Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Hokkaido
Island, prefecture, and region of Japan From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
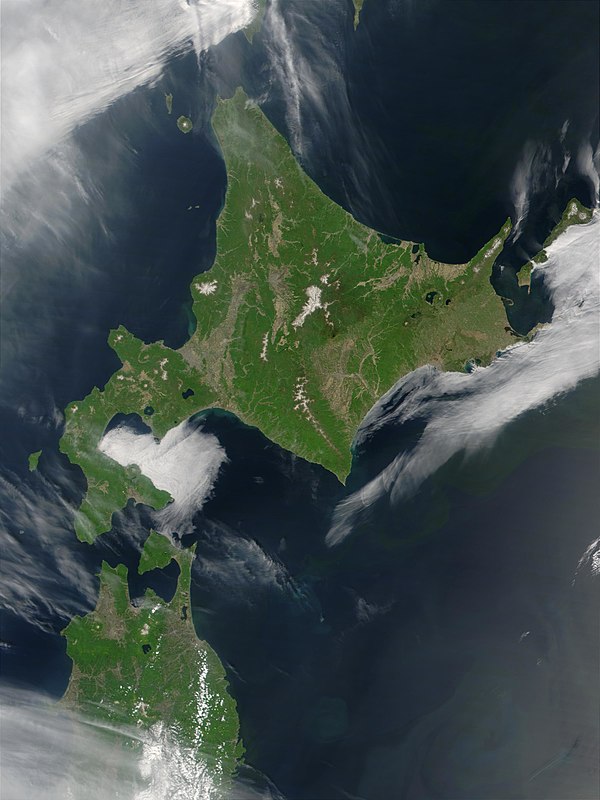
Hokkaido (Japanese: 北海道, Hepburn: Hokkaidō; pronounced [hok.kaꜜi.doː] ⓘ, lit. 'Northern Sea Circuit'; Ainu: Aynu Mosir, lit. 'Land of the Ainu')[2] is the second-largest and most northerly of Japan's four main islands. Together with its surrounding islands, it comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region.[3] The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by railway via the Seikan Tunnel.
The largest city on Hokkaido is its capital, Sapporo, which is also its only ordinance-designated city. Sakhalin lies about 43 kilometres (27 mi) to the north of Hokkaidō, and to the east and northeast are the Kuril Islands, which are administered by Russia, though the four most southerly are claimed by Japan. The position of the island on the northern end of the archipelago results in a colder climate, with the island seeing significant snowfall each winter. Despite the harsher climate, it serves as an agricultural breadbasket for many crops.
Hokkaido was formerly known as Ezo, Yezo, Yeso, or Yesso.[4] Although Japanese settlers ruled the southern tip of the island since the 16th century, Hokkaido was primarily inhabited by the Ainu people.[5] In 1869, following the Meiji Restoration, the entire island was annexed, colonized and renamed Hokkaido by Japan.[6][7][8][9][10][11] Japanese settlers dispossessed the Ainu of their land and forced them to assimilate.[5][9] In the 21st century, the Ainu are almost totally assimilated into Japanese society; as a result, the majority of Japanese people of Ainu descent have no knowledge of their heritage and culture.[12][13][14]
Remove ads
Names
Summarize
Perspective

When establishing the Development Commission, the Meiji government decided to change the name of Ezochi. Matsuura Takeshirō submitted six proposals, including names such as Kaihokudō (海北道) and Hokkaidō (北加伊道), to the government. The government eventually decided to use the name Hokkaidō, but decided to write it as 北海道, as a compromise between 海北道 and 北加伊道 because of the similarity with names such as Tōkaidō (東海道). According to Matsuura, the name was thought up because the Ainu called the region Kai. The kai element also strongly resembles the On'yomi, or Sino-Japanese, reading of the characters 蝦夷 (on'yomi as [ka.i, カイ], kun'yomi as [e.mi.ɕi, えみし]) which have been used for over a thousand years in China and Japan as the standard orthographic form to be used when referring to Ainu and related peoples; it is possible that Matsuura's kai was actually an alteration, influenced by the Sino-Japanese reading of 蝦夷 Ka-i, of the Nivkh exonym for the Ainu, namely Qoy or Gilyak pronunciation: [kʰuɣɪ].[15]
In 1947, Hokkaidō became a full-fledged prefecture. The historical suffix 道 (-dō) translates to "prefecture" in English, ambiguously the same as 府 (-fu) for Osaka and Kyoto, and 県 (-ken) for the rest of the "prefectures". Dō, as shorthand, can be used to uniquely identify Hokkaido, for example as in 道道 (dōdō, "Hokkaido road")[16] or 道議会 (Dōgikai, "Hokkaido Assembly"),[17] the same way 都 (-to) is used for Tokyo. The prefecture's government calls itself the "Hokkaidō Government" rather than the "Hokkaidō Prefectural Government".
With the rise of indigenous rights movements, there emerged a notion that Hokkaido should have an Ainu language name. If a decision to change the name is made, however, whichever Ainu phrase is chosen, its original referent is critically different from the large geographical entity. The phrase aynumosir (アイヌモシㇼ) has been a preferred choice among Japanese activists.[18] Its primary meaning is the "land of humans", as opposed to the "land of gods" (kamuymosir). When contrasted with sisammosir (the land of the neighbors, often pointing to Honshu or Japanese settlements on the southern tip of Hokkaido), it means the land of the Ainu people, which, depending on context, can refer to Hokkaido,[19] although from a modern ethnolinguistic point of view, the Ainu people have extended their domain to a large part of Sakhalin and the entire Kuril Islands. Another phrase, yaunmosir (ヤウンモシㇼ), has gained prominence. It literally means the "onshore land", as opposed to the "offshore land" (repunmosir), which, depending on context, can refer to the Kuril Islands, Honshu, or any foreign country. If the speaker is a resident of Hokkaido, yaunmosir can refer to Hokkaido.[20] Yet another phrase, akor mosir (アコㇿモシㇼ) means "our (inclusive) land". When used by Hokkaido Ainus, it can refer to Hokkaido or Japan as a whole.[19]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Early history
During the Jomon period the local culture and the associated hunter-gatherer lifestyle flourished in Hokkaidō, beginning over 15,000 years ago. In contrast to the island of Honshu, Hokkaidō saw an absence of conflict during this time period. Jomon beliefs in natural spirits are theorized to be the origins of Ainu spirituality. About 2,000 years ago, the island was colonized by Yayoi people, and much of the island's population shifted away from hunting and gathering towards agriculture.[21]
Ebetsu Kofun Cluster is a group of mounds dating from the latter half of the 8th century to the middle of the 9th century, and were surveyed by Juichi Goto in 1931. Along with the Kofun, Warabidetoh (蕨手刀), iron sword, Magatama, Sueki were discovered.[22] Ebetsu Kofun is known to be evidence for the existence of Wajin (和人) and the trading between Hokkaido and Honshu before Feudal Japan.
The Nihon Shoki, finished in 720 AD, is often said to be the first mention of Hokkaidō in recorded history. According to the text, Abe no Hirafu[23] led a large navy and army to northern areas from 658 to 660 and came into contact with the Mishihase and Emishi. One of the places Hirafu went to was called Watarishima (渡島), which is often believed to be present-day Hokkaidō. However, many theories exist concerning the details of this event, including the location of Watarishima and the common belief that the Emishi in Watarishima were the ancestors of the present-day Ainu people.[citation needed]
During the Nara and Heian periods (710–1185), people in Hokkaidō conducted trade with Dewa Province, an outpost of the Japanese central government. From the feudal period, the people in Hokkaidō began to be called Ezo. Hokkaidō subsequently became known as Ezochi (蝦夷地; lit. "Ezo-land")[24] or Ezogashima (蝦夷ヶ島; lit. "Island of the Ezo"). The Ezo mainly relied upon hunting and fishing and obtained rice and iron through trade with the Japanese.[citation needed]
Feudal Japan

During the Muromachi period (1336–1573), the Japanese established a settlement at the south of the Oshima Peninsula, with a series of fortified residences such as that of Shinoridate. As more people moved to the settlement to avoid battles, disputes arose between the Japanese and the Ainu. The disputes eventually developed into war. Takeda Nobuhiro (1431–1494) killed the Ainu leader, Koshamain,[23] and defeated the opposition in 1457. Nobuhiro's descendants became the rulers of the Matsumae-han, which was granted exclusive trading rights with the Ainu in the Azuchi-Momoyama and Edo periods (1568–1868). The Matsumae family's economy relied upon trade with the Ainu,[citation needed] who had extensive trading networks.[25] The Matsumae held authority over the south of Ezochi until the end of the Edo period.[citation needed]


The Matsumae clan rule over the Ainu must be understood[citation needed] in the context of the expansion of the Japanese feudal state. Medieval military leaders in northern Honshu (ex. Northern Fujiwara, Akita clan) maintained only tenuous political and cultural ties to the imperial court and its proxies, the Kamakura shogunate and Ashikaga shogunate. Feudal strongmen sometimes defined their own roles within the medieval institutional order, taking shogunate titles, while in other times they assumed titles that seemed to give them a non-Japanese identity. In fact, many of the feudal strongmen were descended from Emishi military leaders who had been assimilated into Japanese society.[26] The Matsumae clan were of Yamato descent like other ethnic Japanese people, whereas the Emishi of northern Honshu were a distinctive group related to the Ainu. The Emishi were conquered and integrated into the Japanese state dating back as far as the 8th century and as result began to lose their distinctive culture and ethnicity as they became minorities. By the time the Matsumae clan ruled over the Ainu, most of the Emishi were ethnically mixed and physically closer to Japanese than they were to Ainu. From this, the "transformation" theory postulates that native Jōmon peoples changed gradually with the infusion of Yayoi immigrants into the Tōhoku region of northern Honshu, in contrast to the "replacement" theory that posits the Jōmon was replaced by the Yayoi.[27]
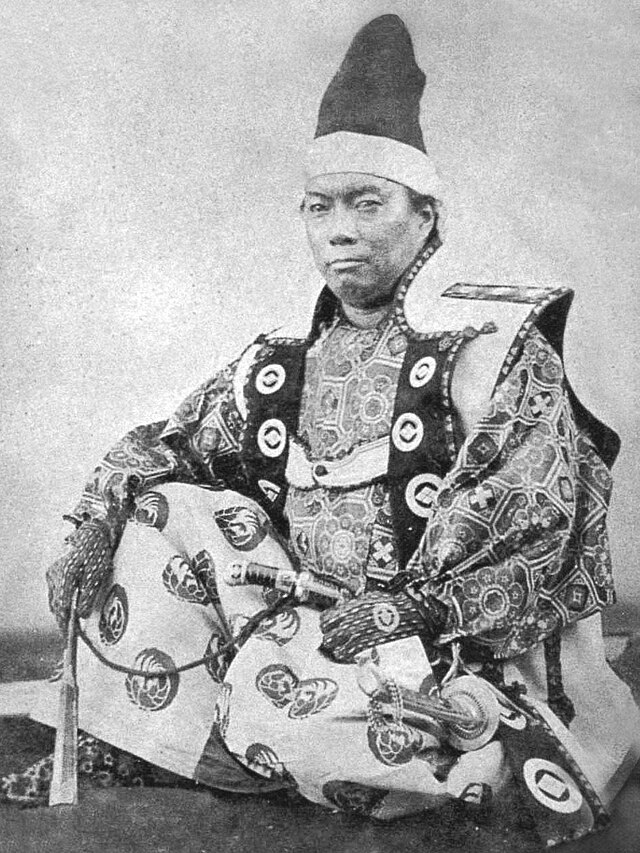

There were numerous revolts by the Ainu against feudal rule. The last large-scale resistance was Shakushain's revolt in 1669–1672. In 1789, a smaller movement known as the Menashi–Kunashir rebellion was crushed. After that rebellion, the terms "Japanese" and "Ainu" referred to clearly distinguished groups, and the Matsumae were unequivocally Japanese.
According to John A. Harrison of the University of Florida, prior to 1868 Japan used proximity as its claim to Hokkaido, Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands; however, Japan had never thoroughly explored, governed, or exploited the areas, and this claim was invalidated by the movement of Russia into the Northeast Pacific area and by Russian settlements on Kamchatka (from 1699), Sakhalin (1850s) and the Sea of Okhotsk Coast (1640s onwards).[28]
Prior to the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the Tokugawa shogunate realized the need to prepare northern defenses against a possible Russian invasion and took over control of most of Ezochi in 1855-1858.[29] Many Japanese settlers regarded the Ainu as "inhuman and the inferior descendants of dogs".[9][30] The Tokugawa irregularly imposed various assimilation programs on the Ainu due to the Tokugawa's perception of a threat from Russia.[9] For example, assimilation programs were implemented in response to perceived threats from Russia, which included the Laxman expedition of 1793 and the Golovnin Incident of 1804.[9] Once the respective Russian threats appeared to subside, the assimilation programs were halted until 1855.[9] However, in 1855, once the Treaty of Shimoda was signed, which defined the borders between Russian Empire and Tokugawa Japan, the Tokugawa again viewed Russia as a threat to Japanese sovereignty over Hokkaido and reinstated assimilation programs on the Ainu.[9]
Meiji era
Colonization of Hokkaido
Prior to the Meiji era, the island was called Ezochi, which can be translated as "land of the barbarians" or "the land for people who did not obey the government."[31] Shortly after the Boshin War in 1868, a group of Tokugawa loyalists led by Enomoto Takeaki temporarily occupied the island (the polity is commonly but mistakenly known as the Republic of Ezo), but the rebellion was defeated in May 1869. Through colonial practices, Ezochi was annexed into Japanese territory.[31][9][11][10] Ezochi was subsequently put under control of Hakodate Prefectural Government. When establishing the Development Commission (開拓使, Kaitakushi), the Meiji government introduced a new name. After 1869, the northern Japanese island was known as Hokkaidō, which can be translated to "northern sea route,"[4] and regional subdivisions were established, including the provinces of Oshima, Shiribeshi, Iburi, Ishikari, Teshio, Kitami, Hidaka, Tokachi, Kushiro, Nemuro and Chishima.[32]
The initiative to colonize Ezo, which later became Hokkaido, traces back to 1869, where Japanese proponents argued that the colonization of Ezo would serve as a strategic move to enhance Japan's standing and influence on the global stage, particularly in negotiations with Western powers, specifically Russia.[33] The Meiji government invested heavily in colonizing Hokkaido for several reasons.[8] Firstly, they aimed to assert their control over the region as a buffer against potential Russian advances.[8] Secondly, they were attracted to Hokkaido's rich natural resources, including coal, timber, fish, and fertile land.[8] Lastly, since Western powers viewed colonial expansion as a symbol of prestige, Japan viewed the colonization of Hokkaido as an opportunity to present itself as a modern and respected nation to Western powers.[8]


The primary purpose of the Development Commission was to secure Hokkaidō before the Russians extended their control of the Far East beyond Vladivostok. The Japanese failed to settle in the interior lowlands of the island because of aboriginal resistance.[34] The resistance was eventually destroyed, and the lowlands were under the control of the commission.[34] The most important goal of the Japanese was to increase the farm population and to create a conducive environment for emigration and settlement.[34] However, the Japanese did not have expertise in modern agricultural techniques, and only possessed primitive mining and lumbering methods.[34] Kuroda Kiyotaka was put in charge of the project, and turned to the United States for help.[34]
His first step was to journey to the United States and recruit Horace Capron, President Ulysses S. Grant's commissioner of agriculture. From 1871 to 1873 Capron bent his efforts to expounding Western agriculture and mining, with mixed results. Frustrated with obstacles to his efforts, Capron returned home in 1875. In 1876, William S. Clark arrived to found an agricultural college in Sapporo. Although he only remained a year, Clark left a lasting impression on Hokkaidō, inspiring the Japanese with his teachings on agriculture as well as Christianity.[35] His parting words, "Boys, be ambitious!", can be found on public buildings in Hokkaidō to this day. The population of Hokkaidō increased from 58,000 to 240,000 during that decade.[36]
Kuroda hired Capron for $10,000 per year and paid for all expenses related to the mission. Kuroda and his government were likely intrigued by Capron's previous colonial experience, particularly his involvement in the forced removal of Native Americans from Texas to new territories after the Mexican–American War.[7] Capron introduced capital-intensive farming techniques by adopting American methods and tools, importing seeds for Western crops, and bringing in European livestock breeds, which included his favorite North Devon cattle.[7] He founded experimental farms in Hokkaido, conducted surveys to assess mineral deposits and agricultural potential, and advocated for improvements in water access, mills, and roads.[7]
The settler colonization of Hokkaido by the Japanese was organized and supported through collaboration between the Japanese state and American experts and technology.[7] From the 1870s to the 1880s, Japanese leaders placed their efforts on settling Hokkaido by systematically migrating former samurai lords, samurai retainers, and common citizens, which included farmers and peasants, providing them with "free" land and financial assistance.[7] This transformation was facilitated with the expertise of American advisors who introduced various colonization technologies, transforming Hokkaido into land suitable for Japan's capitalist aspirations.[7]
Japanese leaders drew inspiration from American settler colonialism during their diplomatic visits to the United States.[8] Japanese colonial officials learned settler colonial techniques from Western imperial powers, particularly the United States. This included declaring large portions of Hokkaido as ownerless land, providing a pretext for the dispossession of the Ainu people.[8][37] Japan established the Hokkaido Colonization Board in 1869, a year after the start of the Meiji era, with the goal of encouraging Japanese settlers to Hokkaido.[38] Mainland Japanese settlers began migrating to Hokkaido, leading to Japan's colonization of the island.[37] Motivated by capitalist and industrial goals, the Meiji government forcefully appropriated fertile land and mineral-rich regions throughout Hokkaido, without consideration for their historical Ainu inhabitancy.[37] The Meiji government implemented land seizures and enacted land ownership laws that favored Japanese settlers, effectively stripping Ainu people of their customary land rights and traditional means of subsistence.[37] The 1899 Hokkaido Former Aborigines Protection Act further marginalized and impoverished the Ainu people by forcing them to leave their traditional lands and relocating them to the rugged, mountainous regions in the center of the island.[39][40] The act prohibited the Ainu from fishing and hunting, which were their main source of subsistence.[41] The Ainu were valued primarily as a source of inexpensive manual labor, and discriminatory assimilation policies further entrenched their sense of inferiority as well as worsened poverty and disease within Ainu communities.[42] These policies exacerbated diasporic trends among the Ainu population, as many sought employment with the government or private enterprises, often earning meager wages that barely sustained their families.[37]
The Meiji government embarked on assimilation campaigns aimed not only at assimilating the Ainu but also eradicating their language and culture entirely.[37] They were forced to take on Japanese names and language, and gradually saw their culture and traditions eroded.[39] The Ainu were forbidden to speak their own language and taught only Japanese at school.[38] Facing pervasive stigma, many Ainu concealed their heritage.[39] UNESCO has recognized the Ainu language as critically endangered.[43] Given the Meiji state's full political control over the island, the subsequent subjugation of its indigenous inhabitants, aggressive economic exploitation, and ambitious permanent settlement endeavors, Hokkaido emerged as the sole successful settler colony of Japan.[37]
After the Meiji colonization of Hokkaido, Meiji Japan depended on prison labour to accelerate the colonization process.[9] The Japanese built three prisons and rendered Hokkaido a prison island, where political prisoners were incarcerated and used as prison labour.[9] During the opening ceremony of the first prison, the Ainu name “Shibetsuputo” was replaced with the Japanese name “Tsukigata,” as an attempt to “Japanize” Hokkaido's geography.[9] The second prison opened near the Hokutan Horonai coal mine, where Ainu people were forced to work.[9] Cheap prison labour played an important role in coal and sulphur mining, as well as road construction in Hokkaido.[9] Eventually, several types of indentured labour, Korean labour, child labour and women labour replaced convict labour in Hokkaido.[9] Working conditions were difficult and dangerous.[9] Japan's transition to capitalism depended heavily on the growth of the coal mining sector in Hokkaidō.[9] The importance of coal from Hokkaidō increased throughout the First World War, and the mines required a large amount of labourers.[9]
World War II
In mid-July 1945, various shipping ports, cities, and military facilities in Hokkaidō were attacked by the United States Navy's Task Force 38. On 14–15 July, aircraft operating from the task force's aircraft carriers sank and damaged a large number of ships in ports along Hokkaidō's southern coastline as well as in northern Honshu. In addition, on 15 July a force of three battleships and two light cruisers bombarded the city of Muroran.[44] Before the Japanese surrender was formalized, the Soviet Union made preparations for an invasion of Hokkaidō, but U.S. President Harry Truman made it clear that the surrender of all of the Japanese home islands would be accepted by General Douglas MacArthur per the 1943 Cairo Declaration.[45]
Present
Hokkaidō became equal with other prefectures in 1947, when the revised Local Autonomy Act became effective. The Japanese central government established the Hokkaidō Development Agency (北海道開発庁, Hokkaidō Kaihatsuchō) as an agency of the Prime Minister's Office in 1949 to maintain its executive power in Hokkaidō. The agency was absorbed by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport in 2001. The Hokkaidō Bureau (北海道局, Hokkaidō-kyoku) and the Hokkaidō Regional Development Bureau (北海道開発局, Hokkaidō Kaihatsukyoku) of the ministry still have a strong influence on public construction projects in Hokkaidō.
Remove ads
Geography
Summarize
Perspective
The island of Hokkaidō is located in the north of Japan, near Russia (Sakhalin Oblast). It has coastlines on the Sea of Japan (to the west of the island), the Sea of Okhotsk (to the north), and the Pacific Ocean (to the east). The center of the island is mountainous, with volcanic plateaux. Hokkaidō has multiple plains such as the Ishikari Plain 3,800 km2 (1,500 sq mi), Tokachi Plain 3,600 km2 (1,400 sq mi), the Kushiro Plain 2,510 km2 (970 sq mi) (the largest wetland in Japan) and Sarobetsu Plain 200 km2 (77 sq mi). Hokkaidō is 83,423.84 km2 (32,210.12 sq mi) which make it the second-largest island of Japan.
The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu (Aomori Prefecture);[4] La Pérouse Strait separates Hokkaidō from the island of Sakhalin in Russia; Nemuro Strait separates Hokkaidō from Kunashir Island in the Russian Kuril Islands.
The governmental jurisdiction of Hokkaidō incorporates several smaller islands, including Rishiri, Okushiri Island, and Rebun. (By Japanese reckoning, Hokkaidō also incorporates several of the Kuril Islands.) Hokkaidō Prefecture is the largest and northernmost Japanese prefecture. The island ranks 21st in the world by area.
- Hokkaido seen from the International Space Station
- The Oyashio Current colliding with the Kuroshio Current off the coast of Hokkaido
Flora and fauna
There are three populations of the Ussuri brown bear found on the island. There are more brown bears in Hokkaidō than anywhere else in Asia besides Russia. The Hokkaidō brown bear is separated into three distinct lineages. There are only eight lineages in the world.[46] Those on Honshu died out long ago.
The native conifer species in northern Hokkaidō is the Sakhalin fir (Abies sachalinensis).[47] The flowering plant Hydrangea hirta is also found on the island.
Geologic activity
Like many areas of Japan, Hokkaidō is seismically active. Aside from numerous earthquakes, the following volcanoes are considered still active (at least one eruption since 1850):
In 1993, an earthquake of magnitude 7.7 generated a tsunami which devastated Okushiri, killing 202 inhabitants. An earthquake of magnitude 8.3 struck near the island on September 26, 2003. On September 6, 2018, an earthquake of magnitude 6.6 struck with its epicenter near the city of Tomakomai, causing a blackout across the whole island.[49]
On May 16, 2021, an earthquake measuring 6.1 on the Richter scale struck off Japan's Hokkaidō prefecture.[50]
Parks
| Shiretoko National Park* | 知床 |
| Akan Mashu National Park | 阿寒 |
| Kushiro-shitsugen National Park | 釧路湿原 |
| Daisetsuzan National Park | 大雪山 |
| Shikotsu-Tōya National Park | 支笏洞爺 |
| Rishiri-Rebun-Sarobetsu National Park | 利尻礼文サロベツ |
| Hidakasanmyaku-Erimo-Tokachi National Park | 日高山脈襟裳十勝 |
* designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO on 2005-07-14.
| Abashiri Quasi-National Park | 網走 |
| Niseko-Shakotan-Otaru Kaigan Quasi-National Park | ニセコ積丹小樽海岸 |
| Ōnuma Quasi-National Park | 大沼 |
| Shokanbetsu-Teuri-Yagishiri Quasi-National Park | 暑寒別天売焼尻 |
- Overview of Kushiro Wetland
- View of Lake Mashū
- Sōunkyō, a gorge in the Daisetsu-zan Volcanic Area
- Twelve prefectural natural parks (道立自然公園). The prefectural natural parks cover 146,802 ha, the largest area of any prefecture.[51]
- Akkeshi Prefectural Natural Park
- Esan Prefectural Natural Park
- Furano-Ashibetsu Prefectural Natural Park
- Hiyama Prefectural Natural Park
- Kariba-Motta Prefectural Natural Park
- Matsumae-Yagoshi Prefectural Natural Park
- North Okhotsk Prefectural Natural Park
- Nopporo Shinrin Kōen Prefectural Natural Park
- Notsuke-Fūren Prefectural Natural Park
- Sharidake Prefectural Natural Park
- Shumarinai Prefectural Natural Park
- Teshiodake Prefectural Natural Park
Climate


As Japan's coldest region, Hokkaidō has relatively cool summers and icy/snowy winters. Most of the island falls in the humid continental climate zone with Köppen climate classification Dfb (hemiboreal) in most areas but Dfa (hot summer humid continental) in some inland lowlands. The average August temperature ranges from 17 to 22 °C (62.6 to 71.6 °F), while the average January temperature ranges from −12 to −4 °C (10.4 to 24.8 °F), in both cases depending on elevation and distance from the ocean, though temperatures on the western side of the island tend to be a little warmer than on the eastern. The highest temperature ever recorded is 39.5 °C (103.1 °F) on 26 May 2019.[52]
The northern portion of Hokkaidō falls into the taiga biome[53] with significant snowfall. Snowfall varies widely from as much as 11 metres (400 in) on the mountains adjacent to the Sea of Japan down to around 1.8 metres (71 in) on the Pacific coast. The island tends to have isolated snowstorms that develop long-lasting snowbanks. Total precipitation varies from 1,600 millimetres (63 in) on the mountains of the Sea of Japan coast to around 800 millimetres (31 in) (the lowest in Japan) on the Sea of Okhotsk coast and interior lowlands and up to around 1,100 millimetres (43 in) on the Pacific side. The generally high quality of powder snow and numerous mountains in Hokkaidō make it a popular region for snow sports. The snowfall usually commences in earnest in November and ski resorts (such as those at Niseko, Furano, Teine and Rusutsu) usually operate between December and April. Hokkaidō celebrates its winter weather at the Sapporo Snow Festival.
During the winter, passage through the Sea of Okhotsk is often complicated by large floes of drift ice. Combined with high winds that occur during winter, this frequently brings air travel and maritime activity to a halt beyond the northern coast of Hokkaidō. Ports on the open Pacific Ocean and Sea of Japan are generally ice-free year round, though most rivers freeze during the winter.
Unlike the other major islands of Japan, Hokkaidō is normally not affected by the June–July rainy season and the relative lack of humidity and typically warm, rather than hot, summer weather makes its climate an attraction for tourists from other parts of Japan.
Temperature comparison
Remove ads
Administrative divisions
Summarize
Perspective
Subprefectures


As of April 2010[update], Hokkaidō has nine General Subprefectural Bureaus (総合振興局) and five Subprefectural Bureaus (振興局). Hokkaidō is one of eight prefectures in Japan that have subprefectures (支庁 shichō). However, it is the only one of the eight to have such offices covering the whole of its territory outside the main cities (rather than having them just for outlying islands or remote areas). This is mostly because of its great size; many parts of the prefecture are simply too far away to be effectively administered by Sapporo. Subprefectural offices in Hokkaidō carry out many of the duties that prefectural offices fulfill elsewhere in Japan.
Municipalities
Hokkaidō is divided into 179 municipalities.

Government Ordinance Designated City City Town Village
Cities
There are 35 cities in Hokkaidō:
Towns and villages
These are the towns and villages in Hokkaido Prefecture:
Remove ads
Major cities and towns

Hokkaidō's largest city is the capital, Sapporo, which is a designated city. The island has two core cities: Hakodate in the south and Asahikawa in the central region. Other important population centers include Tomakomai, Iwamizawa, Kushiro, Obihiro, Kitami, Abashiri, Wakkanai, and Nemuro.
Gallery
Remove ads
Population
Summarize
Perspective
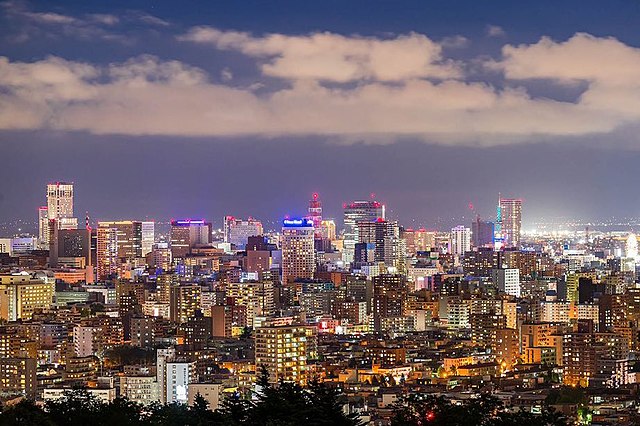


Hokkaidō has the third-largest population of Japan's five main islands, with 5,111,691 people as of 2023[update].[3][55] It has the lowest population density in Japan, with just 61 inhabitants per square kilometre (160/sq mi). Hokkaidō ranks 21st in population among the world's islands. Major cities include Sapporo and Asahikawa in the central region, and the port of Hakodate facing Honshu in the south. Sapporo is Hokkaidō's largest city and the fifth-largest in Japan. It had a population of 1,959,750 as of 31 July 2023[update] and a population density of 1,748/km2 (4,530/sq mi).
Remove ads
Economy
Summarize
Perspective

Although there is some light industry (most notably paper milling and beer brewing) most of the population is employed by the service sector. In 2001, the service sector and other tertiary industries generated more than three-quarters of the gross domestic product.[58]
Agriculture and other primary industries play a large role in Hokkaidō's economy. Hokkaidō has nearly one fourth of Japan's total arable land. It ranks first in the nation in the production of a host of agricultural products, including wheat, soybeans, potatoes, sugar beets, onions, pumpkins, corn, raw milk, and beef. Hokkaidō also accounts for 22% of Japan's forests with a sizable timber industry. The prefecture is first in the nation in production of marine products and aquaculture.[58] The average farm size in Hokkaidō is 26 hectares per farmer in 2013, which is almost 11 times bigger than the national average of 2.4 hectares.[59]

Tourism is an important industry, especially during the cool summertime when visitors are attracted to Hokkaidō's open spaces from hotter and more humid parts of Japan and other Asian countries. During the winter, skiing and other winter sports bring other tourists, and increasingly international ones, to the island.[60]
Coal mining played an important role in the industrial development of Hokkaidō, with the Ishikari coalfield. Cities such as Muroran were primarily developed to supply the rest of the archipelago with coal.[21]
In 2023, Rapidus Corporation announced Hokkaido's largest business investment with a 5 trillion yen plan to build a semiconductor manufacturing factory in Chitose. The site is expected to eventually host over 1,000 employees.[61]
Remove ads
Transportation
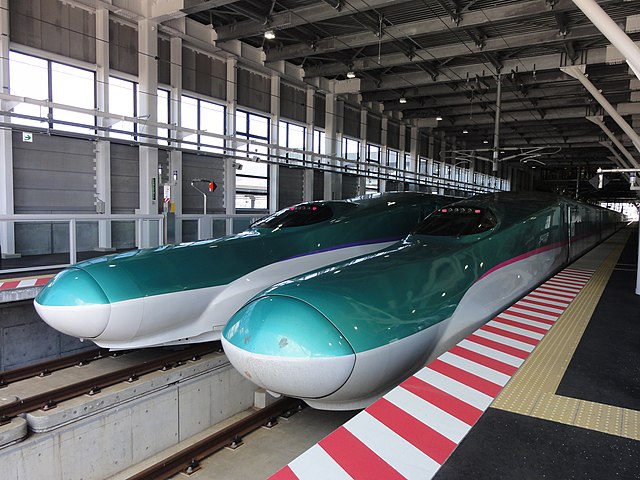

Hokkaido's only land link to the rest of Japan is the Seikan Tunnel. Most travellers travel to the island by air: the main airport is New Chitose Airport at Chitose, just south of Sapporo. Tokyo–Chitose is in the top 10 of the world's busiest air routes, and is currently the 2nd busiest route in the world, handling more than 40 widebody round trips on several airlines each day. One of the airlines, Air Do was named after Hokkaidō.
Hokkaidō can be reached by ferry from Sendai, Niigata and some other cities, with the ferries from Tokyo dealing only in cargo. The Hokkaido Shinkansen takes passengers from Tokyo to near Hakodate in slightly over four hours.[62] There is a fairly well-developed railway network, but many cities can be accessed only by road. The coal railways were constructed around Sapporo and Horonai during the late 19th century, as advised by American engineer Joseph Crawford.[21]
Hokkaidō is home to one of Japan's Melody Roads, which is made from grooves cut into the ground, which when driven over causes a tactile vibration and audible rumbling transmitted through the wheels into the car body.[63][64]
Remove ads
Education
The Hokkaido Prefectural Board of Education oversees public schools (except colleges and universities) in Hokkaidō. Public elementary and junior high schools (except Hokkaido Noboribetsu Akebi Secondary School and schools attached to Hokkaidō University of Education) are operated by municipalities, and public high schools are operated by either the prefectural board or municipalities.
Senior high schools
As of 2016[update],[65] there are 291 high schools in Hokkaido: 4 national schools, 55 private schools,[66] 233 public schools,[67] and 2 integrated junior-senior schools.
Colleges and universities
Hokkaidō has 34 universities (7 national, 6 local public, and 21 private universities), 15 junior colleges, and 6 colleges of technology (3 national, 1 local public, and 2 private colleges).
Culture

Sports

The 1972 Winter Olympics were held in Sapporo.
The sports teams listed below are based in Hokkaidō.
- Consadole Sapporo (association football)
- Hokkaido American Football Association
- Hokkaido Nippon-Ham Fighters
- Japan Basketball League
- Levanga Hokkaido (basketball)
- Loco Solare (curling)
- Nippon Paper Cranes (ice hockey)
- Oji Eagles (ice hockey)
Winter festivals
- Asahikawa Ice Festival
- Big Air – snowboarding freestyle competition
- Sapporo Snow Festival
- Shōwa-Shinzan International Yukigassen - competitive snowballing
- Sōunkyō Ice Festival
Politics
Summarize
Perspective
Governor
The current governor of Hokkaido is Naomichi Suzuki.[68] He won the governorship in the gubernatorial election in 2019 as an independent. In 1999, Hori was supported by all major non-Communist parties and Itō ran without party support. Before 1983, the governorship had been held by Liberal Democrats Naohiro Dōgakinai and Kingo Machimura for 24 years. In the 1971 election when Machimura retired, the Socialist candidate Shōhei Tsukada lost to Dōgakinai by only 13,000 votes;[69] Tsukada was also supported by the Communist Party – the leftist cooperation in opposition to the US-Japanese security treaty had brought joint Socialist-Communist candidates to victory in many other prefectural and local elections in the 1960s and 1970s. In 1959, Machimura had defeated Yokomichi's father Setsuo in the race to succeed Hokkaidō's first elected governor, Socialist Toshibumi Tanaka who retired after three terms. Tanaka had only won the governorship in 1947 in a run-off election against Democrat Eiji Arima because no candidate had received the necessary vote share to win in the first round as required by law at the time.
Assembly
The Hokkaido Legislative Assembly has 100 members from 47 electoral districts. As of April 30, 2015[update], the LDP caucus holds a majority with 51 seats, the DPJ-led group has 26 members. Other groups are the Hokkaidō Yūshikai of New Party Daichi and independents with twelve seats, Kōmeitō with eight, and the Japanese Communist Party with four members.[70] General elections for the Hokkaido assembly are currently held together with gubernatorial elections in the unified local elections (last round: April 2015).
National representation
For the lower house of the National Diet, Hokkaidō is divided into twelve single-member electoral districts. In the 2017 election, candidates from the governing coalition of Liberal Democrats and Kōmeitō won seven districts and the main opposition Constitutional Democrats five. For the proportional election segment, Hokkaidō and Tokyo are the only two prefectures that form a regional "block" district of their own. The Hokkaido proportional representation block elects eight Representatives. In 2017, the Liberal Democratic Party received 28.8% of the proportional vote and won three seats, the Constitutional Democratic Party won three (26.4% of the vote), one seat each went to Kibō no Tō (12.3%) and Kōmeitō (11.0%). The Japanese Communist Party, who won a seat in 2014, lost their seat in 2017 while receiving 8.5% of the votes.
In the upper house of the National Diet, a major reapportionment in the 1990s halved the number of Councillors from Hokkaidō per election from four to two. After the elections of 2010 and 2013, the Hokkaido electoral district – like most two-member districts for the upper house – is represented by two Liberal Democrats and two Democrats. In the 2016 upper house election, the district magnitude will be raised to three, Hokkaidō will then temporarily be represented by five members and six after the 2019 election.
International relations
Hokkaidō has relationships with several provinces, states, and other entities worldwide.[71]
 Alberta, Canada, since 1980[72][73]
Alberta, Canada, since 1980[72][73] Heilongjiang, China, since 1980[72]
Heilongjiang, China, since 1980[72] Massachusetts, United States, since 1988[72][74]
Massachusetts, United States, since 1988[72][74] Sakhalin Oblast, Russia, since 1998[72]
Sakhalin Oblast, Russia, since 1998[72] Busan, South Korea, since 2005
Busan, South Korea, since 2005 Gyeongsangnam-do, South Korea, since 2006
Gyeongsangnam-do, South Korea, since 2006 Seoul, South Korea, since 2010[75]
Seoul, South Korea, since 2010[75] Chiang Mai, Thailand, since 2013[76]
Chiang Mai, Thailand, since 2013[76] Thimphu, Bhutan
Thimphu, Bhutan Hawaii, United States of America[77]
Hawaii, United States of America[77]
As of January 2014[update], 74 individual municipalities in Hokkaidō have sister city agreements with 114 cities in 21 countries worldwide.[78]
See also
- Former Hokkaidō Government Office
- Golden Kamuy, a manga and anime series set mainly in Hokkaido.
- Hokkaido dialects
- List of cities in Hokkaido by population
- People from Hokkaido
- Sankebetsu brown bear incident
- Sinnoh, a fictional region in the Pokémon franchise which is based on Hokkaido.
Notes
General references
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads