Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Probability measure
Measure of total value one, generalizing probability distributions From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In mathematics, a probability measure is a real-valued function defined on a set of events in a σ-algebra that satisfies measure properties such as countable additivity.[1] The difference between a probability measure and the more general notion of measure (which includes concepts like area or volume) is that a probability measure must assign value 1 to the entire space.
Intuitively, the additivity property says that the probability assigned to the union of two disjoint (mutually exclusive) events by the measure should be the sum of the probabilities of the events; for example, the value assigned to the outcome "1 or 2" in a throw of a die should be the sum of the values assigned to the outcomes "1" and "2".
Probability measures have applications in diverse fields, from physics to finance and biology.
Remove ads
Definition
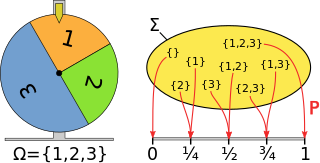
The requirements for a set function to be a probability measure on a σ-algebra are that:
- must take values in the unit interval including on the empty set and on the entire space.
- must satisfy the countable additivity property that for all countable collections of pairwise disjoint sets:
For example, given three elements 1, 2 and 3 with probabilities and the value assigned to is as in the diagram on the right.
The conditional probability based on the intersection of events defined as: satisfies the probability function requirements so long as is not zero.[2][3]
Probability measures are distinct from the more general notion of fuzzy measures in which there is no requirement that the fuzzy values sum up to and the additive property is replaced by an order relation based on set inclusion.
Remove ads
Example applications
Summarize
Perspective
In many cases, statistical physics uses probability measures, but not all measures it uses are probability measures.[clarification needed][4][5]
Market measures which assign probabilities to financial market spaces based on observed market movements are examples of probability measures which are of interest in mathematical finance; for example, in the pricing of financial derivatives.[6] For instance, a risk-neutral measure is a probability measure which assumes that the current value of assets is the expected value of the future payoff taken with respect to that same risk neutral measure (i.e. calculated using the corresponding risk neutral density function), and discounted at the risk-free rate. If there is a unique probability measure that must be used to price assets in a market, then the market is called a complete market.[7]
Not all measures that intuitively represent chance or likelihood are probability measures. For instance, although the fundamental concept of a system in statistical mechanics is a measure space, such measures are not always probability measures.[4] In statistical physics, for sentences of the form "the probability of a system S assuming state A is p," the geometry of the system does not always lead to the definition of a probability measure under congruence, although it may do so in the case of systems with just one degree of freedom.[5]
Probability measures are also used in mathematical biology.[8] For instance, in comparative sequence analysis a probability measure may be defined for the likelihood that a variant may be permissible for an amino acid in a sequence.[9]
Remove ads
See also
- Borel measure – Measure defined on all open sets of a topological space
- Fuzzy measure
- Haar measure – Left-invariant (or right-invariant) measure on locally compact topological group
- Lebesgue measure – Concept of area in any dimension
- Martingale measure – Probability measure
- Set function – Function from sets to numbers
- Probability distribution
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads


![{\displaystyle [0,1],}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/971caee396752d8bf56711f55d2c3b1207d4a236)










