
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Cranial nerve IX, for the tongue and pharynx / From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dear Wikiwand AI, let's keep it short by simply answering these key questions:
Can you list the top facts and stats about Glossopharyngeal nerve?
Summarize this article for a 10 year old
SHOW ALL QUESTIONS
The glossopharyngeal nerve (/ˌɡlɒsoʊfəˈrɪn(d)ʒiəl, -ˌfærənˈdʒiːəl/[1]), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX,[2] is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.
Quick Facts Details, To ...
| Glossopharyngeal nerve | |
|---|---|
 Plan of the upper portions of the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. | |
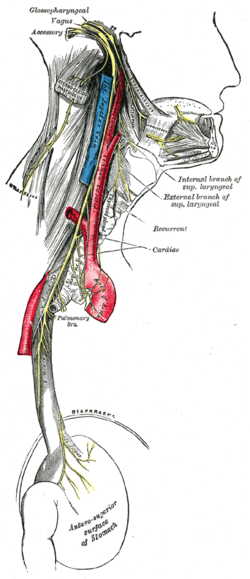 Course and distribution of the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. (Label for glossopharyngeal is at upper left.) | |
| Details | |
| To | Tympanic nerve |
| Innervates | Motor: stylopharyngeus Sensory: Oropharynx, Eustachian tube, middle ear, posterior third of tongue, carotid sinus, carotid body Special sensory: Taste to posterior third of tongue |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus glossopharyngeus |
| MeSH | D005930 |
| NeuroNames | 701, 793 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1274 |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.135 |
| TA2 | 6320 |
| FMA | 50870 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Close