热门问题
时间线
聊天
视角
2010年航天活动列表
来自维基百科,自由的百科全书
Remove ads
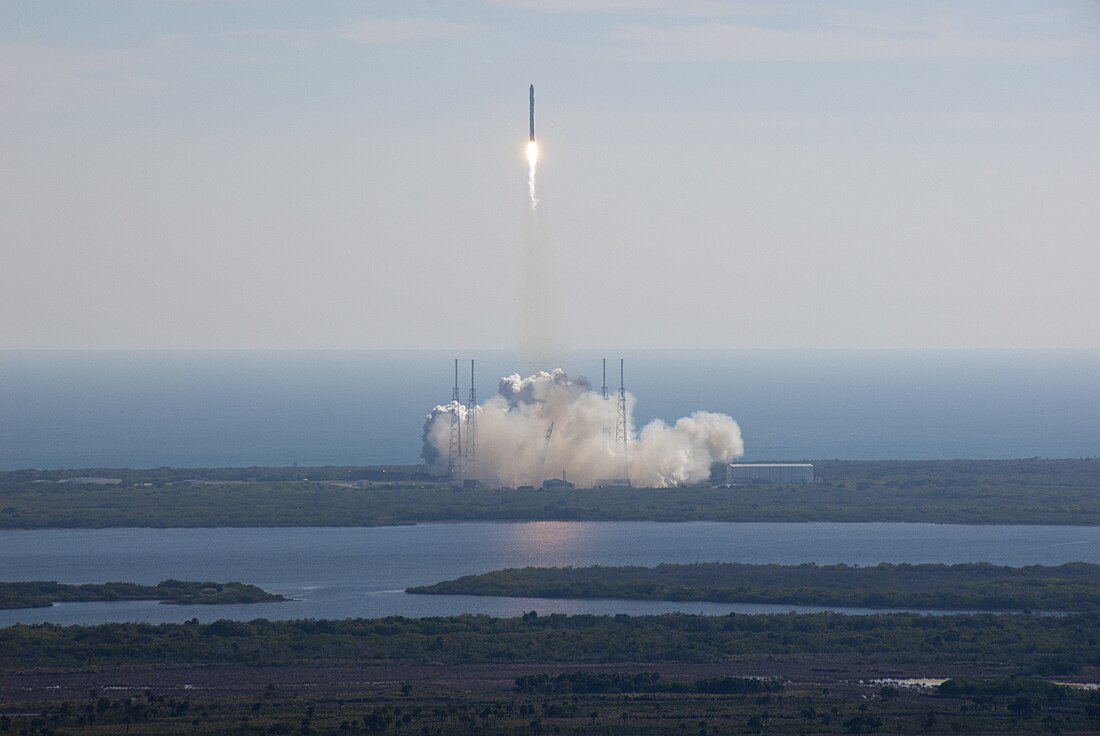
2010年,全球航天活动中出现了许多重大事件。包括用于商业轨道运输服务(英语:Commercial Orbital Transportation Services)的SpaceX龙飞船的首次飞行,该飞船旨在为国际空间站运输补给,以及猎鹰9号和米诺陶4号运载火箭的首飞。2010年6月,韩国进行了第二次罗老运载火箭的发射,该火箭在2009年首飞失败;然而,第二次尝试也失败了。宇宙3号M型运载火箭退役,于4月进行了其最后一次飞行;在9月进行了最后一次飞行后,闪电-M运载火箭(英语:Molniya-M)也宣布退役。[1]
Remove ads
概述
2010年的全球首次亚轨道发射于1月10日23:00(UTC)进行,当时一枚黑雁IX探空火箭(英语:Black Brant (rocket))作为波音YAL-1机载雷射系统的目标发射。1月11日,中国进行了该国首次反弹道导弹试验,涉及两枚导弹。全球首次轨道发射于1月16日16:12(UTC)进行,当时长征三号丙运载火箭从西昌卫星发射中心发射了北斗-G1导航卫星。
2010年共进行了74次轨道发射,其中70次成功,4次失败。最后一次轨道发射是在12月29日,当时阿丽亚娜5号ECA构型从库鲁附近的圭亚那航天中心发射了Hispasat-1E和Koreasat 6号航天器。
深空探测
5月,日本使用H-IIA运载火箭发射发射了该国首个金星探测器“破晓”号。其目的是寻找金星上的闪电和火山。[2]尽管发射成功,但该航天器未能在12月进入环绕金星的轨道[3],最终它在5年后的2015年12月才成功进入金星轨道。第一艘可操作的太阳帆“IKAROS”号与“破晓”号搭乘同一枚火箭升空。
日本的第一个小行星探测器“隼鸟”号于6月13日返回地球,此前它曾降落在小行星25143“丝川”上收集样本。[4]这也是世界上第一个成功从小行星采样返回的航天任务。[5]
10月1日10:59:57(UTC),中国成功发射嫦娥二号探测器,这是嫦娥工程的第二次任务。此次任务使用长征三号丙运载火箭从西昌卫星发射中心发射。嫦娥二号的任务与之前的嫦娥一号类似,但重点是绘制潜在着陆点,为嫦娥三号无人月球着陆器做好准备。[6]
载人航天
2010年按计划进行了7次载人飞行任务,包括3次太空梭和4次联盟号飞船任务,用于国际空间站乘组人员轮换。STS-130使用奋进号,是本年度首次载人飞行,奋进号于2月8日发射,搭载宁静号节点舱和穹顶舱前往国际空间站。4月5日,发现号执行STS-131任务,搭载“莱昂纳多”多功能后勤模块(英语:Multi-Purpose_Logistics_Module)(MPLM)为空间站提供补给。
4月2日,联盟TMA-18飞船将远征23(英语:Expedition 23)乘组人员送往国际空间站;该飞船计划在空间站对接约6个月,以便乘组人员在紧急情况下撤离。此前不久,联盟TMA-16飞船脱离对接,将前一批国际空间站乘组人员送回地球。5月14日,美国太空梭 亚特兰蒂斯号发射升空,执行其倒数第二次飞行——STS-132任务,将晨曦号实验舱(英语:Rassvet (ISS module))送往国际空间站。6月15日,联盟TMA-19飞船搭载远征24(英语:Expedition 24)乘组发射升空。10月8日,联盟TMA-01M飞船发射升空,这是现代化改造的联盟TMA飞船的首次飞行,搭载远征25(英语:Expedition 25)乘组人员前往国际空间站。最后,在年底,远征26(英语:Expedition 26)于12月15日搭乘联盟TMA-20飞船发射升空。
发射失败
2010年共发生了4起轨道发射失败事故。其中两起影响地球同步卫星运载火箭(GSLV),一起影响罗老运载火箭,另一起影响质子运载火箭。第一次失败发生在4月15日,当时是GSLV Mk.II型首次发射。火箭的第三级发生故障,导致火箭和GSAT-4卫星无法进入轨道并坠入大海。第二次失败发生在罗老运载火箭的第二次试飞期间,当时火箭搭载着STSAT-2B航天器。火箭在起飞137秒后爆炸。[7]
第三次故障发生在12月5日,当时搭载首个Blok DM-03上面级的质子-M运载火箭未能将三颗格洛纳斯-M卫星送入轨道。发射前,Blok DM的燃料加注错误,导致火箭太重而无法到达停泊轨道。[8]第四次故障发生在2010年12月25日,当时GSLV Mk.I型在GSAT-5P发射过程中爆炸。由于第一级的液体燃料助推器失控,火箭被发射场安全控制系统下令摧毁。[9]
轨道发射
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
| ← 一月 • 二月 • 三月 • 四月 • 五月 • 六月 • 七月 • 八月 • 九月 • 十月 • 十一月 • 十二月 → |
更多信息 发射时间 (UTC), 运载火箭 ...
| 发射时间 (UTC) | 运载火箭 | 火箭编号 | 发射场 | 发射服务提供商(英语:List of launch service providers) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有效载荷 (⚀ = 立方星) |
载荷用户 | 轨道 | 功能 | 再入时间 (UTC) | 结果 | |||
| 附注 | ||||||||
January | ||||||||
| 16 January 16:12 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Geosynchronous | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 28 January 00:18 |
||||||||
| VKS | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
February | ||||||||
| 3 February 03:45 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 1 July 14:40 |
Successful | ||||
| ISS flight 36P | ||||||||
| 8 February 09:14 |
||||||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS assembly | 22 February 03:22 |
Successful | ||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS assembly | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS assembly | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Crewed flight with six astronauts. | ||||||||
| 11 February 15:23 |
||||||||
| NASA | Geosynchronous | Heliophysics | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 12 February 00:39 |
||||||||
| Intelsat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
March | ||||||||
| 1 March 21:19 |
||||||||
(Glonass-M 731) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
(Glonass-M 732) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
(Glonass-M 735) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| 4 March 23:57 |
||||||||
| NOAA / NASA | Geosynchronous | Meteorology | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Satellite redesignated EWS-G2 after being transferred to the U.S. Space Force in September 2023.[11] | ||||||||
| 5 March 04:55 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | ELINT | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | ELINT | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | ELINT | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| First Long March 4 series launch from Jiuquan. | ||||||||
| 20 March 18:27 |
||||||||
| Echostar | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
April | ||||||||
| 2 April 04:04 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | Expedition 23 | 25 September 05:23 |
Successful | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts. | ||||||||
| 5 April 10:21 |
||||||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 20 April 13:08:35 |
Successful | ||||
| ASI / NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | Successful | |||||
| Crewed flight with seven astronauts. | ||||||||
| 8 April 13:57 |
||||||||
| ESA | Low Earth | Climatology | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 15 April 10:57 |
||||||||
| ISRO | Intended: Geosynchronous | Communications Navigation |
15 April | Launch failure | ||||
| Maiden flight of GSLV Mk. II, third stage failure. | ||||||||
| 16 April 15:00[来源请求] |
||||||||
| VKS | Low Earth | Reconnaissance | 21 July | Successful | ||||
| 22 April 23:52[14] |
||||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 3 December 09:16 |
Successful | ||||
| Maiden flight of Atlas V 501 and Boeing X-37B. | ||||||||
| 24 April 11:19 |
||||||||
| SES World Skies | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 27 April 01:05 |
||||||||
| VKS | Low Earth | Navigation Communications |
在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Final flight of Kosmos-3M. | ||||||||
| 28 April 17:15 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 15 November 09:35:39 |
Successful | ||||
| ISS flight 37P | ||||||||
May | ||||||||
| 14 May 18:20 |
||||||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 26 May 12:48:11 |
Successful | ||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS assembly | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Crewed flight with six astronauts. Rassvet was launched along with the MLM outfittings that included a spare elbow joint for the European Robotic Arm (ERA) (which was launched with Nauka) and an ERA-portable workpost used during EVAs, as well as a heat radiator, internal hardware and an experiment airlock for launching CubeSats to be positioned on the modified passive forward port near the nadir end of the Nauka module.[15] | ||||||||
| 20 May 21:58:22[18] |
||||||||
| JAXA | Intended: Cytherocentric Actual: Heliocentric, corrected to Cytherocentric |
Venus orbiter | 在轨 | Operational after partial spacecraft failure | ||||
| JAXA | Heliocentric | Solar sail | 在轨 | Successful | ||||
| ⚀ |
Waseda | Low Earth | Earth observation | 15 August[19] | Spacecraft failure[16][20] | |||
| ⚀ |
Kagoshima | Low Earth | Earth observation | 28 June[22] – 14[23] July | Partial spacecraft failure | |||
| ⚀ |
Soka | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 26 June[24] | Successful | |||
| UNISEC | Heliocentric | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Spacecraft failure[16][26] | ||||
| JAXA | Heliocentric | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Successful | ||||
| JAXA | Heliocentric | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Successful | ||||
| Waseda-SAT2 never contacted ground, Hayato affected by communications problems, contact lost with Shin'en on 21 May, unclear if data has been received since.[16] DCAM spacecraft deployed from IKAROS and used to observe deployment of the solar sail.[17] Akatsuki malfunctioned during Cytherocentric orbit insertion, and failed to enter orbit. It managed to orbit around Venus five years later. | ||||||||
| 21 May 22:01 |
||||||||
| SES Astra | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Bundeswehr | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 28 May 03:00 |
||||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
June | ||||||||
| 2 June 01:59 |
||||||||
| USEF | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 2 June 15:53:04 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Geosynchronous | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 3 June 22:00:08 |
||||||||
| ARABSAT | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 4 June 18:45[31] |
||||||||
| SpaceX | Low Earth | Boilerplate | 27 June 00:50[36] |
Successful | ||||
| Maiden flight of Falcon 9.[29][30] | ||||||||
| 10 June 08:01[37] |
||||||||
| KARI | Intended: Low Earth | Technology demonstration | +137 seconds | Launch failure | ||||
| Exploded during first stage burn.[7] | ||||||||
| 15 June 01:39[39] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 15 June 14:42 |
||||||||
| SSC | Low Earth (SSO)[42] | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| SSC | Low Earth (SSO)[42] | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNES | Low Earth (SSO)[42] | Helioseismology | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Hartron-Arkos | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| BPA-1 intentionally remained attached to upper stage. | ||||||||
| 15 June 21:35 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | Expedition 24 | 26 November 04:46:53 |
Successful | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts | ||||||||
| 21 June 02:14 |
||||||||
| DLR | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 22 June 19:00 |
||||||||
| IAI / Israeli Defense Forces | Low Earth (retrograde) | Reconnaissance | 在轨 | Operational[45] | ||||
| Known as Ofek-8 before launch.[43] | ||||||||
| 26 June 21:41 |
||||||||
| ARABSAT | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| KARI | Geosynchronous[47] | Communications Meteorology Oceanography |
在轨 | Successful[48] | ||||
| 30 June 15:35 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 6 September 12:53:20 |
Successful | ||||
| ISS flight 38P | ||||||||
July | ||||||||
| 10 July 18:40 |
||||||||
| Echostar | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 12 July[49] 03:53 |
||||||||
| ISRO | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| ASAL | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| ⚀ |
StudSat | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| NDRE | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| ⚀ |
SUPSI | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| AISSat and TIsat cubeSats to be launched as NLS-6, coordinated by UTIAS | ||||||||
| 31 July 21:30 |
||||||||
| CNSA | IGSO | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
August | ||||||||
| 4 August 20:59 |
||||||||
| Nilesat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| RASCOM-QAF | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 9 August 22:49[50] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Reconnaissance | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 14 August 11:07 |
||||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Intended: Geosynchronous Actual: GTO |
Communications | 在轨 | Partial spacecraft failure[51] Operational | ||||
| Maiden flight of Atlas V 531; liquid apogee engine failed to operate during orbital insertion process.[51] | ||||||||
| 24 August 07:10 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
September | ||||||||
| 2 September 00:53:43 |
||||||||
(Glonass-M 736) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
(Glonass-M 737) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
(Glonass-M 738) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| 4 September 16:14 |
||||||||
| Sinosat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 8 September 03:30 |
||||||||
| Gonets Satellite System[52] | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| VKS | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| VKS | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 10 September 10:22 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 20 February 2011 16:12 |
Successful | ||||
| ISS flight 39P | ||||||||
| 11 September[53] 11:17 |
||||||||
| JAXA | Tundra | Navigation | 在轨 | Successful[55] | ||||
| 21 September 04:03:30 |
||||||||
| NRO | Low Earth (retrograde) | 在轨 | Operational | |||||
| NRO Launch 41 | ||||||||
| 22 September 02:42[56] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Reconnaissance | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 26 September 04:41 |
||||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration Space surveillance |
在轨 | Operational | ||||
| First orbital launch of Minotaur IV. | ||||||||
| 30 September[57] 17:01[1] |
||||||||
| VKS | Molniya | Missile defense | 15 October 2022[58] | Successful | ||||
| Final flight of Molniya-M.[1] | ||||||||
October | ||||||||
| 1 October 10:59:57[59] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Selenocentric[60] | Lunar orbiter | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 6 October 00:49 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 7 October 23:10:57 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | Expedition 25 | 16 March 2011 07:54 |
Successful | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts, maiden flight of modernised Soyuz-TMA spacecraft. | ||||||||
| 14 October 18:53[61] |
||||||||
| XM Satellite Radio | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 19 October 17:10:59 |
||||||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 27 October 15:11:53 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 24 January 2011 | Successful[62] | ||||
| ISS flight 40P. | ||||||||
| 28 October[64] 21:51 |
||||||||
| Eutelsat | Intended: Geosynchronous Actual: GTO |
Communications | 在轨 | Spacecraft failure[65] | ||||
| BSAT | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational[67] | ||||
| Eutelsat W3B written-off as a total loss immediately after launch due to an oxidizer leak in the satellite's main propulsion system.[63] | ||||||||
| 31 October 16:26 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Geosynchronous | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
November | ||||||||
| 2 November 00:59[68] |
||||||||
| VKS | Molniya | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 4 November 18:37[69] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Meteorology | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 6 November 02:20 |
||||||||
| ASI | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Final flight of Delta II 7420.[70] | ||||||||
| 14 November 17:29 |
||||||||
| SkyTerra | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational[71] | ||||
| 20 November 01:25 |
||||||||
| STP | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| ⚀ |
NASA AMES | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| ⚀ |
University of Michigan | Low Earth | Auroral | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| NASA | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Partial spacecraft failure | ||||
| ⚀ |
NASA | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 17 September 2011[72] | Successful | |||
| Texas | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| UT Austin | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| USAFA | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Maiden flight of Minotaur IV/HAPS. NanoSail-D2 should have been deployed from FASTSAT seven days after launch, immediate deployment failed but ejection was confirmed almost two months later on 19 January 2011 | ||||||||
| 21 November 22:58[73] |
||||||||
| NRO | Geosynchronous | Reconnaissance | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| NROL-32 mission. | ||||||||
| 24 November 16:09[74] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 26 November 18:39 |
||||||||
| Intelsat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Avanti[76] | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 40th consecutive Ariane 5 launch success. | ||||||||
December | ||||||||
| 5 December 10:25 |
||||||||
| VKS | Intended: Medium Earth | Navigation | 5 December | Launch failure | ||||
| VKS | Intended: Medium Earth | Navigation | ||||||
| VKS | Intended: Medium Earth | Navigation | ||||||
| Maiden flight of Blok DM-03. Incorrect fuelling of upper stage led to mass being too great to achieve parking orbit, reentered over the Pacific Ocean.[8] | ||||||||
| 8 December 15:43 |
||||||||
| SpaceX / NASA | Low Earth | Flight test | 8 December 19:02 |
Successful | ||||
| ⚀ |
U.S. Army | Low Earth | Communications | 12 January 2011 | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
Northrop Grumman / USC | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 22 December | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
NRO | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 6 January 2011 | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
NRO | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 16 January 2011 | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
LANL | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 30 December | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
LANL | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 31 December | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
LANL | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 30 December | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
LANL | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 31 December | Successful | |||
| COTS Demo 1; maiden flight of the SpaceX Dragon; Mayflower included Caerus payload operated by USC. | ||||||||
| 15 December 19:09[77] |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | Expedition 26 | 24 May 2011 02:27 |
Successful | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts. | ||||||||
| 17 December 20:04 |
||||||||
| CNSA | IGSO | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 25 December 10:34 |
||||||||
| ISRO | Intended: Geosynchronous | Communications | 25 December | Launch failure | ||||
| Disintegrated during first stage flight. | ||||||||
| 26 December 22:51 |
||||||||
| Eutelsat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 29 December 21:27 |
||||||||
| Hispasat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Koreasat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
关闭
| ← 一月 • 二月 • 三月 • 四月 • 五月 • 六月 • 七月 • 八月 • 九月 • 十月 • 十一月 • 十二月 → |
Remove ads
亚轨道发射
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
更多信息 发射时间 (UTC), 运载火箭 ...
| 发射时间 (UTC) | 运载火箭 | 火箭编号 | 发射场 | 发射服务提供商(英语:List of launch service providers) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有效载荷 (⚀ = 立方星) |
载荷用户 | 轨道 | 功能 | 再入时间 (UTC) | 结果 | ||
| 附注 | |||||||
| 10 January 23:00:00[80] |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 10 January | Successful | |||
| 11 January 11:55[81] |
|||||||
| PLA | Suborbital | ABM target | 11 January | Successful | |||
| Target | |||||||
| 11 January 12:00 |
|||||||
| PLA | Suborbital | ABM test | 11 January | Successful[82] | |||
| Interceptor | |||||||
| 14 January 06:50[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 14 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 14 January 07:35[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 14 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 14 January[84] 07:45 |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 14 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 548 km(341 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 15 January 06:50[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 15 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 15 January 07:35[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 15 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 15 January 10:30[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 15 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 15 January[84] 07:45 |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 15 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 523 km(325 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 27 January 08:25[81] |
|||||||
| DGA | Suborbital | Missile test | 27 January | Successful | |||
| First launch of M51 from a submarine[85] | |||||||
| 31 January 11:40[86] |
FTG-06 | ||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | ABM target | 30 January | Successful[86] | |||
| Maiden flight of Trident I in LV-2 configuration, interceptor failed[86] | |||||||
| 31 January | FTG-06 | ||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | ABM test | 30 January | Spacecraft failure[86] | |||
| Radar tracking problem caused by unexpected "chuffing", compounded by thruster problem on interceptor, resulted in failure to intercept Trident[86] | |||||||
| 3 February | |||||||
| ISA | Suborbital | Biological | 3 February | Successful[87] | |||
| 4 February 08:03:07 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 4 February | Successful[80] | |||
| 7 February 05:20 |
|||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 7 February | Successful[88] | |||
| Travelled 3,500 km(2,175 mi) downrange | |||||||
| 9 February 09:01:00 |
|||||||
| Alaska | Suborbital | Auroral | 9 February | Successful[80] | |||
| 12 February 04:44[89] |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 12 February | Successful[89] | |||
| Destroyed by Boeing YAL-1 aircraft | |||||||
| 12 February 05:31:20 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 12 February | Successful[80] | |||
| 15 February 09:49:11 |
|||||||
| Dartmouth | Suborbital | Auroral | 15 February | Successful[80] | |||
| Apogee: 803 km(499 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 17 February | |||||||
| US Army | Suborbital | Target | 17 February | Successful | |||
| Target for MIM-104 Patriot PAC-3 MSE test, successful intercept | |||||||
| 4 March 04:50 |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 4 March | Successful | |||
| 15 March | |||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Target | 15 March | Launch failure | |||
| Target for ABM test, deviated from planned course, interceptor not launched[90] | |||||||
| 22 March | |||||||
| DSTO/U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 22 March | Successful | |||
| Hypersonic research experiment | |||||||
| 26 March 13:43 |
|||||||
| SSC / ESA | Suborbital | Microgravity | 26 March 13:55 |
Successful[91] | |||
| Apogee: 700 km(435 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 27 March 00:14[83] |
|||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 27 March | Successful | |||
| 27 March 00:18[83] |
|||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 27 March | Successful | |||
| 27 March 14:09:56[93] |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Test flight | 27 March | Successful | |||
| CalPoly | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 27 March | Successful | |||
| Kentucky Space | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 27 March | Successful | |||
| Maiden flight of Terrier-Improved Malemute, apogee: 270 km(168 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 27 March 19:37[83] |
|||||||
| Indian Army | Suborbital | Missile test | 28 March | Successful | |||
| 22 April 23:00[14] |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 22 April | Spacecraft failure[95] | |||
| Maiden flight of Minotaur IV, loss of contact with HTV nine minutes after launch.[95] | |||||||
| 3 May 09:47:00 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 3 May | Successful | |||
| 3 May 18:32:00 |
|||||||
| CU Boulder | Suborbital | Geospace/Solar | 3 May | Successful | |||
| Used to calibrate the Solar Dynamics Observatory[96] | |||||||
| 4 May 12:41:02[99] |
|||||||
| CSG | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 4 May | Successful | |||
| NMSU | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | Successful | ||||
| UNM | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | Successful | ||||
| Celestis | Suborbital | Space burial | Successful | ||||
| Reached an apogee of 113 km(70 mi), successfully recovered.[98] | |||||||
| 6 May 03:50[100][101] |
Sounding Rocket VII | ||||||
| NSPO/NCU | Suborbital | Ionospheric research | 6 May | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 289 km(180 mi)[100] | |||||||
| 8 May | |||||||
| ASFC | Suborbital | Missile test | 8 May | Successful | |||
| 8 May | |||||||
| ASFC | Suborbital | Missile test | 8 May | Successful | |||
| 17 May 11:29 |
|||||||
| Indian Army | Suborbital | Missile test | 17 May | Successful | |||
| Travelled 2,500 km(1,553 mi) downrange | |||||||
| 21 May 09:00:00 |
|||||||
| CU Boulder | Suborbital | Astronomy | 21 May | Spacecraft failure[80] | |||
| 6 June 22:25[83] |
|||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | Test flight | 6 June | Successful | |||
| Two stage test vehicle, non-intercept test | |||||||
| 8 June | |||||||
| US Navy | Suborbital | Test flight | 8 June | Successful | |||
| Follow-on Commander's Evaluation Test 42 | |||||||
| 8 June | |||||||
| US Navy | Suborbital | Test flight | 8 June | Successful | |||
| Follow-on Commander's Evaluation Test 42 | |||||||
| 9 June | |||||||
| US Navy | Suborbital | Test flight | 9 June | Successful | |||
| Follow-on Commander's Evaluation Test 43 | |||||||
| 9 June | |||||||
| US Navy | Suborbital | Test flight | 9 June | Successful | |||
| Follow-on Commander's Evaluation Test 43 | |||||||
| 16 June 10:01 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Missile test | 16 June | Successful | |||
| Travelled 6,743 km(4,190 mi) to Kwajalein Atoll | |||||||
| 24 June 11:17:00 |
|||||||
| Colorado | Suborbital | Student research | 24 June | Successful | |||
| 30 June 10:40:01[83] |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Missile test | 30 June | Successful | |||
| 10 July 11:32[102] |
|||||||
| DGA/Marine nationale | Suborbital | Test flight | 10 July | Successful | |||
| 11 July | |||||||
| Caltech[103] | Suborbital | Astronomy | 11 July | Successful | |||
| 27 July | |||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Target | 27 July | Successful | |||
| Target for ABM test, intercepted successfully by AAD | |||||||
| 30 July 18:18 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Solar | 30 July | Successful | |||
| 4 August 09:15 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Test flight Technology |
4 August | Successful | |||
| Tests of Nihka rocket motor, with secondary technology experiments | |||||||
| 6 August[104] | |||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 6 August | Successful | |||
| 6 August[104] | |||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 6 August | Successful | |||
| 23 August 17:57 |
|||||||
| SwRI | Suborbital | Solar | 23 August | Successful | |||
| 30 August 20:00[106] |
|||||||
| JAXA/TMU/Kagawa /Shizuoka |
Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 30 August | Partial spacecraft failure[105] | |||
| High-voltage control experiments not conducted as planned[105] | |||||||
| 17 September 10:03 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Test flight | 17 September | Successful | |||
| 21 September 13:07:30[107] |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 21 September 13:23[107] |
Successful[107] | |||
| 6 October | |||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | Aegis radar target | 6 October | Successful | |||
| Aegis radar target, detected by STSS-Satellites | |||||||
| 6 October | |||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | Aegis radar target | 6 October | Successful | |||
| Aegis radar target, detected by STSS-Satellites | |||||||
| 7 October[来源请求] 03:10 |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 7 October | Successful | |||
| 21 October[108] 17:00 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 21 October | Successful | |||
| 27 October 10:15[109] |
|||||||
| DLR | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 27 October | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 153 km(95 mi) | |||||||
| 28 October[来源请求] 09:59 |
|||||||
| RVSN | Suborbital | Missile test | 28 October | Successful | |||
| 28 October 10:30[来源请求] |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 28 October | Successful | |||
| 28 October 10:30[来源请求] |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 28 October | Successful | |||
| 29 October[来源请求] 01:10 |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 29 October | Successful | |||
| 29 October 03:06 |
JFTM-4 | ||||||
| JMSDF/MDA | Suborbital | ABM target | 29 October | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 161 km(100 mi), intercepted by SM-3 | |||||||
| 29 October 03:09 |
JFTM-4 | ||||||
| JMSDF | Suborbital | ABM test | 29 October | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 161 km(100 mi), intercepted target | |||||||
| 25 November 04:40 |
|||||||
| Indian Army | Suborbital | Missile test | 25 November | Successful | |||
| 4 December 04:21[110] |
|||||||
| Andøya/DLR | Suborbital | Aeronomy | 4 December | Successful | |||
| 5 December 19:11 |
|||||||
| RVSN | Suborbital | Missile test | 5 December | Successful | |||
| 6 December 16:45 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 6 December | Successful | |||
| 6 December 17:19 |
|||||||
| INPE | Suborbital | Microgravity | 6 December | Successful | |||
| Test for Operation Maracati 2[111] | |||||||
| 10 December | |||||||
| Indian Army | Suborbital | Missile test | 10 December | Launch failure | |||
| Upgraded Agni II version, fell into the sea shortly after launch | |||||||
| 12 December 06:38[112] |
|||||||
| New Hampshire | Suborbital | Geospace | 12 December | Launch failure[113] | |||
| 12 December 12:35 |
|||||||
| INPE | Suborbital | Microgravity | 12 December 12:51 |
Successful | |||
| Operation Maracati 2, MICROG 1A payload[114] | |||||||
| 13 December 03:24 |
|||||||
| Andøya/DLR | Suborbital | Aeronomy | 13 December | Successful | |||
| 15 December | FTG-06a | ||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | ABM target | 15 December | Successful | |||
| 15 December | FTG-06a | ||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | ABM test | 15 December | Spacecraft failure | |||
| Interceptor failed, the cause is under investigation | |||||||
| 19 December 02:36 |
|||||||
| Andøya/DLR | Suborbital | Aeronomy | 19 December | Successful | |||
| 21 December | |||||||
| Army of Pakistan | Suborbital | Missile test | 21 December | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 100 km(62 mi) | |||||||
| 22 December | |||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 22 December | Successful | |||
| 22 December | |||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 22 December | Successful | |||
关闭
Remove ads
深空机动
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
更多信息 日期 (UTC), 航天器 ...
| 日期 (UTC) | 航天器 | 事件 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 January | Cassini | 65th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 1,073 km(667 mi) |
| 28 January | Cassini | 66th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 7,490 km(4,654 mi) |
| 31 January | Artemis P1 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 11,992 km(7,451 mi) at 08:13 UTC[115] |
| 1 February | Artemis P2 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 69,222 km(43,013 mi) at 14:44 UTC[115] |
| 13 February | Artemis P1 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 2,958 km(1,838 mi) at 10:06 UTC[115] |
| 13 February | Cassini | Flyby of Mimas | Closest approach: 9,520 km(5,915 mi) |
| 16 February | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 991 km(616 mi) |
| 22 February | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 574 km(357 mi) |
| 25 February | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 398 km(247 mi) |
| 28 February | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 226 km(140 mi) |
| 1 March | Artemis P2 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 68,036 km(42,276 mi) at 04:11 UTC[115] |
| 2 March | Cassini | 2nd flyby of Rhea | Closest approach: 100 km(62 mi) |
| 3 March | Cassini | Flyby of Helene | Closest approach: 1,803 km(1,120 mi) |
| 3 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 67 km(42 mi) |
| 7 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 107 km(66 mi) |
| 10 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 286 km(178 mi) |
| 13 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 476 km(296 mi) |
| 16 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 662 km(411 mi) |
| 19 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 848 km(527 mi) |
| 23 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 1,341 km(833 mi) |
| 26 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 1,304 km(810 mi) |
| 28 March | Artemis P2 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 9,366 km(5,820 mi) at 07:34 UTC[115] |
| 5 April | Cassini | 67th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 7,462 km(4,637 mi) |
| 7 April | Cassini | 2nd flyby of Dione | Closest approach: 504 km(313 mi) |
| 28 April | Cassini | 9th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 103 km(64 mi) |
| 18 May | Cassini | 10th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 201 km(125 mi) |
| 20 May | Cassini | 68th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 1,400 km(870 mi) |
| 5 June | Cassini | 69th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 2,044 km(1,270 mi) |
| 13 June | Hayabusa | First sample return mission from asteroid | Sample canister successful recovered to Earth |
| 21 June | Cassini | 70th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 955 km(593 mi) |
| 7 July | Cassini | 71st flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 1,005 km(624 mi) |
| 10 July | Rosetta | Flyby of 21 Lutetia | Closest approach: 3,100 km(1,926 mi)[116] |
| 13 August | Cassini | 11th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 2,554 km(1,587 mi) |
| 25 August | Artemis P1 | LL2 orbit insertion | |
| 24 September | Cassini | 72nd flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 8,175 km(5,080 mi) |
| 6 October | Chang'e 2 | Lunar orbit insertion | |
| 16 October | Cassini | Flyby of Pallene | Closest approach: 36,000 km(22,369 mi) |
| 22 October | Artemis P2 | LL1 orbit insertion | |
| 4 November | Deep Impact | Flyby of Hartley 2 | Closest approach: 700 km(435 mi)[117] |
| 11 November | Cassini | 73rd flyby of Titan | |
| 30 November | Cassini | 12th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 47.9 km(30 mi) |
| 7 December | Akatsuki | 1st flyby of Venus | Cytherocentric orbit insertion failure Closest approach: 550 km(342 mi) |
| 8 December | IKAROS | Flyby of Venus | Closest approach: 80,800 km(50,207 mi) |
| 21 December | Cassini | 13th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 50 km(31 mi) |
| December | Shin'en | Flyby of Venus | not confirmed. |
关闭
Remove ads
舱外活动
这个部分摘自:舱外活动列表 (2000年至2014年) § 2010年[编辑]
更多信息 次数, 航天器 ...
| 次数 | 航天器 | 太空人 | 开始时间(UTC) | 结束时间(UTC) | 时间长度 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 326. | 远征22号 第一次舱外活动 |
Oleg Kotov Maksim Surayev |
2010年1月14日 10:05 |
2010年1月14日 15:49 |
5小时44分钟 | |
| 327. | STS-130 第一次舱外活动 |
Robert L. Behnken Nicholas Patrick |
2010年2月12日 02:17 |
2010年2月12日 08:49 |
6小时30分钟 | |
| 328. | STS-130 第二次舱外活动 |
Robert L. Behnken Nicholas Patrick |
2010年2月14日 02:20 |
2010年2月14日 08:14 |
5小时54分钟 | |
| 329. | STS-130 第三次舱外活动 |
Robert L. Behnken Nicholas Patrick |
2010年2月17日 02:15 |
2010年2月17日 08:03 |
5小时48分钟 | |
| 330. | STS-131 第一次舱外活动 |
Richard Mastracchio Clayton Anderson |
2010年4月9日 05:31 |
2010年4月9日 11:58 |
6小时27分钟 | |
| 331. | STS-131 第二次舱外活动 |
Richard Mastracchio Clayton Anderson |
2010年4月11日 05:20 |
2010年4月11日 12:56 |
7小时26分钟 | |
| 332. | STS-131 第三次舱外活动 |
Richard Mastracchio Clayton Anderson |
2010年4月13日 06:14 |
2010年4月13日 12:36 |
6小时24分钟 | |
| 333. | STS-132 第一次舱外活动 |
Michael T. Good Garrett Reisman |
2010年5月17日 11:54 |
2010年5月17日 19:19 |
7小时25分钟 | |
| 334. | STS-132 第二次舱外活动 |
Michael T. Good Garrett Reisman |
2010年5月19日 10:38 |
2010年5月19日 17:47 |
7小时9分钟 | |
| 335. | STS-132 第三次舱外活动 |
Michael T. Good Garrett Reisman |
2010年5月21日 10:27 |
2010年5月21日 17:13 |
6小时46分钟 | |
| 336. | 远征24 第1次 |
2010年7月27日 04:11 |
2010年7月27日 10:53 |
6小时42分钟 | ||
| 337. | 远征24 第2次 |
2010年8月7日 11:19 |
2010年8月7日 19:22 |
8小时3分钟 | ||
| 338. | 远征24 第3次 |
2010年8月11日 12:27 |
2010年8月11日 19:53 |
7小时26分钟 | ||
| 339. | 远征24 第4次 |
2010年8月16日 10:20 |
2010年8月16日 17:40 |
7小时20分钟 | ||
| 340. | 远征25 第1次 |
2010年11月15日 14:55 |
2010年11月15日 21:22 |
6小时27分钟 |
关闭
Remove ads
轨道发射统计
就本章节的主旨而言,每次航天飞行所属的国家以火箭的原产国为准,而不是发射服务提供商或发射场所在国。例如,第聂伯运载火箭虽然从俄罗斯发射,但被计入乌克兰。
- 中国: 15
- 欧洲: 6
- 印度: 3
- 以色列: 1
- 日本: 2
- 韩国: 1
- 俄罗斯: 28
- 乌克兰: 3
- 美国: 15
Remove ads
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
5
10
15
20
Ariane
Atlas
Delta
Falcon
GSLV
H-II
Long March
Minotaur
R-7
R-36
Shuttle
UR
Others
- Ariane 5
- Atlas V
- Delta II
- Delta IV
- Delta IV Heavy
- Falcon 9
- GSLV
- H-IIA
- Long March 2
- Long March 3
- Long March 4
- Minotaur IV
- Molniya-M
- Soyuz-U
- Soyuz-FG
- Soyuz-2
- Dnepr
- Space Shuttle
- Proton-M
- Rokot
- Others
By family
更多信息 Family, Country ...
| Family | Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angara | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Ariane | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Delta | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Falcon | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| GLSV | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||
| H-II | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Minotaur | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| PSLV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| R-7 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 0 | ||
| R-14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| R-36 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Shavit | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Space Shuttle | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Universal Rocket | 14 | 13 | 1 | 0 |
关闭
By type
更多信息 Rocket, Country ...
| Rocket | Country | Family | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ariane 5 | Ariane | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas V | Atlas | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Delta II | Delta | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Delta IV | Delta | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Dnepr | R-36 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Falcon 9 | Falcon | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| GSLV | GSLV | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||
| H-IIA | H-II | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kosmos | R-12/R-14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 2 | Long March | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 3 | Long March | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 4 | Long March | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Minotaur IV | Minotaur | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Molniya | R-7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Naro | Angara | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Proton | Universal Rocket | 12 | 11 | 1 | 0 | ||
| PSLV | PSLV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Shavit | Shavit | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz | R-7 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz-2 | R-7 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Space Shuttle | Space Shuttle | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| UR-100 | Universal Rocket | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
关闭
By configuration
更多信息 Rocket, Country ...
| Rocket | Country | Type | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ariane 5 ECA | Ariane 5 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas V 401 | Atlas V | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas V 501 | Atlas V | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Atlas V 531 | Atlas V | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Delta II 7420 | Delta II | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight[70] | |
| Delta IV-M+(4,2) | Delta IV | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Delta IV Heavy | Delta IV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Dnepr | Dnepr | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Falcon 9 v1.0 | Falcon 9 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| GSLV Mk I(c) | GSLV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Only flight | |
| GSLV Mk II | GSLV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| H-IIA 202 | H-IIA | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kosmos-3M | Kosmos | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Long March 2D | Long March 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 3A | Long March 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 3B | Long March 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 3C | Long March 3 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 4B | Long March 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 4C | Long March 4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Minotaur IV | Minotaur IV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Minotaur IV / HAPS | Minotaur IV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Molniya-M / 2BL | Molniya | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight[1] | |
| Naro-1 | Naro | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Proton-M / DM-2 | Proton | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Proton-M / DM-03 | Proton | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Proton-M / Briz-M | Proton | 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 | ||
| PSLV-CA | PSLV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Rokot / Briz-KM | UR-100 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Shavit-2 | Shavit | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz-2.1a / Fregat-M | Soyuz-2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz-U | Soyuz | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz-FG | Soyuz | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Space Shuttle | Space Shuttle | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
关闭
Remove ads
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
5
10
15
20
25
30
China
France
India
Israel
Japan
Kazakhstan
South Korea
Russia
United States
- Jiuquan
- Taiyuan
- Xichang
- Kourou
- Satish Dhawan
- Palmachim
- Tanegashima
- Baikonur
- Naro
- Dombarovsky
- Plesetsk
- Cape Canaveral
- Kennedy
- Kodiak
- MARS
- Vandenberg
更多信息 Site, Country ...
| Site | Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baikonur | 24 | 23 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Cape Canaveral | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Dombarovsky | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Jiuquan | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kennedy | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kodiak | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kourou | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Naro | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Palmachim | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Plesetsk | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Satish Dhawan | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Taiyuan | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Tanegashima | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Vandenberg | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Xichang | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 74 | 70 | 4 | 0 | ||
关闭
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
10
20
30
40
- Transatmospheric
- Low Earth
- Low Earth (ISS)
- Low Earth (SSO)
- Low Earth (retrograde)
- Medium Earth
- Geosychronous
(transfer) - Inclined GSO
- High Earth
- Heliocentric
更多信息 Orbital regime, Launches ...
| Orbital regime | Launches | Successes | Failures | Accidentally achieved |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transatmospheric | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Low Earth | 37 | 36 | 1 | 0 | 12 to ISS |
| Medium Earth / Molniya | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | |
| Geosynchronous / GTO | 29 | 27 | 2 | 0 | |
| High Earth / Lunar transfer | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Heliocentric / Planetary transfer | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 74 | 70 | 4 | 0 |
关闭
参考
- 中国国家航天局
- 中国探月网
- Encyclopedia Astronautica
- Gunter's Space Page - Chronology of Space Launches
- 日本宇宙航空研究开发机构
- Jonathan's Space Report(SatCat.txt与Launchlog.txt两项)
- Mission Set Database (NASA GFC)
- NASA
- NASA SpaceFlight.com
- Orbital Report News Agency's Launch Logs
- Space Calander (NASA JPL)
- Southwest Space Archive
- SPACE.com Launch Forecast
- SpaceFlightNow
- Steven Pietrobon's Space Archive
- U.S. Space Objects Registry
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
Remove ads

