Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Gupta Empire
Ancient Indian empire (c. 3rd century CE – 575 CE) From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Gupta Empire was an Indian empire during the classical period of the Indian subcontinent which existed from the mid 3rd century to mid 6th century CE. At its zenith, the dynasty ruled over an empire that spanned much of the northern Indian subcontinent.[15] This period has been considered as the Golden Age of India by some historians,[16] although this characterisation has been disputed by others.[note 1][18][19] The ruling dynasty of the empire was founded by Gupta.[20]
The high points of this period are the great cultural developments which took place primarily during the reigns of Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Kumaragupta I. Many Hindu epics and literary sources, such as the Mahabharata and Ramayana, were canonised during this period.[21] The Gupta period produced scholars such as Kalidasa,[22] Aryabhata, Varahamihira and Vatsyayana, who made significant advancements in many academic fields.[23][24][25] Science and political administration reached new heights during the Gupta era.[24] The period, sometimes described as Pax Gupta, gave rise to achievements in architecture, sculpture, and painting that "set standards of form and taste [that] determined the whole subsequent course of art, not only in India but far beyond her borders".[26] Strong trade ties also made the region an important cultural centre and established the region as a base that would influence nearby kingdoms and regions in India and Southeast Asia.[citation needed] The Puranas, earlier long poems on a variety of subjects, are also thought to have been committed to written texts around this period.[26][27] Hinduism was followed by the rulers and the Brahmins flourished in the Gupta empire but the Guptas were tolerant towards people of other faiths as well.[28]
The empire eventually died out because of factors such as substantial loss of territory and imperial authority caused by their own erstwhile feudatories, as well as the invasion by the Huna peoples (Kidarites and Alchon Huns) from Central Asia.[29][30] After the collapse of the Gupta Empire in the 6th century, India was again ruled by numerous regional kingdoms.
Remove ads
Origin
Summarize
Perspective
Guptas were originally from Magadha.[31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][excessive citations] The first evidence of Gupta connexion with Magadha comes from a foreign source. The Chinese traveller I-tsing, who came to India in A.D. 672 heard of Mahārāja Śrī-Gupta (Che-li-ki-to) who built a temple near Mrigaśikhāvana for Chinese pilgrims and endowed it with 24 villages.[41][42]
Recent numismatic research suggests that Sri Gupta, traditionally regarded as the founder of the Gupta dynasty, likely ruled as an independent monarch in the Magadha region during the late 3rd century CE. A hoard of over one hundred silver coins bearing the legend "Śrī Gupta" in Brahmi script, along with a portrait bust, have been discovered in Bihar, particularly in the Hajipur–Muzaffarpur region, a core area of ancient Magadha. These coins, uniform in typology and silver standard, reflect deliberate state issuance rather than imitation or forgery. Scholars argue that this coinage indicates Sri Gupta's sovereign authority, issued to meet local economic demands following the decline of the Kushans and to assert political identity. The use of the title Maharaja—also common among other independent tribal states of the period—further supports his autonomous status. Moreover, the later marriage alliance between Chandra Gupta I and the Lichchhavi princess Kumaradevi likely reflects the already elevated position of the Gupta family, established during the reigns of Sri Gupta and his son Ghatotkacha. This interpretation places the origin of the Gupta Empire firmly within a local Magadhan context, grounded in both political independence and early monetary sovereignty.[43]
According to one theory, they originated in the present-day lower-Doab region of Uttar Pradesh,[44][b] where most of the inscriptions and coin hoards of the early Gupta emperors have been discovered.[45][46] The recently found silver coin of Sri Gupta in Uttar Pradesh further attest the origin of Guptas around Kāśī–Kannauj region and his rule was only limited to Kāśī (present day Varanasi).[47] There also remains a possibility that this Śrīgupta coin was issued by another king.[48]
Another theory locates the Gupta homeland in the present-day Bengal region in Ganges basin, based on the account of the 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk Yijing. According to Yijing, king Che-li-ki-to (identified with the dynasty's founder Shri Gupta) built a temple for Chinese pilgrims near Mi-li-kia-si-kia-po-no (apparently a transcription of Mriga-shikha-vana). Yijing states that this temple was located more than 40 yojanas east of Nalanda, which would mean it was situated somewhere in the modern Bengal region.[49] Another proposal is that the early Gupta kingdom extended from Prayaga in the west to northern Bengal in the east.[50]
The Gupta records do not mention the dynasty's varna (social class).[51] Some historians, such as A.S. Altekar, have theorised that they were of Vaishya origin, as certain ancient Indian texts prescribe the name "Gupta" for the members of the Vaishya varna.[52][53] According to historian R. S. Sharma, the Vaishyas – who were traditionally associated with trade – may have become rulers after resisting oppressive taxation by the previous rulers.[54] Critics of the Vaishya-origin theory point out that the suffix Gupta features in the names of several non-Vaishyas before as well as during the Gupta period,[55] and the dynastic name "Gupta" may have simply derived from the name of the dynasty's first king Gupta.[56] Some scholars, such as S. R. Goyal, theorise that the Guptas were Brahmins, because they had matrimonial relations with Brahmins, but others reject this evidence as inconclusive.[57] Based on the Pune and Riddhapur inscriptions of the Gupta princess Prabhavatigupta, some scholars believe that the name of her paternal gotra (clan) was "Dharana", but an alternative reading of these inscriptions suggests that Dharana was the gotra of her mother Kuberanaga.[58]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Early rulers
Gupta (Gupta script: ![]()
![]() gu-pta, fl. late 3rd century CE) is the earliest known king of the Gupta dynasty. Different historians variously date the beginning of his reign from the mid-to-late 3rd century CE.[59][60] Gupta founded the Gupta Empire c. 240-280 CE, and was succeeded by his son, Ghatotkacha, c. 280-319 CE, followed by Ghatotkacha's son, Chandragupta I, c. 319-335 CE.[61] "Che-li-ki-to", the name of a king mentioned by the 7th century Chinese Buddhist monk Yijing, is believed to be a transcription of "Shri-Gupta" (IAST: Śrigupta), "Shri" being an honorific prefix.[62] According to Yijing, this king built a temple for Chinese Buddhist pilgrims near "Mi-li-kia-si-kia-po-no" (believed to be a transcription of Mṛgaśikhāvana).[63][relevant?]
gu-pta, fl. late 3rd century CE) is the earliest known king of the Gupta dynasty. Different historians variously date the beginning of his reign from the mid-to-late 3rd century CE.[59][60] Gupta founded the Gupta Empire c. 240-280 CE, and was succeeded by his son, Ghatotkacha, c. 280-319 CE, followed by Ghatotkacha's son, Chandragupta I, c. 319-335 CE.[61] "Che-li-ki-to", the name of a king mentioned by the 7th century Chinese Buddhist monk Yijing, is believed to be a transcription of "Shri-Gupta" (IAST: Śrigupta), "Shri" being an honorific prefix.[62] According to Yijing, this king built a temple for Chinese Buddhist pilgrims near "Mi-li-kia-si-kia-po-no" (believed to be a transcription of Mṛgaśikhāvana).[63][relevant?]

In the Allahabad Pillar inscription, Gupta and his successor Ghatotkacha are described as Maharaja ("Great King"), while the next king Chandragupta I is called a Maharajadhiraja ("King of Great Kings"). In the later period, the title Maharaja was used by feudatory rulers, which has led to suggestions that Gupta and Ghatotkacha were vassals (possibly of the Kushan Empire).[64] However, there are several instances of paramount sovereigns using the title Maharaja, in both pre-Gupta and post-Gupta periods, so this cannot be said with certainty. That said, there is no doubt that Gupta and Ghatotkacha held a lower status and were less powerful than Chandragupta I.[65]
Chandragupta I married the Licchavi princess Kumaradevi, which may have helped him extend his political power and dominions, enabling him to adopt the prestigious title Maharajadhiraja.[66] According to the dynasty's official records, he was succeeded by his son Samudragupta. However, the discovery of the coins issued by a Gupta emperor named Kacha have led to some debate on this topic: according to one theory, Kacha was another name for Samudragupta; another possibility is that Kacha was a rival claimant to the throne.[67]
Samudragupta







 ("Great King, Lord Gupta"), mentioning the first ruler of the dynasty, king Gupta. Inscription by Samudragupta on the Allahabad Pillar, where Samudragupta presents king Gupta as his great-grandfather. Dated circa 350 CE.[68]
("Great King, Lord Gupta"), mentioning the first ruler of the dynasty, king Gupta. Inscription by Samudragupta on the Allahabad Pillar, where Samudragupta presents king Gupta as his great-grandfather. Dated circa 350 CE.[68]Samudragupta succeeded his father around 335 or 350 CE, and ruled until c. 375.[69] The Allahabad Pillar inscription, composed by his courtier Harisena, credits him with extensive conquests.[70] The inscription asserts that Samudragupta uprooted 8 kings of Āryāvarta, the northern region, including the Nagas.[71] It further claims that he subjugated all the kings of the forest region, which was most probably located in central India.[72] It also credits him with defeating 12 rulers of Dakshinapatha, the southern region: the exact identification of several of these kings is debated among modern scholars,[73] but it is clear that these kings ruled areas located on the eastern coast of India.[74] The inscription suggests that Samudragupta advanced as far as the Pallava kingdom in the south, and defeated Vishnugopa, the Pallava regent of Kanchi.[75] During this southern campaign, Samudragupta most probably passed through the forest tract of central India, reached the eastern coast in present-day Odisha, and then marched south along the coast of the Bay of Bengal.[76]
The Allahabad Pillar inscription mentions that rulers of several frontier kingdoms and tribal aristocracies paid Samudragupta tributes, obeyed his orders, and performed obeisance before him.[77][78] These polities and tribes included Samatata, Davaka, Kamarupa, Nepal, Karttripura,[79] Malavas, Arjunayanas, Yaudheyas, Madrakas, and Abhiras.[78]
The inscription also mentions that several foreign kings tried to please Samudragupta by personal attendance, offered him their daughters in marriage (or according to another interpretation, gifted him maidens[80]), and sought the use of the Garuda-depicting Gupta seal for administering their own territories.[81] However, this is likely an exaggeration, and Samudragupta's panegyrist appears to have described acts of diplomacy as ones of subservience. For example, the King of Simhala is listed among these foreign rulers, but it is known that from Chinese sources that the Simhala king Meghavarna merely sent presents to the Gupta emperor requesting his permission to build a Buddhist monastery; he did not express subservience.[82]
Samudragupta appears to have been Vaishnavite, as attested by his Eran inscription,[83][84] and performed several Brahmanical ceremonies.[85] The Gupta records credit him with making generous donations of cows and gold.[83] He performed the Ashvamedha ritual (horse sacrifice), which was used by the ancient Indian kings and emperors to prove their imperial sovereignty, and issued gold coins (see Coinage below) to mark this performance.[86]
The Allahabad Pillar inscription presents Samudragupta as a wise king and strict administrator, who was also compassionate enough to help the poor and the helpless.[87] It also alludes to the king's talents as a musician and a poet, and calls him the "king of poets".[88] Such claims are corroborated by Samudragupta's gold coins, which depict him playing a veena.[89]
Samudragupta appears to have directly controlled a large part of the Indo-Gangetic Plain in present-day India, as well as a substantial part of central India.[90] His empire comprised a number of monarchical and tribal tributary states of northern India, and of the south-eastern coastal region of India.[91][74]
Ramagupta

Ramagupta is known from a sixth-century play, the Devichandragupta, in which he surrenders his queen to the enemy Sakas, forcing his brother Chandragupta to sneak into the enemy camp to rescue her and kill the Saka king. The historicity of these events is unclear, but Ramagupta's existence is confirmed by three Jain statues found at Durjanpur, with inscriptions referring to him as the Maharajadhiraja. A large number of his copper coins also have been found from the Eran-Vidisha region and classified in five distinct types, which include the Garuda,[93] Garudadhvaja, lion and border legend types. The Brahmi legends on these coins are written in the early Gupta style.[94]
Chandragupta II "Vikramaditya"
According to the Gupta records, among his sons, Samudragupta nominated prince Chandragupta II, born of queen Dattadevi, as his successor. Chandragupta II, Vikramaditya (Brave as the Sun), ruled from 375 until 415. He married a Kadamba princess of Kuntala and of Naga lineage (Nāgakulotpannnā), Kuberanaga. His daughter Prabhavatigupta from this Naga queen was married to Rudrasena II, the Vakataka king of Deccan.[95] His son Kumaragupta I was married to a Kadamba princess of the Karnataka region. Chandragupta II expanded his realm westwards, defeating the Saka Western Kshatrapas of Malwa, Gujarat and Saurashtra in a campaign lasting until 409. His main opponent Rudrasimha III was defeated by 395, and he crushed the Bengal chiefdoms. This extended his control from coast to coast, established a second capital at Ujjain and was the high point of the empire.[citation needed] Kuntala inscriptions indicate rule of Chandragupta II in Kuntala country of Karnataka.[96] Hunza inscription also indicate that Chandragupta was able to rule north western Indian subcontinent and proceeded to conquer Balkh, although some scholars have also disputed the identity of the Gupta emperor.[97] Chalukya king Vikramaditya VI (r. 1076 – 1126 CE) mentions Chandragupta with his title and states: "Why should the glory of the Kings Vikramaditya and Nanda be a hindrance any longer? He with a loud command abolished that (era), which has the name of Saka, and made that (era) which has the Chalukya counting".[98]

Despite the creation of the empire through war, his reign is remembered for its very influential style of Hindu art, literature, culture and science. Some excellent works of Hindu art such as the panels at the Dashavatara Temple in Deogarh serve to illustrate the magnificence of Gupta art during his reign. Above all, it was the synthesis of elements that gave Gupta art its distinctive flavour. During this period, the Guptas were supportive of thriving Buddhist and Jain cultures as well, and for this reason, there is also a long history of non-Hindu Gupta period art. In particular, Gupta period Buddhist art was to be influential in most of East and Southeast Asia. Many advances were recorded by the Chinese scholar and traveller Faxian in his diary and published afterwards.
The court of Chandragupta II was made even more illustrious by the fact that it was graced by the Navaratna (Nine Jewels), a group of nine who excelled in the literary arts. Among these men was Kālidāsa, whose works dwarfed the works of many other literary geniuses, not only in his own age but in the years to come. Kalidasa was mainly known for his subtle exploitation of the shringara (romantic) element in his verse.
Campaigns against foreign tribes

The 4th century Sanskrit poet Kalidasa credits Chandragupta Vikramaditya with conquering about twenty-one kingdoms, both in and outside India. After finishing his campaign in East and West India, Vikramaditya (Chandragupta II) proceeded northwards, subjugated the Parasika, then the Huna and Kamboja tribes located in the west and east Oxus valleys respectively. Thereafter, the king proceeded into the Himalaya mountains to reduce the mountain tribes of the Kinnaras, Kiratas, as well as India proper.[99][non-primary source needed] In one of his works Kalidasa also credits him with the removal of the Sakas from the country. He wrote 'Wasn't it Vikramaditya who drove the Sakas out from the lovely city of Ujjain?'.[100]
The Brihatkathamanjari of the Kashmiri writer Kshemendra states, King Vikramaditya (Chandragupta II) had "unburdened the sacred earth of the barbarians like the Sakas, Mlecchas, Kambojas, Greeks, Tusharas, Saka-Greeks, Hunas, and others, by annihilating these sinful Mlecchas completely".[101][non-primary source needed][102][103][unreliable source?]
Faxian
Faxian, a Chinese Buddhist monk, was one of the pilgrims who visited India during the reign of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta II. He started his journey from China in 399 CE and reached India in 405 CE. During his stay in India up to 411 CE, he went on a pilgrimage to Mathura, Kannauj, Kapilavastu, Kushinagar, Vaishali, Pataliputra, Kashi, and Rajagriha, and made careful observations about the empire's conditions. Faxian was pleased with the mildness of administration. The penal code was mild, and offences were punished by fines only. From his accounts, the Gupta Empire was a prosperous period. His writings form one of the most important sources for the history of this period.[104]
Faxian on reaching Mathura comments––
"The snow and heat are finely tempered, and there is neither hoarfrost nor snow. The people are numerous and happy. They have not to register their households. Only those who cultivate the royal land have to pay (a portion of) the gain from it. If they want to go, they go. If they want to stay on, they stay on. The king governs without decapitation or (other) corporal punishments. Criminals are simply fined according to circumstances. Even in cases of repeated attempts at wicked rebellion, they only have their right-hand cut off. The king's bodyguards & attendants all have salaries. Throughout the whole country, the people do not kill any living creature, not drink any intoxicating liquor, nor eat onions or garlic."[104]
Kumaragupta I

Obv: Bust of king with crescents, with traces of corrupt Greek script.[105]
Rev: Garuda standing facing with spread wings. Brahmi legend: Parama-bhagavata rajadhiraja Sri Kumaragupta Mahendraditya.[106]
Chandragupta II was succeeded by his second son Kumaragupta I, born of Mahadevi Dhruvasvamini. Kumaragupta I assumed the title, Mahendraditya.[107] He ruled until 455. Towards the end of his reign a tribe in the Narmada valley, the Pushyamitras, rose in power to threaten the empire. The Kidarites as well probably confronted the Gupta Empire towards the end of the rule of Kumaragupta I, as his son Skandagupta mentions in the Bhitari pillar inscription his efforts at reshaping a country in disarray, through reorganisation and military victories over the Pushyamitras and the Hunas.[108]
He was the founder of Nalanda University which on 15 July 2016 was declared as a UNESCO world heritage site.[109] Kumaragupta I was also a worshipper of Kartikeya.
Skandagupta
Skandagupta, son and successor of Kumaragupta I is generally considered to be the last of the great Gupta emperors. He assumed the titles of Vikramaditya and Kramaditya.[110] He defeated the Pushyamitra threat, but then was faced with invading Kidarites (sometimes described as the Hephthalites or "White Huns", known in India as the Sweta Huna), from the northwest.
He repelled a Huna attack around 455 CE, but the expense of the wars drained the empire's resources and contributed to its decline. The Bhitari Pillar inscription of Skandagupta, the successor of Chandragupta, recalls the near annihilation of the Gupta Empire following the attacks of the Kidarites.[111] The Kidarites seem to have retained the western part of the Gupta Empire.[111]
Skandagupta died in 467 and was succeeded by his agnate brother Purugupta.[112]
Decline of the empire

Following Skandagupta's death, the empire was clearly in decline,[114] and the later Gupta coinage indicates their loss of control over much of western India after 467–469.[15] Skandagupta was followed by Purugupta (467–473), Kumaragupta II (473–476), Budhagupta (476–495), Narasimhagupta (495–530), Kumaragupta III (530–540), Vishnugupta (540–550), two lesser known kings namely, Vainyagupta and Bhanugupta.
In the late 490's the Alchon Huns under Toramana and Mihirakula broke through the Gupta defences in the northwest, and much of the empire in the northwest was overrun by the Huns by 500. According to some scholars the empire disintegrated under the attacks of Toramana and his successor Mihirakula.[115][116] It appears from inscriptions that the Guptas, although their power was much diminished, continued to resist the Huns. The Hun invader Toramana was defeated by Bhanugupta in 510.[117][118] The Huns were defeated and driven out of India in 528 by King Yashodharman from Malwa, and possibly Gupta emperor Narasimhagupta.[119]
These invasions, although only spanning a few decades, had long term effects on India, and in a sense brought an end to Classical Indian civilisation.[120] Soon after the invasions, the Gupta Empire, already weakened by these invasions and the rise of local rulers such as Yashodharman, ended as well.[121] Following the invasions, northern India was left in disarray, with numerous smaller Indian powers emerging after the crumbling of the Guptas.[122] The Huna invasions are said to have seriously damaged India's trade with Europe and Central Asia.[120] In particular, Indo-Roman trade relations, which the Gupta Empire had greatly benefited from. The Guptas had been exporting numerous luxury products such as silk, leather goods, fur, iron products, ivory, pearl, and pepper from centres such as Nasik, Paithan, Pataliputra, and Benares. The Huna invasion probably disrupted these trade relations and the tax revenues that came with them.[citation needed]
Furthermore, Indian urban culture was left in decline, and Buddhism, gravely weakened by the destruction of monasteries and the killing of monks by the hand of the vehemently anti-Buddhist Shaivist Huna king Mihirakula, started to collapse.[120] Great centres of learning were destroyed, such as the city of Taxila, bringing cultural regression.[120] During their rule of 60 years, the Alchons are said to have altered the hierarchy of ruling families and the Indian caste system. For example, the Hunas are often said to have become the precursors of the Rajputs.[120]
Political fragmentation of South Asia after the retreat of the Alchon Huns to the northwest and the end of the Gupta Empire, c. 600 CE[123]
The succession of the 6th-century Guptas is not entirely clear, but the tail end recognised ruler of the dynasty's main line was King Vishnugupta, reigning from 540 to 550. In addition to the Huna invasion, the factors, which contribute to the decline of the empire include competition from the Vakatakas and the rise of Yashodharman in Malwa.[124]
The last known inscription by a Gupta emperor is from the reign of Vishnugupta (the Damudarpur copper-plate inscription),[125] in which he makes a land grant in the area of Kotivarsha (Bangarh in West Bengal) in 542/543 CE.[126] This follows the occupation of most of northern and central India by the Aulikara King Yashodharman c. 532 CE.[126]
Archaeologist Shanker Sharma concluded, based on a 2019 study, that the cause of the Gupta Empire's downfall was a devastating flood which happened around the middle of the 6th century in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.[citation needed]
Post-Gupta successor dynasties
In the heart of the former Gupta Empire, in the Gangetic region, the Guptas were succeeded by the Maukhari dynasty and the Pushyabhuti dynasty.[127] The coinage of the Maukharis and Pushyabhutis followed the silver coin type of the Guptas, with portrait of the ruler in profile (although facing in the reverse direction compared to the Guptas, a possible symbol of antagonism)[128] and the peacock on the reverse, the Brahmi legend being kept except for the name of the ruler.[127]
In the western regions, they were succeeded by Gurjaradesa, the Gurjara-Pratiharas, and later the Chaulukya-Paramara dynasties, who issued so-called Indo-Sasanian coinage, on the model of the coinage of the Sasanian Empire, which had been introduced in India by the Alchon Huns.[127]
Remove ads
Military
Summarize
Perspective

In contrast to the Maurya Empire, the Guptas introduced several military innovations to Indian warfare. Chief among these was the use of siege engines, heavy cavalry archers and heavy sword cavalry. Heavy cavalry formed the core of the Gupta Army and were supported by the traditional Indian Army elements of war elephants and light infantry.[130]
The utilisation of horse archers in the Gupta period is evidenced on the coinage of Chandragupta II, Kumaragupta I and Prakasaditya (postulated to be Purugupta)[131] that depicts the kings as horse-archers.[132][133]
There is a paucity of contemporary sources detailing the tactical operations of the Imperial Gupta Army. The best extant information comes from the Sanskrit mahakavya (epic poem) Raghuvaṃśa written by the Classical Sanskrit writer and dramatist Kalidasa. Many modern scholars put forward the view that Kalidasa lived from the reign of Chandragupta II to the reign of Skandagupta[134][135][136][137] and that the campaigns of Raghu – his protagonist in the Raghuvaṃśa – reflect those of Chandragupta II.[138] In Canto IV of the Raghuvamsa, Kalidasa relates how the king's forces clash against the powerful, cavalry-centric, forces of the Persians and later the Yavanas (probably Huns) in the North-West. Here he makes special mention of the use horse-archers in the king's army and that the horses needed much rest after the hotly contested battles.[139] The five arms of the Gupta military included infantry, cavalry, chariotry, elephantry and ships. Gunaighar copper plate inscription of Vainya Gupta mentions ships but not chariots.[140]
Religion
Summarize
Perspective
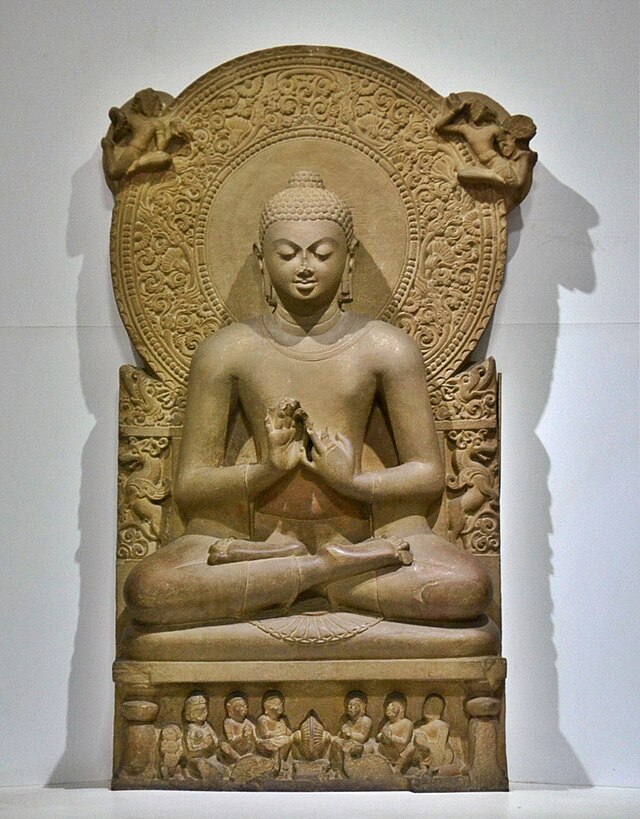

The Guptas were traditionally a Hindu dynasty.[141] They were patronizers of Brahmanism[142][143][144][145] and allowed followers of Buddhism and Jainism to practice their religions.[146] Sanchi remained an important centre of Buddhism.[146] Kumaragupta I (455 CE) is said to have founded Nalanda.[146] Modern genetic studies indicate that it was during the Gupta period that Indian caste groups ceased to intermarry (started practising/enforcing endogamy).[147]
Some later rulers however seem to have especially promoted Buddhism. Narasimhagupta Baladitya (c. 495–?), according to contemporary writer Paramartha, was brought up under the influence of the Mahayanist philosopher, Vasubandhu.[141] He built a sangharama at Nalanda and also a 300 ft (91 m) high vihara with a Buddha statue within which, according to Xuanzang, resembled the "great Vihara built under the Bodhi tree". According to the Manjushrimulakalpa (c. 800 CE), King Narasimhsagupta became a Buddhist monk, and left the world through meditation (Dhyana).[141] The Chinese monk Xuanzang also noted that Narasimhagupta Baladitya's son, Vajra, who commissioned a sangharama as well, "possessed a heart firm in faith".[148]: 45 [149]: 330
Remove ads
Administration
Summarize
Perspective
A study of the epigraphical records of the Gupta Empire shows that there was a hierarchy of administrative divisions from top to bottom. It was divided into 26 provinces, which were called Bhukti, Desha or Rajya. Provinces were also divided into vishayas or pradeshas (districts) and put under the control of Vishayapatis (district lords). A Vishayapati administered the Vishaya with the help of the Adhikarana (council of representatives), which comprised four representatives: Nagarasreshesthi, Sarthavaha, Prathamakulika and Prathama Kayastha. A part of the Vishaya was called Vithi.[150] The Gupta also had trading links with the Sassanid and Byzantine Empires.[citation needed] The four-fold varna system was observed under the Gupta period but occupations were not rigidly constrained by caste. Some Brahmins followed non-Brahmanical professions. Kshatriyas were often involved in trade and commerce.[151]
Urban centres
Gupta administration proved to be highly conducive for the rapid growth of urban centres. The principal and original capital of the Gupta Empire is regarded to be Pataliputra[2] In the fifth century, the capital was moved to Ayodhya under either Kumaragupta or Skandagupta.[3][4][5] Chandragupta Vikramaditya took personal interest in the development of Ujjain as a major cultural center after its conquest.[152] Kāśī is sometimes considered by some scholars to have been a capital, either as the original capital,[153] the principal late 6th-century capital[3] or a minor later capital.[4] The Chinese author Faxian described Magadha as a prosperous country with rich towns and large populations.
Remove ads
Legacy
Summarize
Perspective
Mathematics
Indian mathematics flourished in the Gupta Empire.[154] The Indian numerals which were the first positional base 10 numeral systems in the world originated from Gupta India. The Surya Siddhanta contains the Sine table.[155] Aryabhata wrote the Aryabhatiya, making significant contributions to mathematics including developing a Place value system, an approximation of π of 4 decimal places, trigonometric functions, and Squared triangular numbers.[156][157] Varāhamihira wrote the Pancha Siddhanta developing various formulas relating sine and cosine functions.[158] Yativṛṣabha made contributions on units of measurement.[159] Virahanka described Fibonacci numbers.[160][159]
Astronomy
Indian astronomy also saw progress in this era. The names of the seven days in a week appeared at the start of the Gupta period based on Hindu deities and planets corresponding to the Roman names.[161] Aryabhata made several contributions such as assigning the start of each day to midnight.[162] the earth's rotation on its axis, westward motion of the stars.[162] Aryabhata also mentioned that reflected sunlight is the cause behind the shining of the Moon.[162] In his book, Aryabhata, he suggested that the Earth was sphere, containing a circumference of 24,835 miles (39,967 km).[163] Varāhamihira approximates the method for determination of the meridian direction from any three positions of the shadow using a gnomon.[164]
Medicine
The Sushruta Samhita, which is a Sanskrit redaction text on all of the major concepts of Ayurveda medicine with innovative chapters on surgery, dates to the Gupta period.[165]
Metallurgy and Engineering
The Iron Pillar of Delhi high resistance to corrosion .[166][167] The corrosion resistance results from an even layer of crystalline iron(III) hydrogen phosphate hydrate forming on the high-phosphorus-content iron, which serves to protect it from the effects of the corrosion[166][167] The earliest evidence of the cotton gin was found in the fifth century, in the form of Buddhist paintings depicting a single-roller gin in the Ajanta Caves.[168] The gins consisted of a single roller made of iron or wood and a flat piece of stone or wood.[168]
Education
Various Mahavihara operated throughout the Gupta Empire serving as centuries of education.[169] Nalanda played a vital role in promoting the patronage of arts and academics during the 5th and 6th century CE.[170]
Literature
The highest point of Sanskrit literature is also said to have belonged to this period.[171] Harisena was an early writer of Kāvya poetry.[172] his works include Apabramsa Dharmapariksa, Karpuraprakara (Suktavall), the medical treatise Jagatsundari-Yogamaladhikara, Yasodharacanta, Astahnikakatha and Brhatkathakosa.[173] Amarasimha wrote various on Sanskrit grammar.[174] Kalidasa, a playwright, wrote plays such as the Abhijnanashakuntalam and Shakuntala.[175] Bhartṛhari published major works including the Trikāṇḍī and Śatakatraya.[176]
Leisure
Chess is said to have developed in this period.[177] Its early form in the 6th century, caturaṅga, which translates as "four divisions [of the military]" (infantry, cavalry, chariotry, and elephantry), was represented by the pieces that would evolve into the modern pawn, knight, rook, and bishop respectively. Doctors also invented several medical instruments, and even performed surgical operations. The ancient Gupta text Kama Sutra by the Indian scholar Vatsyayana is widely considered to be the standard work on human sexual behaviour in Sanskrit literature.
Art and architecture
- A tetrastyle prostyle Gupta period temple at Sanchi besides the Apsidal hall with Maurya foundation, an example of Buddhist architecture and Hindu architecture.[178][failed verification][179][180] 5th century CE.
- Pataini temple is a Jain temple built during the Gupta period.
The Gupta period is generally regarded as a classic peak of North Indian art for all the major religious groups. Although painting was evidently widespread, the surviving works are almost all religious sculptures. The period saw the emergence of the iconic carved stone deity in Hindu art, as well as the Buddha-figure and Jain tirthankara figures, the latter often on a very large scale. The two great centres of sculpture were Mathura and Gandhara, the latter the centre of Greco-Buddhist art. Both exported sculpture to other parts of northern India.
The most famous remaining monuments in a broadly Gupta style, the caves at Ajanta, Elephanta, and Ellora (respectively Buddhist, Hindu, and mixed including Jain) were in fact produced under later dynasties, but primarily reflect the monumentality and balance of Gupta style. Ajanta contains by far the most significant survivals of painting from this and the surrounding periods, showing a mature form which had probably had a long development, mainly in painting palaces.[181] The Hindu Udayagiri Caves actually record connections with the dynasty and its ministers,[182] and the Dashavatara Temple at Deogarh is a major temple, one of the earliest to survive, with important sculpture.[183]
- Buddha from Sarnath, 5–6th century CE
- The Colossal trimurti at the Elephanta Caves
- Nalrajar Garh fortification wall in Chilapata Forests, West Bengal, is one of the last surviving fortification remains from the Gupta period, currently 5–7 m high
- Nalanda University was first established under Gupta Empire
- Bitargaon temple from the Gupta period provide one of the earliest examples of pointed arches anywhere in the world
- Ajanta caves from Gupta era
- Krishna fighting the horse demon Keshi, 5th century
Remove ads
Family tree and list of rulers
See also
Notes
- The first two kings were titled Maharaja, all others were titled Maharajadhiraja.
- Gupta's origin:
- Bihar :
- Chakrabarty (2010, p. 70): "Magadha and its capital Pataliputra come back into focus under the Gupta dynasty. Initially, the dynasty establishes its base by coming into a matrimonial alliance with the Lichchhavis of Vaisali or north Bihar. At this stage, it is likely that the Gupta power was stretched along the northern and southern banks of the Ganga in modern Bihar."
- Mackay (2006, p. 29): "A Magadha (Bihar) kingdom, with its capital at Patna, emerged in the late 3rd century AD under Srigupta founder of a dynasty that lasted for 300 years. His grandson, Chandragupta 1 (305-25), created the splendid Gupta Empire."
- Brown (1999, p. 41): "The territory which the Guptas are first found ruling lay near Pāțaliputra, the modern Patna; it was much enlarged by one Gupta, on the decline of the Kushāņa power in its eastern territories."
- Higham (2014, p. 121): "The Gupta empire had its genesis under King Srigupta (270-290 C.E.), who ruled one of the many small kingdoms in the Ganga (Ganges) Valley in India from his capital at Pataliputra."
- Thapar (2013, p. 360): "There is some evidence of interest during the Gupta period in forms created during Mauryan times. This may have arisen from a curiosity about antecedent dynasties and their artifacts, originating in approximately the same area in which the beginnings of Gupta power were located. For both the Mauryas and the Guptas, Pāțaliputra was an important city."
- Magadha :
- Gupta (1994, p. 8): "the historicity of Sri Gupta's political career around Magadha."
- Ishikawa (2020, p. 156): "Ruling from the Magadha Kingdom in the lower Gangetic Valley, the imperial Guptas were the second pan-Indian state in history."
- Hart-Davis (2010, p. 125): "the region of Magadha gave birth to another great dynasty and empire, the Guptas."
- Kumar Maity (1975, p. 7): "the founder of this dynasty was Mahārāja Sri Gupta who was apparently a subordinate ruler and ruling somewhere near Magadha."
- Keay (2000, p. 134): "Sri Gupta was probably not a Buddhist but was raja of some minor polity near or within erstwhile Magadha."
- Jha (1998, p. 148): "Guptas... political control in the region of Magadha."
- Bemmann (2015, p. 659): "The royal dynasty of the Gupta had its origin in the central Ganges plain."
- Uttar Pradesh :
- Agrawal (2016, p. 1): "The origin has been variously traced to Magadha in Bihar, Murshidabad in West Bengal, and eastern Uttar Pradesh. [....] The last two identifications are based on the account of the travels of the Chinese pilgrim Yijing (I-Tsing), who visited India in the last quarter of the 7th century. He states that a king named Che-li-ki-to (Shri-Gupta) built a temple for the Chinese pilgrims at a place called Mi-li-kia-si-kia-po-no. According to the translation given by S. Beal, it was located 40 stages east of Nalanda when traveling along the Ganges, which would bring one to the Murshidabad district of West Bengal. However, this can easily be ruled out as the Puranas do not include West Bengal in early possessions of the Guptas. In the Allahabad Pillar inscription of Samudragupta, Bengal is described as a frontier kingdom. There is no evidence of Gupta rule in Bengal before the beginning of the 5th century. On the basis of the same account of the Chinese traveler, Mi-li-kia-si-kia-po-no has been identified with Mrigashikhavana (Sarnath), [....] This is vouched for by the recent discovery of an inscribed image of the Buddhist goddess Hariti from Sarnath, installed by King Gupta."
- Goyal (1967, pp. 44–52): "We ourselves have tackled the problem of the original home of the Guptas from an entirely different angle, and out approach has led us to conclude that they originally belonged to the eastern part of the U. P. [...] This conclusion is consonant with the facts that at least two hoards of the Gupta gold coins and five out of the eight inscriptions of the early Gupta period including the famous prasasti of Samudragupta, have been found crowded at or in the vicinity of Prayaga alone."
- Kumar (2024, p. 1): "The original home of the Guptas was the Kāśī–Kannauj region, Uttar Pradesh. Sealings and coins attributed to Śrīgupta have been found mostly in the Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, and Punjāb region."
- Khandalavala (1991, p. 1): "The progenitor of this dynasty was one named Gupta whose territory probably existed in the districts of Varanasi and Ghazipur."
- Sharma (1989, pp. 39–40): "The cumulative evidence so far available supports the theory that some region in Uttar Pradesh, most probably Eastern Uttar Pradesh, was the original home of the Guptas."
- Sharma, R.S. (2007), India's Ancient Past, Oxford University Press, p. 242, ISBN 978-0-19-568785-9,
UP therefore seems to have been the place from where the Guptas operated and fanned out in different directions. Probably with their centre of power at Prayag.
- Zhang (1996, p. 26): "Many authorities on Gupta history believe that they came from Magadha or northern Bengal... historians have now come to accept the lower Doab region as the original home of the Guptas."
- Bengal :
- Ganguly (1987, p. 19): "The Guptas, as is evident from the aforesaid discussion, laid the foundation of their kingdom in what was called the Magadha-Varendra region in ancient times."
- Bihar :
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads