Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Abacus (architecture)
Architecture term for a flat slab forming the uppermost part of a column From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In architecture, an abacus (from the Ancient Greek ἄβαξ (ábax), 'slab'; or French abaque, tailloir; pl.: abacuses or abaci)[1] is a flat slab forming the uppermost member or division of the capital of a column, above the bell. Its chief function is to provide a large supporting surface, tending to be wider than the capital, as an abutment to receive the weight of the arch or the architrave above. The diminutive of abacus, abaculus, is used to describe small mosaic tiles, also called abaciscus or tessera, used to create ornamental floors with detailed patterns of chequers or squares in a tessellated pavement.

Remove ads
Definition
Summarize
Perspective
In classical architecture, the shape of the abacus and its edge profile varies in the different classical orders. In the Greek Doric order, the abacus is a plain square slab without mouldings, supported on an echinus.[2] In the Roman and Renaissance Doric orders, it is crowned by a moulding (known as "crown moulding"). In the Tuscan and Roman Doric capital, it may rest on a boltel.
In the archaic Greek Ionic order, owing to the greater width of the capital, the abacus is rectangular in plan, and consists of a carved ovolo moulding. In later examples, the slab is thinner and the abacus remains square, except where there are angled volutes, where the slab is slightly curved. In the Roman and Renaissance Ionic capital, the abacus is square with a fillet on the top of an ogee moulding with curved edges over angled volutes.[2]

In an angular capital of the Greek Corinthian order, the abacus is moulded, its sides are concave, and its angles canted[3] (except in one or two exceptional Greek capitals, where it is brought to a sharp angle); the volutes of adjacent faces meet and project diagonally under each corner of the abacus. The same shape is adopted in the Roman and Renaissance Corinthian and Composite capitals, in some cases with the carved ovolo moulding, fillet, and cavetto.[2][4]
In Romanesque architecture, the abacus survives as a heavier slab, generally moulded and decorated. It is often square with the lower edge splayed off and moulded or carved, and the same was retained in France during the medieval period; but in England, in Early English work, a circular deeply moulded abacus was introduced, which in the 14th and 15th centuries was transformed into an octagonal one.
In Gothic architecture, the moulded forms of the abacus vary in shape, such as square, circular, or even octagonal,[5] it may even be a flat disk or drum.[2] The form of the Gothic abacus is often affected by the shape of a vault that springs from the column, in which case it is called an impost block.
Remove ads
Indian architecture (śilpaśāstra)

In śilpaśāstra, the ancient Indian science of sculpture, the abacus is commonly termed as phalaka (or phalakā).[6] It consists of a flat plate and forms part of the standard pillar (stambha). The phalaka should be constructed below the potikā ("bracket"). It is commonly found together with the dish-like maṇḍi as a single unit. The term is found in encyclopedic books such as the Mānasāra, Kāmikgāgama and the Suprabhedāgama.
Remove ads
Examples in England
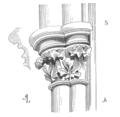
Early Saxon abaci are frequently simply chamfered, but sometimes grooved as in the crypt at Repton (fig. 1) and in the arcade of the refectory at Westminster Abbey. The abacus in Norman work is square where the columns are small; but on larger piers it is sometimes octagonal, as at Waltham Abbey. The square of the abacus is often sculptured with ornaments, as at the White Tower and at Alton, Hampshire (fig. 2). In Early English work, the abacus is generally circular, and in larger work, a group of circles (fig. 4), with some examples of octagonal and square shapes. The mouldings are generally half-rounds, which overhang deep hollows in the capital. In France, the abacus in early work is generally square, as at Chateau de Blois (fig. 3).

Examples in France
The first abacus pictured below (fig. 5) is decorated with simple mouldings and ornaments, common during the 12th century, in Île-de-France, Normandy, Champagne, and Burgundy regions, and from the choir of Vézelay Abbey (fig. 6). Figure 7 shows a circular abacus used at windows in the side chapels of Notre Dame de Paris. Towards the end of the 13th century, this element decreases in importance—they became short with a narrow profile during the 14th century, and disappeared almost entirely during the 15th century (fig. 8).
- Fig. 5
- Fig. 6
- Fig. 7
- Fig. 8
Remove ads
Sources
- Wikisource has original text related to the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition article: Abacus.
See also
Footnotes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads