1] = new CircleShape(5, 7, 11, new DrawingAPI2());
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
shape.resizeByPercentage(2.5);
shape.draw();
}
}
}
Remove ads
在下面的C#例子中,泛型形式的CircleShape<T>,通过T来接受接口IDrawingAPI的struct形式的继承者。
using System;
/** "Implementor" */
interface IDrawingAPI {
void DrawCircle(double x, double y, double radius);
}
/** "ConcreteImplementor" 1/2 */
struct DrawingAPI1 : IDrawingAPI {
public void DrawCircle(double x, double y, double radius) {
System.Console.WriteLine("API1.circle at {0}:{1} radius {2}", x, y, radius);
}
}
/** "ConcreteImplementor" 2/2 */
struct DrawingAPI2 : IDrawingAPI {
public void DrawCircle(double x, double y, double radius) {
System.Console.WriteLine("API2.circle at {0}:{1} radius {2}", x, y, radius);
}
}
/** "Abstraction" */
interface IShape {
void Draw(); // low-level (i.e. Implementation-specific)
void ResizeByPercentage(double pct); // high-level (i.e. Abstraction-specific)
}
/** "Refined Abstraction" */
class CircleShape<T> : IShape
where T : struct, IDrawingAPI {
private double x, y, radius;
private static IDrawingAPI drawingAPI = new T();
public CircleShape(double x, double y, double radius) {
this.x = x; this.y = y; this.radius = radius;
}
// low-level (i.e. Implementation-specific)
public void Draw() { drawingAPI.DrawCircle(x, y, radius); }
// high-level (i.e. Abstraction-specific)
public void ResizeByPercentage(double pct) { radius *= pct; }
}
/** "Client" */
class BridgePattern {
public static void Main(string[] args) {
IShape[] shapes = new IShape[2];
shapes[0] = new CircleShape<DrawingAPI1>(1, 2, 3);
shapes[1] = new CircleShape<DrawingAPI2>(5, 7, 11);
foreach (IShape shape in shapes) {
shape.ResizeByPercentage(2.5);
shape.Draw();
}
}
}
Remove ads
在《设计模式》书中所举的示例是设计部件工具箱,就像GTK与GDK之间的关系那样,关于部件的抽象Abstraction及其具体化,与关于图形库的实现者接口Implementor及其跨越既有第三方平台(比如X11、Wayland、Quartz和GDI)的不同具体实现,二者中实现者接口Implementor是先决条件,根据它才能制定抽象Abstraction的特性和方法,并编写不同的具体实现来适配不同的平台。
下面是Python的具有绘制为主要功能的图形类层级例子,这里的抽象Abstraction所具有的特性和方法是先决条件,接着根据它来制定其绘图功能的实现者接口Implementor,并编写不同的具体实现者比如栅格图绘制和矢量图绘制,通过传递显式的self参数,在运行时由具体图形对象选择其绘图功能的具体实现者:
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod
class Shape(metaclass=ABCMeta):
def __init__(self, implement):
self.draw_impl = implement.draw
def draw(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.draw_impl(self, *args, **kwargs)
@abstractmethod
def resize_by_percentage(self): pass
class Circle(Shape):
def __call__(self, x, y, radius):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.radius = radius
return self
def resize_by_percentage(self, percent):
self.radius *= 1 + percent/100
class Drawing(metaclass=ABCMeta):
@abstractmethod
def draw(self): pass
class DrawingCircle1(Drawing):
def draw(self):
print("Implementor1: drawing circle at "
+ f"({self.x},{self.y}) and radius={self.radius}")
class DrawingCircle2(Drawing):
def draw(self):
print("Implementor2: drawing circle at "
+ f"({self.x},{self.y}) and radius={self.radius}")
def test():
shape_list = [
Circle(DrawingCircle1)(1.0, 2.0, 3.0),
Circle(DrawingCircle2)(5.0, 7.0, 11.0)]
for shape in shape_list:
shape.resize_by_percentage(25)
shape.draw()
其执行:
>>> test()
Implementor1: drawing circle at (1.0,2.0) and radius=3.75
Implementor2: drawing circle at (5.0,7.0) and radius=13.75
Remove ads
引用
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
