Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Austenite
Metallic, non-magnetic allotrope of iron or a solid solution of iron, with an alloying element From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
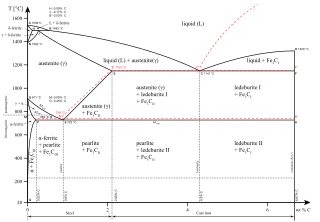
Austenite, also known as gamma-phase iron (γ-Fe), is a metallic, non-magnetic allotrope of iron or a solid solution of iron with an alloying element.[1] In plain-carbon steel, austenite exists above the critical eutectoid temperature of 1000 K (727 °C); other alloys of steel have different eutectoid temperatures. The austenite allotrope is named after Sir William Chandler Roberts-Austen (1843–1902).[2] It exists at room temperature in some stainless steels due to the presence of nickel stabilizing the austenite at lower temperatures.

Remove ads
Allotrope of iron
From 912 to 1,394 °C (1,674 to 2,541 °F) alpha iron undergoes a phase transition from body-centered cubic (BCC) to the face-centered cubic (FCC) configuration of gamma iron, also called austenite. This is similarly soft and ductile but can dissolve considerably more carbon (as much as 2.03% by mass at 1,146 °C (2,095 °F)). This gamma form of iron is present in the most commonly used type of stainless steel[citation needed] for making hospital and food-service equipment.
Remove ads
Material
Austenitization means to heat the iron, iron-based metal, or steel to a temperature at which it changes crystal structure from ferrite to austenite.[3] The more-open structure of the austenite is then able to absorb carbon from the iron-carbides in carbon steel. An incomplete initial austenitization can leave undissolved carbides in the matrix.[4]
For some iron metals, iron-based metals, and steels, the presence of carbides may occur during the austenitization step. The term commonly used for this is two-phase austenitization.[5]
Remove ads
Austempering
Austempering is a hardening process that is used on iron-based metals to promote better mechanical properties. The metal is heated into the austenite region of the iron-cementite phase diagram and then quenched in a salt bath or other heat extraction medium that is between temperatures of 300–375 °C (572–707 °F). The metal is annealed in this temperature range until the austenite turns to bainite or ausferrite (bainitic ferrite + high-carbon austenite).[6]
By changing the temperature for austenitization, the austempering process can yield different and desired microstructures.[7] A higher austenitization temperature can produce a higher carbon content in austenite, whereas a lower temperature produces a more uniform distribution of austempered structure.[7] The carbon content in austenite as a function of austempering time has been established.[8]
Behavior in plain carbon-steel
Summarize
Perspective

As austenite cools, the carbon diffuses out of the austenite and forms carbon-rich iron-carbide (cementite) and leaves behind carbon-poor ferrite. Depending on alloy composition, a layering of ferrite and cementite, called pearlite, may form. If the rate of cooling is very swift, the carbon does not have sufficient time to diffuse, and the alloy may experience a large lattice distortion known as martensitic transformation in which it transforms into martensite, a body centered tetragonal structure (BCT). The rate of cooling determines the relative proportions of martensite, ferrite, and cementite, and therefore determines the mechanical properties of the resulting steel, such as hardness and tensile strength.
A high cooling rate of thick sections will cause a steep thermal gradient in the material. The outer layers of the heat treated part will cool faster and shrink more, causing it to be under tension and thermal straining. At high cooling rates, the material will transform from austenite to martensite which is much harder and will generate cracks at much lower strains. The volume change (martensite is less dense than austenite)[9] can generate stresses as well. The difference in strain rates of the inner and outer portion of the part may cause cracks to develop in the outer portion, compelling the use of slower quenching rates to avoid this. By alloying the steel with tungsten, the carbon diffusion is slowed and the transformation to BCT allotrope occurs at lower temperatures, thereby avoiding the cracking. Such a material is said to have its hardenability increased. Tempering following quenching will transform some of the brittle martensite into tempered martensite. If a low-hardenability steel is quenched, a significant amount of austenite will be retained in the microstructure, leaving the steel with internal stresses that leave the product prone to sudden fracture.
As austenite cools, its decomposition plays a crucial role in determining the final microstructure of steel. The kinetics of this transformation are highly influenced by the morphology of the carbides present in the material. The presence of coarse carbides, for instance, can slow down the rate of austenite formation during intercritical annealing, due to their slow dissolution kinetics.[10] Pearlite, a lamellar structure consisting of alternating layers of ferrite and cementite, forms through cooperative nucleation and growth processes from austenite. The thickness of these layers has a direct impact on the mechanical properties of the steel.[10]
The decomposition of austenite is influenced by the cooling rate, which affects the morphology of carbides and thus the final steel structure. Slow cooling rates allow for the development of coarse cementite particles at grain boundaries, while faster cooling rates promote the formation of fine pearlitic colonies. Coiling temperature, in particular, has a significant impact on carbide morphology: lower coiling temperatures (below the eutectoid temperature) promote fine pearlite formation, while higher temperatures encourage the formation of coarse cementite.[10] This difference in carbide morphology influences the rate and temperature at which austenite forms and decomposes during subsequent heat treatments.[10]
Remove ads
Behavior in cast iron
Heating white cast iron (containing iron carbide, i.e. cementite, but no uncombined carbon) above 727 °C (1,341 °F) causes the formation of austenite in crystals of primary cementite.[11] This austenisation of white iron occurs in primary cementite at the interphase boundary with ferrite.[11] When the grains of austenite form in cementite, they occur as lamellar clusters oriented along the cementite crystal layer surface.[11] Austenite is formed by diffusion of carbon atoms from cementite into ferrite.[11][12]
Remove ads
Stabilization at lower temperatures
The addition of certain alloying elements, such as manganese and nickel, can stabilize the austenitic structure, facilitating heat-treatment of low-alloy steels. In the extreme case of austenitic stainless steel, much higher alloy content makes this structure stable even at room temperature.
On the other hand, such elements as silicon, molybdenum, and chromium tend to de-stabilize austenite, raising the eutectoid temperature.
Thin films
Austenite is only stable above 910 °C (1,670 °F) in bulk metal form. However, fcc transition metals can be grown on a face-centered cubic (fcc) or diamond cubic.[13] The epitaxial growth of austenite on the diamond (100) face is feasible because of the close lattice match and the symmetry of the diamond (100) face is fcc. More than a monolayer of γ-iron can be grown because the critical thickness for the strained multilayer is greater than a monolayer.[13] The determined critical thickness is in close agreement with theoretical prediction.[13]
Remove ads
Transformation and Curie point
In many magnetic ferrous alloys, the Curie point, the temperature at which magnetic materials cease to behave magnetically, occurs at nearly the same temperature as the austenite transformation. This behavior is attributed to the paramagnetic nature of austenite, while both martensite[14] and ferrite[15][16] are strongly ferromagnetic.
Thermo-optical emission, colour indicates temperature
During heat treating, a blacksmith causes phase changes in the iron-carbon system to control the material's mechanical properties, often using the annealing, quenching, and tempering processes. In this context, the color of light, or "blackbody radiation", emitted by the workpiece is an approximate gauge of temperature. Temperature is often gauged by watching the color temperature of the work, with the transition from a deep cherry-red to orange-red (815 °C (1,499 °F) to 871 °C (1,600 °F)) corresponding to the formation of austenite in medium and high-carbon steel. In the visible spectrum, this glow increases in brightness as temperature increases. When cherry-red, the glow is near its lowest intensity and may not be visible in ambient light. Hence blacksmiths usually austenitize steel in low-light conditions to accurately judge the color of the glow.
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
