Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Lactose
Carbohydrate From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from lact (gen. lactis), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix -ose used to name sugars. The compound is a white, water-soluble, non-hygroscopic solid with a mildly sweet taste. It is used in the food industry.[5]
Remove ads
Structure and reactions


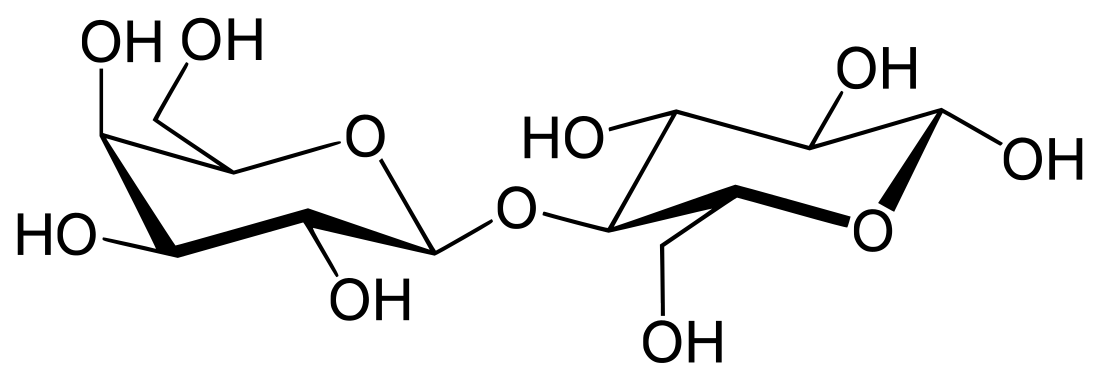
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose, which form a β-1→4 glycosidic linkage. Its systematic name is β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucose. The glucose can be in either the α-pyranose form or the β-pyranose form, whereas the galactose can have only the β-pyranose form: hence α-lactose and β-lactose refer to the anomeric form of the glucopyranose ring alone. Detection reactions for lactose are the Wöhlk[6] and Fearon tests.[7] They can be used to detect the different lactose content of dairy products such as whole milk, lactose free milk, yogurt, buttermilk, coffee creamer, sour cream, kefir, etc.[8]
Lactose is hydrolysed to glucose and galactose, isomerised in alkaline solution to lactulose, and catalytically hydrogenated to the corresponding polyhydric alcohol, lactitol.[9] Lactulose is a commercial product, used for treatment of constipation.[10]
Remove ads
Occurrence and isolation
Lactose comprises about 2–8% of milk by weight. Several million tons are produced annually as a by-product of the dairy industry.[citation needed]
Whey or milk plasma is the liquid remaining after milk is curdled and strained, for example in the production of cheese. Whey is made up of 6.5% solids, of which 4.8% is lactose, which is purified by crystallisation.[11] Industrially, lactose is produced from whey permeate – whey filtrated for all major proteins. The protein fraction is used in infant nutrition and sports nutrition while the permeate can be evaporated to 60–65% solids and crystallized while cooling.[12] Lactose can also be isolated by dilution of whey with ethanol.[13]
Remove ads
Metabolism
Summarize
Perspective
Infant mammals nurse on their mothers to drink milk, which is rich in lactose. The intestinal villi secrete the enzyme lactase (β-D-galactosidase) to digest it. This enzyme cleaves the lactose molecule into its two subunits, the simple sugars glucose and galactose, which can be absorbed. Since lactose occurs mostly in milk, in most mammals, the production of lactase gradually decreases with maturity due to weaning; the removal of lactose from the diet removes the metabolic pressure to continue to produce lactase for its digestion.[14][15]
Many people with ancestry in Europe, West Asia, South Asia, the Sahel belt in West Africa, East Africa and a few other parts of Central Africa maintain lactase production into adulthood due to selection for genes that continue lactase production. In many of these areas, milk from mammals such as cattle, goats, and sheep is used as a large source of food. It was in these regions that genes for lifelong lactase production first evolved.[16] The genes of adult lactose tolerance have evolved independently in various ethnic groups.[17] By descent, more than 70% of western Europeans can digest lactose as adults, compared with less than 30% of people from areas of Africa, eastern and south-eastern Asia and Oceania.[18] In people who are lactose intolerant, lactose is not broken down and provides food for gas-producing gut flora, which can lead to diarrhea, bloating, flatulence, and other gastrointestinal symptoms.
Biological properties
Summarize
Perspective
The sweetness of lactose is 0.2 to 0.4, relative to 1.0 for sucrose.[19] For comparison, the sweetness of glucose is 0.6 to 0.7, of fructose is 1.3, of galactose is 0.5 to 0.7, of maltose is 0.4 to 0.5, of sorbose is 0.4, and of xylose is 0.6 to 0.7.[19]
When lactose is completely digested in the small intestine, its caloric value is 4 kcal/g, or the same as that of other carbohydrates.[19] However, lactose is not always fully digested in the small intestine. Depending on ingested dose, combination with meals (either solid or liquid), and lactase activity in the intestines, the caloric value of lactose ranges from 2 to 4 kcal/g.[19] Undigested lactose acts as dietary fiber. It also has positive effects on absorption of minerals, such as calcium and magnesium.[19]
The glycemic index of lactose is 46 to 65.[20] For comparison, the glycemic index of glucose is 100 to 138, of sucrose is 68 to 92, of maltose is 105, and of fructose is 19 to 27.[19][20]
Lactose has relatively low cariogenicity among sugars.[21] This is because it is not a substrate for dental plaque formation and it is not rapidly fermented by oral bacteria.[21] The buffering capacity of milk also reduces the cariogenicity of lactose.[19]
Remove ads
Applications
Summarize
Perspective
Its mild flavor and easy handling properties have led to its use as a carrier and stabiliser of aromas and pharmaceutical products.[5] Lactose is not commonly added directly to food, because its low solubility can lead to a gritty mouthfeel.[22] Infant formula is a notable exception, where lactose is added to match the composition of human milk.[23] However, lactose-reduced formulas are increasing in popularity.[24]
One of the undesirable properties of lactose utilization is its low solubility, which can result in crystallization, giving a gritty and sandy mouthfeel in the final product. Usually, in supersaturated solution, sugars tend to crystallize, also forming big agglomerates, depending on the process condition.
Lactose is not fermented by most yeast during brewing, which may be used to advantage.[9] For example, lactose may be used to sweeten stout beer; the resulting beer is usually called a milk stout or a cream stout.
Yeast belonging to the genus Kluyveromyces have a unique industrial application, as they are capable of fermenting lactose for ethanol production. Surplus lactose from the whey by-product of dairy operations is a potential source of alternative energy.[25]
Another significant lactose use is in the pharmaceutical industry. Lactose is added to tablet and capsule drug products as an ingredient because of its physical and functional properties (examples are atorvastatin, levocetirizine or thiamazole among many others).[5][26] For similar reasons, it can be used to dilute illicit drugs such as cocaine or heroin.[27]
Remove ads
History
The first crude isolation of lactose, by Italian physician Fabrizio Bartoletti (1576–1630), was published in 1633.[28] In 1700, the Venetian pharmacist Lodovico Testi (1640–1707) published a booklet of testimonials to the power of milk sugar (saccharum lactis) to relieve, among other ailments, the symptoms of arthritis.[29] In 1715, Testi's procedure for making milk sugar was published by Antonio Vallisneri.[30] Lactose was identified as a sugar in 1780 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele.[31][9]
In 1812, Heinrich Vogel (1778–1867) recognized that glucose was a product of hydrolyzing lactose.[32] In 1856, Louis Pasteur crystallized the other component of lactose, galactose.[33] By 1894, Emil Fischer had established the configurations of the component sugars.[34]
Lactose was named by the French chemist Jean Baptiste André Dumas (1800–1884) in 1843.[35] In 1856, Pasteur named galactose "lactose".[36] In 1860, Marcellin Berthelot renamed it "galactose", and transferred the name "lactose" to what is now called lactose.[37] It has a formula of C12H22O11 and the hydrate formula C12H22O11·H2O, making it an isomer of sucrose.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads