Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
MiniDisc
Magneto-optical storage medium, mainly for audio (1992–2013) From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
MiniDisc (MD) is a discontinued erasable magneto-optical disc-based data storage format offering a capacity of 60, 74, or 80 minutes of digitized audio.

Sony announced the MiniDisc in September 1992 and released it in November[2] of that year for sale in Japan and in December in Europe, North America, and other countries.[3] The music format was based on ATRAC audio data compression, Sony's own proprietary compression code. Its successor, Hi-MD, would later introduce the option of linear PCM digital recording to meet audio quality comparable to that of a compact disc. MiniDiscs were very popular in Japan and found moderate success in Europe.[4] Although it was designed to succeed the cassette tape, it did not manage to supplant it globally.[5]
By March 2011, Sony had sold 22 million MD players, but discontinued further development.[6] Sony ceased manufacturing and sold the last of the players by March 2013.[7] On January 23, 2025, Sony announced they would end the production of recordable MD media in February 2025.[8]
Remove ads
Market history
Summarize
Perspective
In 1983, just a year after the introduction of the compact disc, Kees Schouhamer Immink and Joseph Braat presented the first experiments with erasable magneto-optical compact discs during the 73rd AES Convention in Eindhoven.[9] It took almost 10 years, however, before their idea was commercialized.
Sony's MiniDisc was one of two rival digital systems introduced in 1992 that were intended to replace the Philips Compact Cassette analog audio tape system: the other was the Digital Compact Cassette (DCC), created by Philips and Matsushita (now Panasonic). Sony had originally intended the Digital Audio Tape (DAT) to be the dominant home digital audio recording format, replacing the analog cassette. Because of technical delays, the DAT was not launched until 1989, and by then the U.S. dollar had fallen so far against the yen that the introductory DAT machine Sony had intended to market for about $400 in the late 1980s then had to retail for $800 or even $1,000 to break even, putting it out of reach of most users.
Relegating DAT to professional use, Sony set to work to come up with a simpler, more economical digital home format. By the time Sony came up with the MiniDisc in late 1992, Philips had introduced a competing system, DCC, on a magnetic tape cassette. This created marketing confusion very similar to the videocassette format war of the late 1970s and early 1980s. Sony licensed MD technology to other manufacturers, with JVC, Sharp, Pioneer, Panasonic and others producing their own MD products. However, non-Sony machines were not widely available in North America, and companies such as Technics and Radio Shack tended to promote DCC instead.

Despite having a loyal customer base largely of musicians and audio enthusiasts,[citation needed] the MiniDisc met with only limited success in the United States. It was very popular in Japan and parts of Asia, and relatively so in Europe during the 1990s and into the 2000s, but did not enjoy comparable sales success in other markets. Meanwhile, recordable CDs, flash memory and HDD and solid-state-based digital audio players such as iPods became increasingly popular as playback devices.
The slow uptake of MiniDisc was attributed to the small number of pre-recorded albums available on MD, because relatively few record labels embraced the format. The initial high cost of equipment and blank media was also a factor. Additionally, home MiniDisc decks were less widely available, with most consumers instead connecting a portable MD device to their hi-fi system in order to record.
MiniDisc technology was faced with new competition from the recordable compact disc (CD-R) when it became more affordable to consumers beginning around 1996. Initially, Sony believed that it would take around a decade for CD-R prices to become affordable – the cost of a typical blank CD-R disc was around $12 in 1994 – but CD-R prices fell much more rapidly than envisioned, to the point where CD-R blanks sank below $1 per disc by the late 1990s, compared to at least $2 for the cheapest 80-minute MiniDisc blanks.
The biggest competition for MiniDisc came with the emergence of MP3 players. With the Diamond Rio player in 1998 and the Apple iPod in 2001, the mass market began to eschew physical media in favor of more convenient file-based systems.

By 2007, because of the waning popularity of the format and the increasing popularity of solid-state MP3 players, Sony was producing only one model, the Hi-MD MZ-RH1, available as the MZ-M200 in North America packaged with a Sony microphone and limited macOS software support.[10][11][12]
The MZ-RH1 allowed users to freely move uncompressed digital recordings back and forth from the MiniDisc to a computer without the copyright protection limitations previously imposed upon the NetMD series. This allowed the MiniDisc to better compete with HD recorders and MP3 players. However, most pro users like broadcasters and news reporters had already abandoned MiniDisc in favor of solid-state recorders, because of their extended recording time, open digital content sharing, high-quality digital recording capabilities and reliable, lightweight design.
On 7 July 2011, Sony announced that it would no longer ship MiniDisc Walkman products as of September 2011,[6] effectively killing the format.[13]
On 1 February 2013, Sony issued a press release on the Nikkei stock exchange that it would cease shipment of all MD devices, with last of the players to be sold in March 2013. However, it would continue to sell blank discs and offer repair services.[2] Other manufacturers continued to release MiniDisc players long after Sony stopped, with TEAC & TASCAM producing new decks up until 2020 when both its consumer and professional products, TEAC MD-70CD and TASCAM MD-CD1MKIII, were discontinued.[14] In January 2025 Sony announced, that production of blank MiniDiscs (together BD-R and MiniDV) will be discontinued.[15]
Remove ads
Design
Summarize
Perspective
Physical characteristics

The disc is fixed in a cartridge (68×72×5 mm) with a sliding door, similar to the casing of a 3.5" floppy disk. This shutter is opened automatically when inserted into a drive. MiniDiscs can either be blank or prerecorded. Recordable MiniDiscs use a magneto-optical system to write data: a laser below the disc heats a spot to its Curie point, making the material in the disc susceptible to a magnetic field. A magnetic head above the disc then alters the polarity of the heated area, recording the digital data onto the disk. Playback is accomplished with the laser alone: taking advantage of the magneto-optic Kerr effect, the player senses the polarization of the reflected light as a 1 or a 0. Recordable MDs can be rerecorded repeatedly, with Sony claiming up to one million times. By May 2005, there were 60-minute, 74-minute and 80-minute discs available. 60-minute blanks, which were widely available in the early years of the format's introduction, were phased out.
MiniDiscs use a mastering process and optical playback system that is very similar to CDs. The recorded signal of the premastered pits and of the recordable MD are also very similar. Eight-to-Fourteen Modulation (EFM) and a modification of CD's CIRC code, called Advanced Cross Interleaved Reed-Solomon Code (ACIRC) are employed.
Differences from cassette and CDs
MiniDiscs use rewritable magneto-optical storage to store data. Unlike DCC or the analog Compact Cassette, MiniDisc is a random-access medium, making seek time very fast. MiniDiscs can be edited very quickly even on portable machines. Tracks can be split, combined, moved or deleted with ease either on the player or uploaded to a PC with Sony's SonicStage V4.3 software and edited there. Transferring data from an MD unit to a non-Windows PC can only be done in real time, preferably via optical I/O, by connecting the audio out port of the MD to an available audio in port of the computer. With the release of the Hi-MD format, Sony began to use Mac OS X-compatible software. However, the Mac OS X-compatible software was still not compatible with legacy MD formats (SP, LP2, LP4). This means that an MD recorded on a legacy unit or in a legacy format still requires a Windows PC for faster than real-time transfers.
The beginning of the disc has a table of contents (TOC, the System File area), which stores the start positions of the various tracks, as well as metadata (title, artist) and free blocks. Unlike a conventional cassette, a recorded song does not need to be stored as one piece on the disc and can be scattered in fragments, similar to a hard drive. Early MiniDisc equipment had a fragment granularity of four seconds of audio. Fragments smaller than the granularity are not monitored, which may lead to the usable capacity of a disc shrinking over time. No means of defragmenting the disc is provided in consumer-grade equipment.
All consumer-grade MiniDisc devices have a copy-protection scheme called the Serial Copy Management System. An unprotected disc or song can be copied without limit, but the copies can no longer be digitally copied. However, as a concession, the last Hi-MD players can upload to PC a digitally recorded file which can be resaved as a WAV (PCM) file and thus replicated.
Audio data compression
The digitally encoded audio signal on a MiniDisc has traditionally been data-compressed using the ATRAC (Adaptive Transform Acoustic Coding) format.
ATRAC was devised to allow MiniDisc to have the same runtime as a CD. ATRAC reduces the 1.4 Mbit/s of a CD to a 292 kbit/s data stream,[16] roughly a 5:1 reduction. ATRAC was also used on nearly all flash memory Walkman devices until the 8 series.
The ATRAC codec differs from uncompressed PCM in that it is a psychoacoustic lossy audio data reduction scheme. Like other lossy audio compression formats, it is intended to be acoustically transparent.
There have been four versions of ATRAC, each claimed by Sony to more accurately reflect the original audio. Early players are guaranteed to play later version ATRAC audio. Version 1 could only be copied on consumer equipment three or four times before artifacts became objectionable, as the ATRAC on the recorder attempted to compress the already compressed data. By version 4, the potential number of generations of copy had increased to around 15 to 20 depending on audio content.
The latest versions of Sony's ATRAC are ATRAC3 and ATRAC3plus. Original ATRAC3 at 132 kbit/s (also known as ATRAC-LP2 mode) was the format that was used by Sony's defunct Connect audio download store. ATRAC3plus was not used in order to retain backwards compatibility with earlier NetMD players.
In the MiniDisc's final iteration, Hi-MD, uncompressed CD-quality linear PCM audio recording and playback is offered, placing Hi-MD on par with CD-quality audio. Hi-MD also supports both ATRAC3 and ATRAC3plus at various bitrates.
Anti-skip
MiniDisc has a feature that prevents disc skipping under all but the most extreme conditions. Older CD players had been a source of annoyance to users as they were prone to mistracking from vibration and shock. MiniDisc solved this problem by reading the data into a memory buffer at a higher speed than was required before being read out to the digital-to-analog converter at the standard rate of the format. The size of the buffer varies by model.
If a MiniDisc player is bumped, playback continues unimpeded while the laser repositions itself to continue reading data from the disc. This feature allows the player to stop the spindle motor for significant periods, increasing battery life.
A buffer of at least six seconds is required on all MiniDisc players, whether portable or full-sized units. This ensures uninterrupted playback in the presence of file fragmentation.
Operation


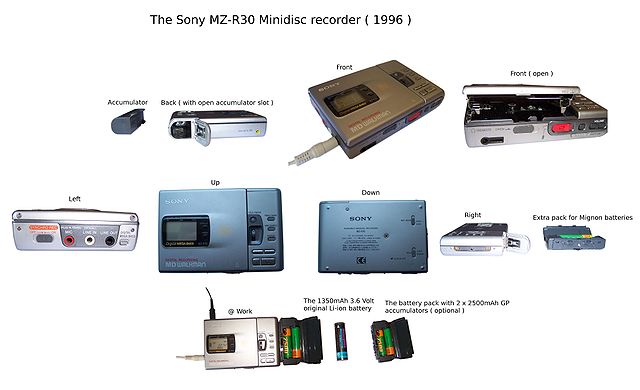
The data structure and operation of a MiniDisc is similar to that of a computer's hard disk drive. The bulk of the disc contains audio data, and a small section contains the table of contents (TOC), providing the playback device with vital information about the number and location of tracks on the disc. Tracks and discs can be named. Tracks may easily be added, erased, combined and divided, and their preferred order of playback modified. Erased tracks are not physically erased, but are only marked as deleted. When a disc becomes full, the recorder can simply direct the data into sections where erased tracks reside. This can lead to fragmentation but unless many erasures and replacements are performed, the only likely problem is excessive searching, reducing battery life.
The data structure of the MiniDisc, where music is recorded in a single stream of bytes while the TOC contains pointers to track positions, allows for gapless playback of music, something which competing portable players such as most MP3 players, fail to implement properly. Notable exceptions are CD players, as well as all recent iPods.
At the end of recording, after the "Stop" button has been pressed, the MiniDisc may continue to write music data for a few seconds from its memory buffers. During this time, it may display a message ("Data Save", on at least some models) and the case will not open. After the audio data is written out, the final step is to write the TOC track denoting the start and endpoints of the recorded data. Sony points out in the manual that the power should not be interrupted or the unit exposed to undue physical shock during this time.
Copy protection
All MiniDisc recorders (except professional models) use the SCMS copy protection system which uses two bits in the S/PDIF digital audio stream and on disc to differentiate between "protected" vs. "unprotected" audio, and between "original" vs. "copy":
- Recording digitally from a source marked "protected" and "original" (produced by a prerecorded MD or an MD that recorded an analogue input) was allowed, but the recorder would change the "original" bit to the "copy" state on the disc to prevent further copying of the copy. A CD imported via a digital connection does not have the SCMS bits (as the CD format predates SCMS), but the recording MD recorder treats any signal where the SCMS bits are missing as protected and original. The MD copy, therefore, cannot be further copied digitally.
- Recording digitally from a source marked "protected" and "copy" was not allowed: an error message would be shown on the display.
- Recording digitally from a source marked "unprotected" was also allowed; the "original/copy" marker was ignored and left unchanged.
Recording from an analogue source resulted in a disc marked "protected" and "original" allowing one further copy to be made (this contrasts with the SCMS on the Digital Compact Cassette where analogue recording was marked as "unprotected").
In recorders that could be connected to a PC via USB, it was possible to transfer audio from the PC to the MiniDisc recorder, but for many years it was not possible to transfer audio in the other direction. This restriction existed in both the SonicStage software and in the MiniDisc player itself. SonicStage V3.4 was the first version of the software where this restriction was removed, but it still required a MiniDisc recorder/player that also had the restriction removed. The Hi-MD model MZ-RH1 was the only such player available.
Remove ads
Format extensions
Summarize
Perspective
MD Data
MD Data, a format for storing computer data, was announced by Sony in 1993.[18] Its media stored 140 MB[18] and were generally incompatible with standard audio MiniDiscs.[19] MD Data cannot be written to audio MDs; it can only be written to the considerably more expensive data blanks. It did see some success in a small number of multi-track recorders such as Sony's MDM-X4, Tascam's 564 (which could also record using standard audio MD discs, albeit only two tracks), and Yamaha's MD8, MD4, & MD4S.
MD Data2
In 1997, MD Data2 blanks were introduced with 650 MB. They were only implemented in Sony's short-lived MD-based camcorder, the DCM-M1.
MDLP
In 2000, Sony announced MDLP (MiniDisc Long Play), which added new recording modes based on the new codec ATRAC3. In addition to the standard, high-quality mode, now called SP, MDLP adds LP2 mode, which doubles the recording time – 160 minutes on an 80-minute disc – of good-quality stereo sound, and LP4, which allows four times more recording time – 320 minutes on an 80-minute disc – of medium-quality stereo sound.
The bitrate of the standard SP mode is 292 kbit/s, and it uses separate stereo coding with discrete left and right channels. LP2 mode uses a bitrate of 132 kbit/s and also uses separate stereo coding. The third mode, LP4, has a bitrate of 66 kbit/s and uses joint stereo coding. The sound quality is noticeably degraded compared to the other two modes, but is sufficient for many uses.
Tracks recorded in LP2 or LP4 mode play back as silence on non-MDLP players.
NetMD

Debuting in late 2001, NetMD recorders allow music files to be transferred from a computer to a recorder (but not in the other direction) over a USB connection. In LP4 mode, speeds of up to 32× real-time are possible and three Sony NetMD recorders (MZ-N10, MZ-N910, and MZ-N920) are capable of speeds up to 64× real-time. NetMD recorders all support MDLP.
When transferring music in SP mode using NetMD with SonicStage, what is transferred is actually padded LP2. That is to say that the quality of the music is that of LP2 but recorded as SP.
NetMD is a proprietary protocol that initially required proprietary software such as SonicStage. A free *nix based implementation, libnetmd, has been developed. The library allows the user to upload SP files in full quality. In 2019, a programmer named Stefano Brilli compiled the linux-minidisc CLI into a web browser-based application,[20] allowing users to transfer music via USB on modern devices.[21]
Hi-MD
Hi-MD is a further development of the MiniDisc format. Hi-MD media will not play on non-Hi-MD equipment, including NetMD players. The Hi-MD format, introduced in 2004, marked a return to the data storage arena with its 1 GB discs and ability to act as a USB drive.[22] Hi-MD units allow the recording and playback of audio and data on the same disc, and can write both audio and data to standard MiniDisc media – an 80-minute MiniDisc blank could be formatted to store 305 MB of data.
Remove ads
Recording and transfer modes
Modes marked in green are available for recordings made on the player, while those marked in red are available for music transferred from a PC. Capacities are official Sony figures; real world figures are usually slightly higher. Native MP3 support was added in second-generation Hi-MD players in the spring of 2005.[23] SonicStage version 3.4, released in Feb 2006,[24] introduced ripping CDs in bitrates 320 and 352[25] and added track transfer in ATRAC 192 kbit/s to Hi-MD devices.
Remove ads
See also
- Capacitance Electronic Disc (SelectaVision) – an RCA-developed format that uses a disc inside a sleeve, like MD
- Fidelipac
- Universal Media Disc (UMD) – a similar Sony format, but read-only. Used on the PlayStation Portable handheld game console.
- Mini CD
- MiniDVD
- Mini Blu-ray
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads


