Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Geography of Fiji
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Fiji is an Oceanian archipelago of volcanic islands with two main islands in the South Pacific, lying about 1,770 km (1,100 mi) north of New Zealand and 4,450 kilometres (2,765 mi) southwest of Honolulu. Of the 332 islands and 522 smaller islets making up the archipelago, about 106 are permanently inhabited.[1] The total land size is 18,272 km2 (7,055 sq mi). It has the 26th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,282,978 km2 (495,361 sq mi).

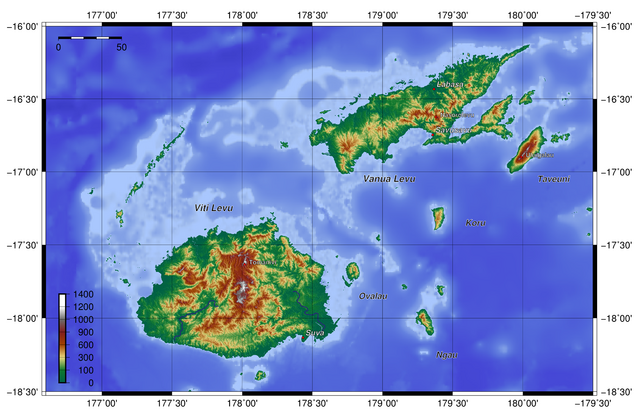
Viti Levu, the largest island, covers about 57% of the nation's land area, hosts the two official cities (the capital Suva, and Lautoka) and most other major towns, such as Nausori, Vaileka, Ba, Tavua, Kororvou, Nasinu, and Nadi (the site of the international airport), and contains some 69% of the population. Vanua Levu, 64 km (40 mi) to the northeast of Viti Levu, covers just over 30% of the land area though is home to only some 15% of the population. Its main towns are Labasa and Savusavu. In the northeast it features Natewa Bay, carving out the Loa peninsula.
Both islands are mountainous, with peaks up to 1,300 m (4,300 ft) rising abruptly from the shore, and covered with tropical forests. Heavy rains (up to 304 cm or 120 inches annually) fall on the windward (southeastern) side, covering these sections of the islands with dense tropical forest. Lowlands on the western portions of each of the main islands are sheltered by the mountains and have a well-marked dry season favorable to crops such as sugarcane.
Other islands and island groups, which cover just 12.5% of the land area and house some 16% of the population, include Taveuni southeast off Vanua Levu and Kadavu Island, south off Viti Levu (the third and fourth largest islands respectively), the Mamanuca Group (just off Nadi) and Yasawa Group (to the north of the Mamanucas), which are popular tourist destinations, the Lomaiviti Group (just off Suva) with Levuka, the former capital and the only major town on any of the smaller islands, located on the island of Ovalau, and the remote Lau Group over the Koro Sea to the east near Tonga, from which it is separated by the Lakeba Passage.
Two outlying regions are Rotuma, 400 km (250 mi) to the north, and the uninhabited coral atoll and cay Ceva-i-Ra or Conway Reef, 450 km (280 mi) to the southwest of main Fiji. Culturally conservative Rotuma with its 2,000 people on 44 km2 (17 sq mi) geographically belongs to Polynesia, and enjoys relative autonomy as a Fijian dependency.
Fiji Television reported on 21 September 2006 that the Fiji Islands Maritime and Safety Administration (FIMSA), while reviewing its outdated maritime charts, had discovered the possibility that more islands could lie within Fiji's Exclusive Economic Zone.[citation needed]
More than half of Fiji's population lives on the island coasts, either in Suva or in smaller urban centers. The interior is sparsely populated because of its rough terrain.
Remove ads
Statistics
- Location
- Oceania, island group in the South Pacific Ocean; geographic coordinates:
- 18°00′S 179°00′E
- Map references
- Oceania
- Area
- Total: 18,274 km2 (7,056 sq mi)
- Land: 18,274 km2 (7,056 sq mi)[2]
- Water: 0 km2 (0 sq mi)
- Area – comparative
- Slightly smaller than New Jersey; slightly less than one third Nova Scotia's size; slightly smaller than Wales
- Land boundaries
- 0 km (0 mi)
- Coastline
- 1,120 km (700 mi)
- Maritime claims
- Measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
- Territorial sea: 12 nautical miles (22 km; 14 mi)
- Exclusive economic zone: 1,282,978 km2 (495,361 sq mi). 200 nmi (370 km; 230 mi)
- Continental shelf: 200 m (660 ft) depth or to the depth of exploitation; rectilinear shelf claim added
- Terrain
-
- Mostly mountains of volcanic origin, beaches
- A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 438 km2 of tidal flats in Fiji, making it the 49th ranked country in terms of tidal flat area.[3]
- Elevation extremes
- Lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 km (0 mi)
- Highest point: Mount Tomanivi 1,324 metres (4,344 ft)
- Natural resources
- Timber, fish, gold, copper, offshore oil potential, hydropower
- Land use
-
- Arable land: 9.03%
- Permanent crops: 4.65%
- Other: 86.32% (2011)
- Irrigated land
- 30 km2 (12 sq mi) (2003)
- Total renewable water resources
- 28.55 km3 (6.85 cu mi) (2011)
- Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
- total: 0.08 km3/a (0.019 cu mi/a) (30%/11%/59%)
- per capita: 100.1 m3/a (130.9 cu yd/a) (2005)
- Natural hazards
- Cyclonic storms can occur from November to January
- Environment – current issues
- Deforestation; soil erosion
- Environment – international agreements
-
- Party to: biodiversity, climate change-Kyoto Protocol, desertification, endangered species, law of the sea, marine life conservation, ozone layer protection, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, wetlands
- Signed, but not ratified: None of the selected agreements
- Geography – note
- Includes 322 islands and islets of which approximately 110 are inhabited
Remove ads
Climate
Summarize
Perspective
Fiji has a tropical rainforest climate and a tropical monsoon climate (Af and Am according to the Köppen climate classification). Suva, the capital city, receives more rainfall than Nadi or the other side of Viti Levu. El Niño and La Niña events have significant impacts on rainfall.[4] Tropical cyclones can impact Fiji and in some cases they can cause severe damage and many deaths.[5][6] In 2016, Cyclone Winston caused widespread destruction and affected hundreds of thousands of people after striking Fiji.[7][8] A few years later, Cyclone Harold also caused widespread damage.[9]
Climate change in Fiji is an exceptionally pressing issue for the country – as an island nation, Fiji is particularly vulnerable to rising sea levels, coastal erosion and extreme weather.[10] These changes, along with temperature rise, will displace Fijian communities and will prove disruptive to the national economy – tourism, agriculture and fisheries, the largest contributors to the nation's GDP, will be severely impacted by climate change causing increases in poverty and food insecurity.[10] As a party to both the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Climate Agreement, Fiji hopes to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 which, along with national policies, will help to mitigate the impacts of climate change.[11]
Remove ads
Tectonics
Fiji is located on the northeast corner of the Indo-Australian plate near where it subducts under the Pacific plate on the North Fiji Basin microplate between the North Fiji Fracture Zone on the north and the Hunter fracture zone on the south. It is part of the Ring of Fire, the string of volcanoes around the boundary of the Pacific Ocean.[14]
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Fiji, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point – Uea Island, Rotuma, Eastern Division
- Easternmost point – Vatoa Island, Eastern Division
- Southernmost point – Ceva-i-Ra island, Western Division
- Westernmost point – Viwa Island, Western Division
Ecology
Fiji has more than three hundred islands, four of which are of a significant size. From largest to smallest, these four islands are Viti Levu, Vanua Levu, Kadavu Island, and Taveuni Island. The Fiji islands are home to numerous indigenous flora and fauna. These include:
Fiji once hosted several now-extinct Pleistocene and Holocene species, including a large crocodilian of the genus Volia, which was likely the apex predator of its environment. Other notable extinct species include Lapitiguana impensa, a giant iguana, as well as the flightless Viti Levu giant pigeon.
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

