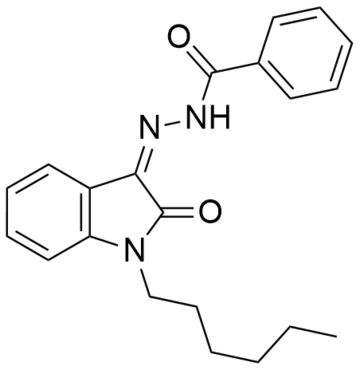
MDA-19 (also known as BZO-HEXOXIZID)[2][3] is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2, with reasonable selectivity over the psychoactive CB1 receptor, though with some variation between species. In animal studies it was effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain, but did not effect rat locomotor activity in that specific study. The pharmacology of MDA-19 in rat cannabinoid receptors have been demonstrated to function differently than human cannabinoid receptors with MDA-19 binding to human CB1 receptors 6.9× higher than rat CB1 receptors.[4][5]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H23N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 349.434 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Discovery
MDA-19 was first synthesized and studied in the late 2000s by researchers at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.[6] [7][5]
Pharmacology
MDA-19 binds to human CB2 receptors at Ki = 43.3 ± 10.3 nM and human CB1 receptors at Ki = 162.4 ± 7.6 nM and functions as an agonist in human cannabinoid receptors but functions differently in rat cannabinoid receptors binding to rat cannabinoid CB2 receptors at Ki = 16.3 ± 2.1 and CB1 receptors at Ki = 1130 ± 574 nM binding to rat CB1 receptors 6.9× weaker than human CB1 receptors but increased binding for CB2. MDA-19 is an agonist at human CB1 and CB2 receptors as well as rat CB1 receptors but functions as an inverse agonist in rat CB2 receptors.[4]
Society and Culture
MDA-19 along with its shortened Pentyl tailchain analog (MDA-19-Pentyl / 5Carbon-MDA-19/ BZO-POXIZID)[8] and its 5-Fluoro Pentyl analog (5F-MDA-19 /5F-BZO-POXIZID)[9] and its Cyclohexylmethyl analog (CHM-MDA-19 / BZO-CHMOXIZID)[7] was identified in synthetic smoke blends seized in the United States as early as September 2021.[8][7][9][10] United States Border Protection Officers identified BZO-4en-POXIZID (also known as 4en-pentyl-MDA-19) as early as February, 2022[11] The Center for Forensic Science Research & Education (CFSRE) analyzed 11 samples of suspected synthetic smoke blends between May and September 2022 within the Philadelphia area and found the pentyl analog of MDA-19 in 5 out of 11 samples.[12] Despite their reported lower CB1 binding affinity, other low CB1 binding synthetic cannabinoids such as UR-144 (Ki = 150 nM CB1 and Ki = 1.8 nM CB2) and XLR-11 (EC50 values of 98 nM CB1 and 83 nM CB2) have been previously identified in smoke blends in 2012.[13][14][15][16]
Legality
In the United States, As of May 22, 2023 MDA-19 is legal at the federal level, but may be considered illegal if intended for human consumption under the federal analogue act.[17]
North Dakota has placed MDA-19 (along with BZO-CHMOXIZID (CHM-MDA-19), BZO-POXIZID (Pentyl MDA-19), 5F-BZO-POXIZID (5F-MDA-19) and BZO-4en-POXIZID (4en-pentyl MDA-19) into Schedule I on 04/27/23.[18]
In China, the May 2021 ban on specific synthetic cannabinoid core classes does not include the class of cannabinoids MDA-19 belongs to.[19][20]
See also
References
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.