Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Programmable logic controller
Programmable digital computer used to control machinery From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that requires high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis.

PLCs can range from small modular devices with tens of inputs and outputs (I/O), in a housing integral with the processor, to large rack-mounted modular devices with thousands of I/O, and which are often networked to other PLC and SCADA systems.[1] They can be designed for many arrangements of digital and analog I/O, extended temperature ranges, immunity to electrical noise, and resistance to vibration and impact.
PLCs were first developed in the automobile manufacturing industry to provide flexible, rugged and easily programmable controllers to replace hard-wired relay logic systems. Dick Morley, who invented the first PLC, the Modicon 084, for General Motors in 1968, is considered the father of PLC.
A PLC is an example of a hard real-time system since output results must be produced in response to input conditions within a limited time, otherwise unintended operation may result. Programs to control machine operation are typically stored in battery-backed-up or non-volatile memory.
Remove ads
Invention and early development
Summarize
Perspective
The PLC originated in the late 1960s in the automotive industry in the US and was designed to replace relay logic systems.[2] Before, control logic for manufacturing was mainly composed of relays, cam timers, drum sequencers, and dedicated closed-loop controllers.[3]
The hard-wired nature of these components made it difficult for design engineers to alter the automation process. Changes would require rewiring and careful updating of the documentation. Troubleshooting was a tedious process.[4] When general-purpose computers became available, they were soon applied to control logic in industrial processes. These early computers were unreliable[5] and required specialist programmers and strict control of working conditions, such as temperature, cleanliness, and power quality.[6]
The PLC provided several advantages over earlier automation systems. It was designed to tolerate the industrial environment better than systems intended for office use, and was more reliable, compact, and required less maintenance than relay systems. It was easily expandable with additional I/O modules. While relay systems required tedious and sometimes complicated hardware changes in case of reconfiguration, a PLC can be reconfigured by loading new or modified code. This allowed for easier iteration over manufacturing process design. With a simple programming language focused on logic and switching operations, it was more user-friendly than computers using general-purpose programming languages. Early PLCs were programmed in ladder logic, which strongly resembled a schematic diagram of relay logic. It also permitted its operation to be monitored.[7][8]
Here is an older timeline with product milestones from the significant manufacturers of the early PLC's. It has not been updated in quite a while but it's a reasonably accurate reference for the early days of the PLC: https://archive.control.lth.se/media/Education/DoctorateProgram/2012/HistoryOfControl/Vanessa_Albert-PLCDCS.pdf
Virtual PLCs
In recent years, the introduction of virtual PLCs has expanded the scope of programmable logic controllers. Virtual PLCs are software-based controllers that simulate the functions of traditional PLCs but are executed on general-purpose hardware, offering a more cost-effective and flexible alternative. These controllers enable automation systems to be managed without the need for dedicated hardware, making them ideal for applications requiring simulation, remote control, or cloud-based systems.[9]
Modicon
In 1968, GM Hydramatic, the automatic transmission division of General Motors, issued a request for proposals for an electronic replacement for hard-wired relay systems based on a white paper written by engineer Edward R. Clark. The winning proposal came from Bedford Associates from Bedford, Massachusetts. The result, built in 1969, was the first PLC and designated the 084, because it was Bedford Associates' eighty-fourth project.[10][11]
Bedford Associates started a company, Modicon, Inc.,[12] dedicated to developing, manufacturing, selling, and servicing this new product, which they named Modicon (standing for "modular digital controller"). One of the people who worked on that project was Dick Morley, who is considered to be the father of the PLC.[13] The Modicon brand was sold in 1977 to Gould Electronics and later to Schneider Electric, its current owner.[11] About this same time, Modicon created Modbus, a data communications protocol to be used with its PLCs. Modbus has since become a standard open protocol commonly used to connect many industrial electrical devices.[14]
One of the first Modicon 084 models built is now on display at Schneider Electric's facility in North Andover, Massachusetts. It was presented to Modicon by GM, when the unit was retired after nearly twenty years of uninterrupted service. Modicon used the 84 moniker at the end of its product range like Modicon Micro 84 and Modicon TSX CSY 84 until after the 984 made its appearance.[15]
Allen-Bradley
In a parallel development, Odo Josef Struger is sometimes known as the "father of the programmable logic controller" as well.[13] He was involved in the invention of the Allen-Bradley programmable logic controller.[16][17][18] Prior to the release of the IBM "Personal Computer" in 1981, these devices were commonly known simply as "Programmable Controllers", or "PC's. But but rapid expansion of the personal computer industry in the early 1980's, the abbreviation "PC" was rapidly and universally accepted as a reference to "Personal Computers". Odo was later credited with coining the "PLC" acronym[13][16] to distinguish these two technologies, And the inclusion of the word "Logic" was an easy choice as "Ladder Logic" had already been accepted as the name of the programming language. Allen-Bradley (now a brand owned by Rockwell Automation) went on to become the dominant PLC manufacturer in the United States during his tenure.[19] Struger played a leadership role in developing IEC 61131-3 PLC programming language standards.[13] Allen-Bradley's PLC-5 family, preceded by the 1774-PLC (released in the 1980's, was the first modular design found in modern-day systems.[20]
While Modicon was perhaps the most popular of the first full featured PLC's through the early 1980's, Allen Bradley quickly overtook them in the mid-1980's and grew to own the largest market share (by far) of PLC hardware and software in North America. [21] A primary reason for this rapid growth and market share was the pioneering use of a "limited distribution" model for Rockwell PLC's and other products throughout the US. As of 2025 there are more than 200 authorized distributors in the US. Rockwell assigns just one single authorized distributor to each geographic territory and limits support and resources to customers who do not purchase from their local authorized distributor (or from an OEM/SI who used an authorized distributor). In addition, each distributor is required to have a staff of multiple product "Specialists" for PLC's, Industrial Controls (buttons, relays, contactors etc.), Network security, Variable Speed Drives, Motion products, Safety solutions, Life-Cycle services and other value-Add services and other categories. This mix of "protected" territory and multiple local experts made it easy for customers to get local assistance with design, selection and configuration of increasingly complex systems.[22] This large and knowledgeable network of local distributors contributes to Rockwell's reputation of being one of the highest priced manufacturers. But the quantity and quality of their distribution network (and the quality of the products themselves) has earned them the stable market share they have enjoyed since the mid to late 1980's.
Early methods of programming
Many early PLC programming applications were not capable of graphical representation of the logic, and so it was instead represented as a series of logic expressions in some kind of Boolean format, similar to Boolean algebra. As programming terminals evolved, because ladder logic was a familiar format used for electro-mechanical control panels, it became more commonly used. Newer formats, such as state logic,[23] function block diagrams, and structured text exist. Ladder logic remains popular because PLCs solve the logic in a predictable and repeating sequence, and ladder logic allows the person writing the logic to see any issues with the timing of the logic sequence more easily than would be possible in other formats.[24]
Up to the mid-1990s, PLCs were programmed using proprietary programming panels or special-purpose programming terminals, which often had dedicated function keys representing the various logical elements of PLC programs.[10] Some proprietary programming terminals displayed the elements of PLC programs as graphic symbols, but plain ASCII character representations of contacts, coils, and wires were common. Programs were stored on cassette tape cartridges. Facilities for printing and documentation were minimal due to a lack of memory capacity. The oldest PLCs used magnetic-core memory.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Architecture
Summarize
Perspective
A PLC is an industrial microprocessor-based controller with programmable memory used to store program instructions and various functions.[25] It consists of:
- A processor unit (CPU) which interprets inputs, executes the control program stored in memory and sends output signals,
- A power supply unit which converts AC voltage to DC,
- A memory unit storing data from inputs and program to be executed by the processor,
- An input and output interface, where the controller receives and sends data from and to external devices,
- A communications interface to receive and transmit data on communication networks from and to remote PLCs.[26]
PLCs require a programming device which is used to develop and later download the created program into the memory of the controller.[26]
Modern PLCs generally contain a real-time operating system, such as OS-9 or VxWorks.[27]
Mechanical design


There are two types of mechanical design for PLC systems. A single box (also called a brick) is a small programmable controller that fits all units and interfaces into one compact casing, although, typically, additional expansion modules for inputs and outputs are available. The second design type – a modular PLC – has a chassis (also called a rack) that provides space for modules with different functions, such as power supply, processor, selection of I/O modules and communication interfaces – which all can be customized for the particular application.[28] Several racks can be administered by a single processor and may have thousands of inputs and outputs. Either a special high-speed serial I/O link or comparable communication method is used so that racks can be distributed away from the processor, reducing the wiring costs for large plants.[citation needed]
Discrete and analog signals
Discrete (digital) signals can only take on or off value (1 or 0, true or false). Examples of devices providing a discrete signal include limit switches and photoelectric sensors.[29]
Analog signals can use voltage or current that is analogous to the monitored variable and can take any value within their scale. Pressure, temperature, flow, and weight are often represented by analog signals. These are typically interpreted as integer values with various ranges of accuracy depending on the device and the number of bits available to store the data.[29] For example, an analog 0 to 10 V or 4-20 mA current loop input would be converted into an integer value of 0 to 32,767. The PLC will take this value and translate it into the desired units of the process so the operator or program can read it.
Redundancy
Some special processes need to work permanently with minimum unwanted downtime. Therefore, it is necessary to design a system that is fault tolerant. In such cases, to increase the system availability in the event of hardware component failure, redundant CPU or I/O modules with the same functionality can be added to a hardware configuration to prevent a total or partial process shutdown due to hardware failure. Other redundancy scenarios could be related to safety-critical processes, for example, large hydraulic presses could require that two PLCs turn on output before the press can come down in case one PLC does not behave properly.
Remove ads
Programming
Summarize
Perspective

Programmable logic controllers are intended to be used by engineers without a programming background. For this reason, a graphical programming language called ladder logic was first developed. It resembles the schematic diagram of a system built with electromechanical relays and was adopted by many manufacturers and later standardized in the IEC 61131-3 control systems programming standard. As of 2015,[update] it is still widely used, thanks to its simplicity.[30]
As of 2015,[update] the majority of PLC systems adhere to the IEC 61131-3 standard that defines 2 textual programming languages: Structured Text (similar to Pascal) and Instruction List; as well as 3 graphical languages: ladder logic, function block diagram and sequential function chart.[30][31] Instruction List was deprecated in the third edition of the standard.[32]
Modern PLCs can be programmed in a variety of ways, from the relay-derived ladder logic to programming languages such as specially adapted dialects of BASIC and C.[33]
While the fundamental concepts of PLC programming are common to all manufacturers, differences in I/O addressing, memory organization, and instruction sets mean that PLC programs are never perfectly interchangeable between different makers. Even within the same product line of a single manufacturer, different models may not be directly compatible.[34]
Programming device
Manufacturers develop programming software for their PLCs. In addition to being able to program PLCs in multiple languages, they provide common features like hardware diagnostics and maintenance, software debugging, and offline simulation.[35]
PLC programs are typically written in a programming device, which can take the form of a desktop console, special software on a personal computer, or a handheld device.[35] The program is then downloaded to the PLC through a cable connection or over a network. It is stored either in non-volatile flash memory or battery-backed-up RAM on the PLC. In some PLCs, the program is transferred from the programming device using a programming board that writes the program into a removable chip, such as EPROM that is then inserted into the PLC.
Simulation
An incorrectly programmed PLC can result in lost productivity and dangerous conditions for programmed equipment. PLC simulation is a feature often found in PLC programming software. It allows for testing and debugging early in a project's development. Testing the project in simulation improves its quality, increases the level of safety associated with equipment and can save time during the installation and commissioning of automated control applications since many scenarios can be tried and tested before the system is activated.[35][36]
Remove ads
Functionality
Summarize
Perspective
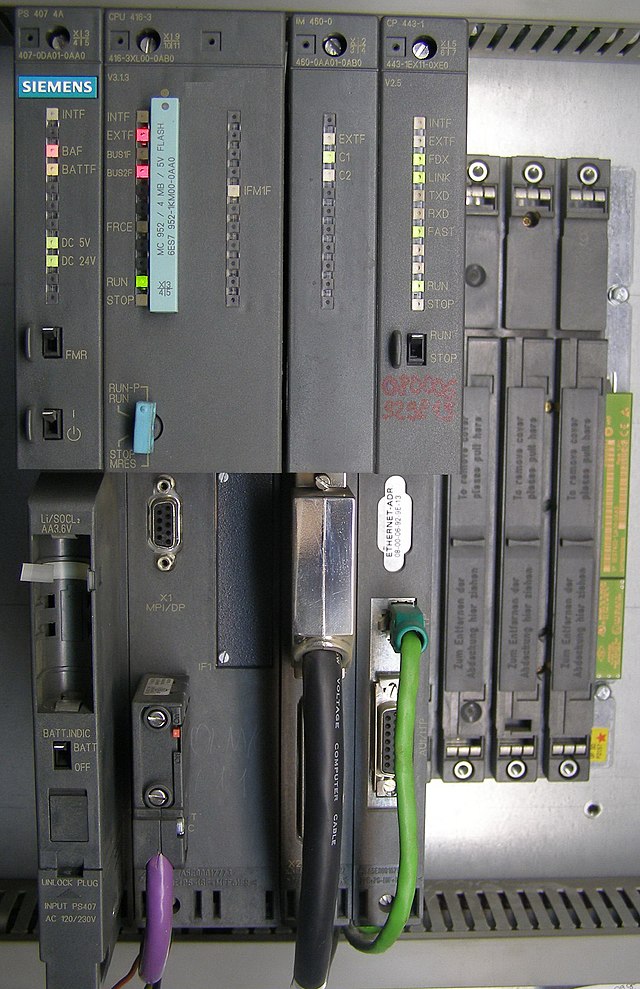

The main difference compared to most other computing devices is that PLCs are intended for and therefore tolerant of more severe environmental conditions (such as dust, moisture, heat, cold), while offering extensive input/output (I/O) to connect the PLC to sensors and actuators. PLC input can include simple digital elements such as limit switches, analog variables from process sensors (such as temperature and pressure), and more complex data such as that from positioning or machine vision systems.[37] PLC output can include elements such as indicator lamps, sirens, electric motors, pneumatic or hydraulic cylinders, magnetic relays, solenoids, or analog outputs. The input/output arrangements may be built into a simple PLC, or the PLC may have external I/O modules attached to a fieldbus or computer network that plugs into the PLC.
The functionality of the PLC has evolved over the years to include sequential relay control, motion control, process control, distributed control systems, and networking. The data handling, storage, processing power, and communication capabilities of some modern PLCs are approximately equivalent to desktop computers. PLC-like programming combined with remote I/O hardware allows a general-purpose desktop computer to serve as a PLC in certain applications.[citation needed] Desktop computer controllers have not been generally accepted in heavy industry because desktop computers run on less stable operating systems than PLCs, and because the desktop computer hardware is typically not designed to the same levels of tolerance to temperature, humidity, vibration, and longevity as PLCs.
Basic functions
The most basic function of a programmable logic controller is to emulate the functions of electromechanical relays. Within the PLC programming environment, discrete inputs are given a unique address, and a PLC instruction can test if the input state is on or off. Just as a series of relay contacts perform a logical AND function, not allowing current to pass unless all the contacts are closed, so a series of examine if on instructions will energize its output storage bit if all the input bits are on. Similarly, a parallel set of instructions will perform a logical OR. In an electromechanical relay wiring diagram, a group of contacts controlling one coil is called a rung of a ladder diagram, and this concept is also used to describe PLC logic.[a] The output of each rung sets or clears a storage bit, which may be associated with a discrete output or which may be an internal coil with no physical connection. Such internal coils can be used, for example, as a common element in multiple separate rungs.
More advanced instructions of the PLC may be implemented as functional blocks, which carry out some operation, such as manipulating internal variable, when enabled by a logical input and which produce outputs to signal, for example, completion or errors.
Communication
PLCs use built-in ports, such as USB, Ethernet, RS-232, RS-485, or RS-422 to communicate with external devices (sensors, actuators) and systems (programming tools, SCADA and other user interfaces). Communication is carried over various industrial network protocols, like Modbus, or EtherNet/IP. Many of these protocols are vendor specific. Formerly, some manufacturers offered dedicated communication modules as an add-on function where the processor had no network connection built-in.
PLCs used in larger I/O systems may have peer-to-peer (P2P) communication between processors. This allows separate parts of a complex process to have individual control while allowing the subsystems to coordinate over the communication link.
User interface

PLCs may need to interact with people for the purpose of configuration, alarm reporting, or everyday control. A human-machine interface (HMI) is employed for this purpose. HMIs are also referred to as man-machine interfaces (MMIs) and graphical user interfaces (GUIs). A simple system may use buttons and lights to interact with the user. Text displays are available as well as graphical touch screens. More complex systems use programming and monitoring software installed on a computer, with the PLC connected via a communication interface.
Remove ads
Process of a scan cycle
Summarize
Perspective
A PLC works in a program scan cycle, where it executes its program repeatedly. The simplest scan cycle consists of 3 steps:[38]
- Read inputs
- Execute the program
- Write outputs
The program follows the sequence of instructions. It typically takes a time span of tens of milliseconds for the processor to evaluate all the instructions and update the status of all outputs.[39] If the system contains remote I/O—for example, an external rack with I/O modules—then that introduces additional uncertainty in the response time of the PLC system.[38]
Special-purpose I/O modules may be used where the scan time of the PLC is too long to allow predictable performance. Precision timing modules, or counter modules for use with shaft encoders, are used where the scan time would be too long to reliably count pulses or detect the sense of rotation of an encoder. This allows even a relatively slow PLC to still interpret the counted values to control a machine, as the accumulation of pulses is done by a dedicated module that is unaffected by the speed of program execution.[40]
As PLCs became more advanced, methods were developed to change the sequence of ladder execution, and subroutines were implemented.[41]
Remove ads
Security
Summarize
Perspective
In his book from 1998, E. A. Parr pointed out that even though most programmable controllers require physical keys and passwords, the lack of strict access control and version control systems, as well as an easy-to-understand programming language make it likely that unauthorized changes to programs will happen and remain unnoticed.[42]
Prior to the discovery of the Stuxnet computer worm in June 2010, the security of PLCs received little attention. Modern programmable controllers generally contain real-time operating systems, which can be vulnerable to exploits in a similar way as desktop operating systems, like Microsoft Windows. PLCs can also be attacked by gaining control of a computer they communicate with.[27] Since 2011,[update] these concerns have grown – networking is becoming more commonplace in the PLC environment, connecting the previously separated plant floor networks and office networks.[43]
In February 2021, Rockwell Automation publicly disclosed a critical vulnerability affecting its Logix controllers family. The secret cryptographic key used to verify communication between the PLC and workstation could be extracted from the programming software (Studio 5000 Logix Designer) and used to remotely change program code and configuration of a connected controller. The vulnerability was given a severity score of 10 out of 10 on the CVSS vulnerability scale. At the time of writing, the mitigation of the vulnerability was to limit network access to affected devices.[44][45]
Remove ads
Safety PLCs
Safety PLCs can be either a standalone device or a safety-rated hardware and functionality added to existing controller architectures (Allen-Bradley GuardLogix, Siemens F-series, etc.). These differ from conventional PLC types by being suitable for safety-critical applications for which PLCs have traditionally been supplemented with hard-wired safety relays and areas of the memory dedicated to the safety instructions. The standard of safety level is the SIL.
A safety PLC might be used to control access to a robot cell with trapped-key access, or to manage the shutdown response to an emergency stop button on a conveyor production line. Such PLCs typically have a restricted regular instruction set augmented with safety-specific instructions designed to interface with emergency stop buttons, light screens, and other safety-related devices.
The flexibility that such systems offer has resulted in rapid growth of demand for these controllers.[citation needed]
Remove ads
PLC compared with other control systems
Summarize
Perspective


PLCs are well adapted to a range of automation tasks. These are typically industrial processes in manufacturing where the cost of developing and maintaining the automation system is high relative to the total cost of the automation, and where changes to the system would be expected during its operational life. PLCs contain input and output devices compatible with industrial pilot devices and controls; little electrical design is required, and the design problem centers on expressing the desired sequence of operations. PLC applications are typically highly customized systems, so the cost of a packaged PLC is low compared to the cost of a specific custom-built controller design. On the other hand, in the case of mass-produced goods, customized control systems are economical. This is due to the lower cost of the components, which can be optimally chosen instead of a "generic" solution, and where the non-recurring engineering charges are spread over thousands or millions of units.[citation needed]
Programmable controllers are widely used in motion, positioning, or torque control. Some manufacturers produce motion control units to be integrated with PLC so that G-code (involving a CNC machine) can be used to instruct machine movements.[citation needed]
PLC chip / embedded controller
These are for small machines and systems with low or medium volume. They can execute PLC languages such as Ladder, Flow-Chart/Grafcet, etc. They are similar to traditional PLCs, but their small size allows developers to design them into custom printed circuit boards like a microcontroller, without computer programming knowledge, but with a language that is easy to use, modify and maintain. They sit between the classic PLC / micro-PLC and microcontrollers.[citation needed]
Microcontrollers
A microcontroller-based design would be appropriate where hundreds or thousands of units will be produced and so the development cost (design of power supplies, input/output hardware, and necessary testing and certification) can be spread over many sales, and where the end-user would not need to alter the control. Automotive applications are an example; millions of units are built each year, and very few end-users alter the programming of these controllers. However, some specialty vehicles such as transit buses economically use PLCs instead of custom-designed controls, because the volumes are low and the development cost would be uneconomical.[46]
Single-board computers
Very complex process control, such as those used in the chemical industry, may require algorithms and performance beyond the capability of even high-performance PLCs. Very high-speed or precision controls may also require customized solutions; for example, aircraft flight controls. Single-board computers using semi-customized or fully proprietary hardware may be chosen for very demanding control applications where the high development and maintenance cost can be supported. "Soft PLCs" running on desktop-type computers can interface with industrial I/O hardware while executing programs within a version of commercial operating systems adapted for process control needs.[46]
The rising popularity of single board computers has also had an influence on the development of PLCs. Traditional PLCs are generally closed platforms, but some newer PLCs (e.g. groov EPIC from Opto 22, ctrlX from Bosch Rexroth, PFC200 from Wago, PLCnext from Phoenix Contact, and Revolution Pi from Kunbus) provide the features of traditional PLCs on an open platform.
Programmable logic relays (PLR)
This section possibly contains original research. (March 2020) |
In more recent years,[when?] small products called programmable logic relays (PLRs) or smart relays, have become more common and accepted. These are similar to PLCs and are used in light industries where only a few points of I/O are needed, and low cost is desired. These small devices are typically made in a common physical size and shape by several manufacturers and branded by the makers of larger PLCs to fill their low-end product range. Most of these have 8 to 12 discrete inputs, 4 to 8 discrete outputs, and up to 2 analog inputs. Most such devices include a tiny postage stamp-sized LCD screen for viewing simplified ladder logic (only a very small portion of the program being visible at a given time) and status of I/O points, and typically these screens are accompanied by a 4-way rocker push-button plus four more separate push-buttons, similar to the key buttons on a VCR remote control, and used to navigate and edit the logic. Most have an RS-232 or RS-485 port for connecting to a PC so that programmers can use user-friendly software for programming instead of the small LCD and push-button set for this purpose. Unlike regular PLCs that are usually modular and greatly expandable, the PLRs are usually not modular or expandable, but their cost can be significantly lower than that a PLC, and they still offer robust design and deterministic execution of the logic.
A variant of PLCs, used in remote locations is the remote terminal unit or RTU. An RTU is typically a low power, ruggedized PLC whose key function is to manage the communications links between the site and the central control system (typically SCADA) or in some modern systems, "The Cloud". Unlike factory automation using wired communication protocols such as Ethernet, communications links to remote sites are often radio-based and are less reliable. To account for the reduced reliability, RTU will buffer messages or switch to alternate communications paths. When buffering messages, the RTU will timestamp each message so that a full history of site events can be reconstructed. RTUs, being PLCs, have a wide range of I/O and are fully programmable, typically with languages from the IEC 61131-3 standard that is common to many PLCs, RTUs and DCSs. In remote locations, it is common to use an RTU as a gateway for a PLC, where the PLC is performing all site control and the RTU is managing communications, time-stamping events and monitoring ancillary equipment. On sites with only a handful of I/O, the RTU may also be the site PLC and will perform both communications and control functions.
Remove ads
See also
Notes
- Some models of PLC limit the number of series and parallel instructions in one "rung" of logic. Some PLCs enforce a strict left-to-right, top-to-bottom execution order for evaluating the rung logic. This is different from electro-mechanical relay contacts, which, in a sufficiently complex circuit, may either pass current left-to-right or right-to-left, depending on the configuration of surrounding contacts. The elimination of these sneak paths is either a bug or a feature, depending on the programming style.
Remove ads
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
