Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Neoclassical economics
Approach to economics From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption, and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model.[1] According to this line of thought, the value of a good or service is determined through a hypothetical maximization of utility by income-constrained individuals and of profits by firms facing production costs and employing available information and factors of production. This approach has often been justified by appealing to rational choice theory.[2]
Neoclassical economics is the dominant approach to microeconomics and, together with Keynesian economics, formed the neoclassical synthesis which dominated mainstream economics as "neo-Keynesian economics" from the 1950s onward.
Remove ads
Classification
Summarize
Perspective
The term was originally introduced by Thorstein Veblen in his 1900 article "Preconceptions of Economic Science", in which he related marginalists in the tradition of Alfred Marshall et al. to those in the Austrian School.[3][4]
No attempt will here be made even to pass a verdict on the relative claims of the recognized two or three main "schools" of theory, beyond the somewhat obvious finding that, for the purpose in hand, the so-called Austrian school is scarcely distinguishable from the neo-classical, unless it be in the different distribution of emphasis. The divergence between the modernized classical views, on the one hand, and the historical and Marxist schools, on the other hand, is wider, so much so, indeed, as to bar out a consideration of the postulates of the latter under the same head of inquiry with the former.[5]
It was later used by John Hicks, George Stigler, and others[6] to include the work of Carl Menger, William Stanley Jevons, Léon Walras, John Bates Clark, and many others.[3] Today it is usually used to refer to mainstream economics, although it has also been used as an umbrella term encompassing a number of other schools of thought,[7] notably excluding institutional economics, various historical schools of economics, and Marxian economics, in addition to various other heterodox approaches to economics.
Neoclassical economics is characterized by several assumptions common to many schools of economic thought. There is not a complete agreement on what is meant by neoclassical economics, and the result is a wide range of neoclassical approaches to various problem areas and domains—ranging from neoclassical theories of labor to neoclassical theories of demographic changes.
Remove ads
Theory
Summarize
Perspective
Assumptions and objectives
It was expressed by E. Roy Weintraub that neoclassical economics rests on three assumptions, although certain branches of neoclassical theory may have different approaches:[8]
- People have rational preferences between outcomes that can be identified and associated with values.
- Individuals maximize utility and firms maximize profits.
- People act independently on the basis of full and relevant information.
From these three assumptions, neoclassical economists have built a structure to understand the allocation of scarce resources among alternative ends—in fact, understanding such allocation is often considered the definition of economics to neoclassical theorists. Here is how William Stanley Jevons presented "the problem of Economics".
Given, a certain population, with various needs and powers of production, in possession of certain lands and other sources of material: required, the mode of employing their labor which will maximize the utility of their produce.[9]
From the basic assumptions of neoclassical economics comes a wide range of theories about various areas of economic activity. For example, profit maximization lies behind the neoclassical theory of the firm, while the derivation of demand curves leads to an understanding of consumer goods, and the supply curve allows an analysis of the factors of production. Utility maximization is the source for the neoclassical theory of consumption, the derivation of demand curves for consumer goods, and the derivation of labor supply curves and reservation demand.[10]
Supply and demand model
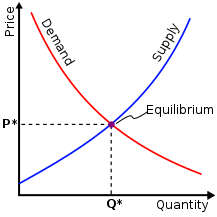
Market analysis is typically the neoclassical answer to price questions, such as why does an apple cost less than an automobile, why does the performance of work command a wage, or how to account for interest as a reward for saving. An important device of neoclassical market analysis is the graph presenting supply and demand curves. The curves reflect the behavior of individual buyers and individual sellers. Buyers and sellers interact with each other in and through these markets, and their interactions determine the market prices of anything they buy and sell. In the following graph, the specific price of the commodity being bought/sold is represented by P*.[11]
In reaching agreed outcomes of their interactions, the market behaviors of buyers and sellers are driven by their preferences (= wants, utilities, tastes, choices) and productive abilities (= technologies, resources). This creates a complex relationship between buyers and sellers. Thus, the geometrical analytics of supply and demand is only a simplified way how to describe and explore their interaction.[12] Market supply and demand are aggregated across firms and individuals. Their interactions determine equilibrium output and price. The market supply and demand for each factor of production is derived analogously to those for market final output[13] to determine equilibrium income and the income distribution. Factor demand incorporates the marginal productivity relationship of that factor in the output market.[6][14][15][16]
Neoclassical economics emphasizes equilibria, which are the solutions of agent maximization problems. Regularities in economies are explained by methodological individualism, the position that economic phenomena can be explained by aggregating over the behavior of agents. The emphasis is on microeconomics. Institutions, which might be considered as before and conditioning individual behavior, are de-emphasized. Economic subjectivism accompanies these emphases. See also general equilibrium.
Utility theory of value
Neoclassical economics uses the utility theory of value, which states that the value of a good is determined by the marginal utility experienced by the user. This is one of the main distinguishing factors between neoclassical economics and other earlier economic theories, such as Classical and Marxian, which use the labor theory of value that value is determined by the labor required for production.[17]
The partial definition of the neoclassical theory of value states that the value of an object of market exchange is determined by human interaction between the preferences and productive abilities of individuals. This is one of the most important neoclassical hypotheses. However, the neoclassical theory also asks what exactly is causing the supply and demand behaviors of buyers and sellers, and how exactly the preferences and productive abilities of people determine the market prices. Therefore, the neoclassical theory of value is a theory of these forces: the preferences and productive abilities of humans. They are the final causal determinants of the behavior of supply and demand and therefore of value. According to neoclassical economics, individual preferences and productive abilities are the essential forces that generate all other economic events (demands, supplies, and prices).[18]
Market failure and externalities
Despite favoring markets to organize economic activity, neoclassical theory acknowledges that markets do not always produce the socially desirable outcome due to the presence of externalities.[17] Externalities are considered a form of market failure. Neoclassical economists vary in terms of the significance they ascribe to externalities in market outcomes.
Pareto criterion
In a market with a very large number of participants and under appropriate conditions, for each good, there will be a unique price that allows all welfare–improving transactions to take place. This price is determined by the actions of the individuals pursuing their preferences. If these prices are flexible, meaning that all parties are able to pursue transactions at any rates they find mutually beneficial, they will, under appropriate assumptions, tend to settle at price levels that allow for all welfare–improving transactions. Under these assumptions, free-market processes yield an optimum of social welfare. This type of group welfare is called the Pareto optimum (criterion) after its discoverer Vilfredo Pareto.[19] Wolff and Resnick (2012) describe the Pareto optimality in another way. According to them, the term "Pareto optimal point" signifies the equality of consumption and production, which indicates that the demand (as a ratio of marginal utilities) and supply (as a ratio of marginal costs) sides of an economy are in balance with each other. The Pareto optimum point also signifies that society has fully realized its potential output.[20]
Normative judgments in neoclassical economics are shaped by the Pareto criterion. As a result, many neoclassical economists favor a relatively laissez-faire approach to government intervention in markets, since it is very difficult to make a change where no one will be worse off. However, many less conservative neoclassical economists instead use the compensation principle, which says that an intervention is good if the total gains are larger than the total losses, even if losers are not compensated in practice.[17]
International trade
Neoclassical economics favors free trade according to David Ricardo's theory of comparative advantage.[21] This idea holds that free trade between two countries is mutually beneficial because it allows the greatest total consumption in both countries.
Remove ads
Origins
Summarize
Perspective
Classical economics, developed in the 18th and 19th centuries, included a value theory and distribution theory. The value of a product was thought to depend on the costs involved in producing that product. The explanation of costs in classical economics was simultaneously an explanation of distribution. A landlord received rent, workers received wages, and a capitalist tenant farmer received profits on their investment. This classic approach included the work of Adam Smith and David Ricardo.
However, some economists gradually began emphasizing the perceived value of a good to the consumer. They proposed a theory that the value of a product was to be explained with differences in utility (usefulness) to the consumer. (In England, economists tended to conceptualize utility in keeping with the utilitarianism of Jeremy Bentham and later of John Stuart Mill.)
The third step from political economy to economics was the introduction of marginalism and the proposition that economic actors made decisions based on margins. For example, a person decides to buy a second sandwich based on how full he or she is after the first one, a firm hires a new employee based on the expected increase in profits the employee will bring. This differs from the aggregate decision-making of classical political economy in that it explains how vital goods such as water can be cheap, while luxuries can be expensive.
Marginal revolution
The change in economic theory from classical to neoclassical economics has been called the "marginal revolution", although it has been argued that the process was slower than the term suggests.[22] It is frequently dated from William Stanley Jevons's Theory of Political Economy (1871), Carl Menger's Principles of Economics (1871), and Léon Walras's Elements of Pure Economics (1874–1877). Historians of economics and economists have debated:
- Whether utility or marginalism was more essential to this revolution (whether the noun or the adjective in the phrase "marginal utility" is more important)
- Whether there was a revolutionary change of thought or merely a gradual development and change of emphasis from their predecessors
- Whether grouping these economists together disguises differences more important than their similarities.[23]
In particular, Jevons saw his economics as an application and development of Jeremy Bentham's utilitarianism and never had a fully developed general equilibrium theory. Menger did not embrace this hedonic conception, explained diminishing marginal utility in terms of subjective prioritization of possible uses, and emphasized disequilibrium and the discrete; further, Menger had an objection to the use of mathematics in economics, while the other two modeled their theories after 19th-century mechanics.[24] Jevons built on the hedonic conception of Bentham or of Mill, while Walras was more interested in the interaction of markets than in explaining the individual psyche.[23]
Alfred Marshall's textbook, Principles of Economics (1890), was the dominant textbook in England a generation later. Marshall's influence extended elsewhere; Italians would compliment Maffeo Pantaleoni by calling him the "Marshall of Italy". Marshall thought classical economics attempted to explain prices by the cost of production. He asserted that earlier marginalists went too far in correcting this imbalance by overemphasizing utility and demand. Marshall thought that "We might as reasonably dispute whether it is the upper or the under blade of a pair of scissors that cuts a piece of paper, as to whether the value is governed by utility or cost of production".
Marshall explained price by the intersection of supply and demand curves. The introduction of different market "periods" was an important innovation of Marshall's:
- Market period. The goods produced for sale on the market are taken as given data, e.g. in a fish market. Prices quickly adjust to clear markets.
- Short period. Industrial capacity is taken as given. The level of output, the level of employment, the inputs of raw materials, and prices fluctuate to equate marginal cost and marginal revenue, where profits are maximized. Economic rents exist in short period equilibrium for fixed factors, and the rate of profit is not equated across sectors.
- Long period. The stock of capital goods, such as factories and machines, is not taken as given. Profit-maximizing equilibria determine both industrial capacity and the level at which it is operated.
- Very long period. Technology, population trends, habits, and customs are not taken as given but allowed to vary in very long period models.
Marshall took supply and demand as stable functions and extended supply and demand explanations of prices to all runs. He argued supply was easier to vary in longer runs, and thus became a more important determinant of price in the very long run.
Cambridge and Lausanne school
Cambridge and Lausanne School of economics form the basis of neoclassical economics. Until the 1930s, the evolution of neoclassical economics was determined by the Cambridge school and was based on the marginal equilibrium theory. At the beginning of the 1930s, the Lausanne general equilibrium theory became the general basis of neoclassical economics and the marginal equilibrium theory was understood as its simplification.[25]
The thinking of the Cambridge school continued in the steps of classical political economics and its traditions but was based on the new approach that originated from the marginalist revolution. Its founder was Alfred Marshall, and among the main representatives were Arthur Cecil Pigou, Ralph George Hawtrey and Dennis Holme Robertson. Pigou worked on the theory of welfare economics and the quantity theory of money. Hawtrey and Robertson developed the Cambridge cash balance approach to theory of money and influenced the trade cycle theory. Until the 1930s, John Maynard Keynes was also influencing the theoretical concepts of the Cambridge school. The key characteristic of the Cambridge school was its instrumental approach to the economy – the role of the theoretical economist is first to define theoretical instruments of economic analysis and only just then apply them to real economic problems.[25]
The main representatives of the Lausanne school of economic thought were Léon Walras, Vilfredo Pareto and Enrico Barone. The school became famous for developing the general equilibrium theory. In the contemporary economy, the general equilibrium theory is the methodologic basis of mainstream economics in the form of New classical macroeconomics and New Keynesian macroeconomics.[25]
Remove ads
Evolution
Summarize
Perspective
This section may be too technical for most readers to understand. (April 2021) |
Periodization
The evolution of neoclassical economics is sometimes divided into three phases.
The pre-Keynesian phase began when neoclassical economics initially formed (in the second half of the nineteenth century) and continued until the arrival of Keynesian economics in the 1930s.
The Keynesian phase occurred from 1940 through the first half of the 1970s. During this era, Keynesian economics dominated the world's economy but neoclassical economics did not cease to exist. It continued in the development of its microeconomic theory and began creating its own macroeconomic theory. The development of the neoclassical macroeconomic theory was based on the development of the quantity theory of money and the theory of distribution. One of the products of the second phase was the Neoclassical synthesis, representing a special combination of neoclassical microeconomics and Keynesian macroeconomics.
The third phase began in the 1970s when neoclassical schools of thoughts such as Monetarism and New classical macroeconomics were developed and rose to prominence. Despite the diverse focus and approach of these theories, they are all based on the theoretical and methodological principles of traditional neoclassical economics.[26]
Evolution
An important change in neoclassical economics occurred around 1933. Joan Robinson and Edward H. Chamberlin, with the nearly simultaneous publication of their respective books, The Economics of Imperfect Competition (1933) and The Theory of Monopolistic Competition (1933), introduced models of imperfect competition. Theories of market forms and industrial organization grew out of this work. They also emphasized certain tools, such as the marginal revenue curve. In her book, Robinson formalized a type of limited competition. The conclusions of her work for welfare economics were worrying: they were implying that the market mechanism operates in a way that the workers are not paid according to the full value of their marginal productivity of labor and that also the principle of consumer sovereignty is impaired. This theory heavily influenced the anti–trust policies of many Western countries in the 1940s and 1950s.[27]
Joan Robinson's work on imperfect competition, at least, was a response to certain problems of Marshallian partial equilibrium theory highlighted by Piero Sraffa. Anglo-American economists also responded to these problems by turning towards general equilibrium theory, developed on the European continent by Walras and Vilfredo Pareto. J. R. Hicks's Value and Capital (1939) was influential in introducing his English-speaking colleagues to these traditions. He, in turn, was influenced by the Austrian School economist Friedrich Hayek's move to the London School of Economics, where Hicks then studied.[citation needed]
These developments were accompanied by the introduction of new tools, such as indifference curves and the theory of ordinal utility. The level of mathematical sophistication of neoclassical economics increased. Paul Samuelson's Foundations of Economic Analysis (1947) contributed to this increase in mathematical modeling.
The interwar period in American economics has been argued to have been pluralistic, with neoclassical economics and institutionalism competing for allegiance. Frank Knight, an early Chicago school economist attempted to combine both schools. But this increase in mathematics was accompanied by greater dominance of neoclassical economics in Anglo-American universities after World War II. Some[28] argue that outside political interventions, such as McCarthyism, and internal ideological bullying played an important role in this rise to dominance.
Hicks' book, Value and Capital had two main parts. The second, which was arguably not immediately influential, presented a model of temporary equilibrium. Hicks was influenced directly by Hayek's notion of intertemporal coordination and paralleled by earlier work by Lindhal. This was part of an abandonment of disaggregated long-run models. This trend probably reached its culmination with the Arrow–Debreu model of intertemporal equilibrium. The Arrow–Debreu model has canonical presentations in Gérard Debreu's Theory of Value (1959) and in Arrow and Hahn's "General Competitive Analysis" (1971).
Neoclassical synthesis
Many of these developments were against the backdrop of improvements in both econometrics, that is the ability to measure prices and changes in goods and services, as well as their aggregate quantities, and in the creation of macroeconomics, or the study of whole economies. The attempt to combine neo-classical microeconomics and Keynesian macroeconomics would lead to the neoclassical synthesis[29] which was the dominant paradigm of economic reasoning in English-speaking countries from the 1950s till the 1970s. Hicks and Samuelson were for example instrumental in mainstreaming Keynesian economics.
The dominance of Keynesian economics was upset by its inability to explain the economic crises of the 1970s-[30] neoclassical economics emerged distinctly in macroeconomics as the new classical school, which sought to explain macroeconomic phenomenon using neoclassical microeconomics.[31] It and its contemporary New Keynesian economics contributed to the new neoclassical synthesis of the 1990s, which informs much of mainstream macroeconomics today.[32][33]
Cambridge capital controversy
Problems exist with making the neoclassical general equilibrium theory compatible with an economy that develops over time and includes capital goods. This was explored in a major debate in the 1960s—the "Cambridge capital controversy"—about the validity of neoclassical economics, with an emphasis on economic growth, capital, aggregate theory, and the marginal productivity theory of distribution.[34] There were also internal attempts by neoclassical economists to extend the Arrow–Debreu model to disequilibrium investigations of stability and uniqueness. However, a result known as the Sonnenschein–Mantel–Debreu theorem suggests that the assumptions that must be made to ensure that equilibrium is stable and unique are quite restrictive.
Remove ads
Criticisms
Summarize
Perspective
Although the neoclassical approach is dominant in economics, the field of economics includes others, such as Marxist, behavioral, Schumpeterian, developmentalist, Austrian, post-Keynesian, Humanistic economics, real-world economics and institutionalist schools.[17] All of these schools differ with the neoclassical school and each other, and incorporate various criticisms of the neoclassical economics.[35] Not all criticism comes from other schools: some prominent economists such as Nobel Prize recipient and former chief economist of the World Bank Joseph Stiglitz are vocally critical of mainstream neoclassical economics.[36]
Methodology and mathematical models
This section needs expansion with: supporting views citing basis in statistical science, comparability with other social sciences. You can help by adding to it. (August 2021) |
Some see mathematical models used in contemporary research in mainstream economics as having transcended neoclassical economics,[37] while others disagree.[38] Mathematical models also include those in game theory, linear programming, and econometrics. Critics of neoclassical economics are divided into those who think that highly mathematical method is inherently wrong and those who think that mathematical method is useful even if neoclassical economics has other problems.[39]
Critics such as Tony Lawson contend that neoclassical economics' reliance on functional relations is inadequate for social phenomena in which knowledge of one variable does not reliably predict another.[40] The different factors affecting economic outcomes cannot be experimentally isolated from one another in a laboratory; therefore the explanatory and predictive power of mathematical economic analysis is limited. Lawson proposes an alternative approach called the contrast explanation which he says is better suited for determining causes of events in social sciences. More broadly, critics of economics as a science vary, with some believing that all mathematical economics is problematic or even pseudoscience and others believing it is still useful but has less certainty and higher risk of methodology problems than in other fields.[41][42]
Milton Friedman, one of the most prominent and influential neoclassical economists of the 20th century, responded to criticisms that assumptions in economic models were often unrealistic by saying that theories should be judged by their ability to predict events rather than by the supposed realism of their assumptions.[43] He claimed that, on the contrary, a theory with more absurd assumptions has stronger predictive power. He argued that a theory's ability to theoretically explain reality is irrelevant compared to its ability to empirically predict reality, no matter the method of getting to that prediction.
Objectivity and pluralism
Neoclassical economics is often criticized for having a normative bias despite sometimes claiming to be "value-free".[44][45] Such critics argue an ideological side of neoclassical economics, generally to argue that students should be taught more than one economic theory and that economics departments should be more pluralistic.[46][47]
Rational behavior assumptions
One of the most widely criticized aspects of neoclassical economics is its set of assumptions about human behavior and rationality. The "economic man", or a hypothetical human who acts according to neoclassical assumptions, does not necessarily behave the same way as humans do in reality.[48] The economist and critic of capitalism Thorstein Veblen claimed that neoclassical economics assumes a person to be "a lightning calculator of pleasures and pains, who oscillates like a homogeneous globule of desire of happiness under the impulse of stimuli that shift about the area, but leave him intact."[49]
Veblen's characterization references a number of commonly criticized rationality assumptions: that people make decisions using a rigid utilitarian framework, have perfect information available about their options, have perfect information processing ability allowing them to immediately calculate utility for all possible options, and are independent decision-makers whose choices are unaffected by their surroundings or by other people. While Veblen is from the Institutional school, the Behavioral school of economics is focused on studying the mechanisms of human decision-making and how they differ from neoclassical assumptions of rationality. Altruistic or empathy-based behavior is another form of "non-rational" decision making studied by behavioral economists, which differs from the neoclassical assumption that people only act in self-interest.[50][51] Behavioral economists account for how psychological, neurological, and even emotional factors significantly affect economic perceptions and behaviors.[52]
Rational choice theory need not be problematic according to a paper written by the economist Gary Becker which was published in 1962 in the Journal of Political Economy called "Irrational Behavior and Economic Theory".[53] According to Becker, this paper demonstrates "how the important theorems of modern economics result from a general principle which not only includes rational behavior and survivor arguments as special cases, but also much irrational behavior." The specific important theorems and results which are shown to result from a broad range of different type of irrational behavior, as well as rational behavior by market participants in the paper, are that market demand curves are downward sloping or "negatively inclined", and that if an industry transformed from a competitive industry to a completely monopolistic cartel and profits are always maximized, then output per firm under the cartel would decrease compared to its equilibrium level when the industry was competitive.
This paper was largely based on the 1950 paper "Uncertainty, Evolution, and Economic Theory" by Armen Alchian.[54] The paper sets out a justification for supply analysis separate from relying on the assumption of rational consumption, the representative firm and the way neoclassical economists analyze firm behavior in markets which does not rely on rational behavior by the decision makers in those firms, nor any other type of foresighted or goal directed behavior by them. Becker's subsequent 1962 paper provides an independent justification for neoclassical market demand analysis. The two papers offer separate justifications for the use of neoclassical methodology for supply and demand analysis without relying on assumptions otherwise criticised as implausible.
Methodological individualism
This section may be too technical for most readers to understand. (May 2021) |
Neoclassical economics offers an approach to studying the economic behavior of homo-economicus. This theory is based on methodological individualism and adopts an atomistic approach to social phenomena, according to which social atoms are the individuals and their actions.[55] According to this doctrine, individuals are independent of social phenomena, but the opposite is not true. Individuals' actions can explain macro-scale behavior, and social collections are nothing more than aggregates, and they do not add anything to its components (Ibid). Although methodological individualism does not negate complex social phenomena such as institutions or behavioral rules, it argues any explanation should be based on constituent components' characteristics of those institutions. This is a reductionist approach based on which it is believed that the characteristics of the social system are derived from the individuals' preferences and their actions.[56]
A critique of this approach is that the individuals' preferences and interests are not fixed. The structures contextualize individual's. According to social constructivists, systems are co-constituted alongside the actors, and ideas within the system define actors' identities, their interests, and thus their behavior.[57] In this regard, actors in various circumstances (exposed to different impressions and experiences) will construct their interests and preferences differently, both within each other and over time.[58] Given the individualistic foundation of the economic theory, critics argue that this theory should consider individual action's structural contexts.
Inequality
Neoclassical economics is often criticized as promoting policies that increase inequality and as failing to recognise the impact of inequality on economic outcomes. In the case of the former claim, neoclassical economics is often used for analysis in support of policies reducing economic inequality—in particular through determining the diminishing marginal utility of income, whereby poorer individuals gain greater net benefits from a given increase in income than comparable richer individuals,[59][60] but more generally by being the primary means by which the impact on inequality of any given policy is assessed. In the case of the latter claim, neoclassical economics is the prevailing lens through which the relationship between inequality and economic outcomes is studied.[61]
Ethics of markets
Neoclassical economics tends to promote commodification and privatization of goods due to its principle that market exchange generally results in the most effective allocation of goods. For example, some economists support markets for human organs, on the basis that it increases supply of life-saving organs and benefits willing donors financially.[62] However, there are arguments in moral philosophy that use of markets for certain goods is inherently unethical. Political philosopher Michael Sandel summarizes that market exchanges have two ethical problems: coercion and corruption.[63] Coercion happens because market participation may not be as free as proponents often claim: people often participate in markets because it is the only way to survive, which is not truly voluntary. Corruption describes how commodification of a good can inherently degrade its value.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads