Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
RYB color model
Subtractive color model From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
RYB (an abbreviation of red–yellow–blue) is a subtractive color model used in art and applied design in which red, yellow, and blue pigments are considered primary colors.[1] Under traditional color theory, this set of primary colors was advocated by Moses Harris, Michel Eugène Chevreul, Johannes Itten and Josef Albers, and applied by countless artists and designers. The RYB color model underpinned the color curriculum of the Bauhaus, Ulm School of Design and numerous art and design schools that were influenced by the Bauhaus, including the IIT Institute of Design (founded as the New Bauhaus), Black Mountain College, Design Department Yale University, the Shillito Design School, Sydney, and Parsons School of Design, New York.




In this context, the term primary color refers to three exemplar colors (red, yellow, and blue) as opposed to specific pigments. As illustrated, in the RYB color model, red, yellow, and blue are intermixed to create secondary color segments of orange, green, and purple. This set of primary colors emerged at a time when access to a large range of pigments was limited by availability and cost, and it encouraged artists and designers to explore the many diverse colors through mixing and intermixing a limited range of pigment colors. In art and design education, gray, red, yellow, and blue pigments were usually augmented with white and black pigments, enabling the creation of a larger gamut of colors and details including tints and shades.
Although scientifically obsolete because it does not meet the definition of a complementary color in which a neutral or black color must be mixed,[clarification needed] it is still a model used in artistic environments, causing confusion about primary and complementary colors. It can be considered an approximation of the CMY color model.
The RYB color model relates specifically to color in the form of paint and pigment application in art and design.[2] Other common color models include the light model (RGB) and the paint, pigment and ink CMY color model, which is much more accurate in terms of color gamut and intensity compared to the traditional RYB color model, the latter emerging in conjunction with the CMYK color model in the printing industry.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
The first scholars to propose that there are three primary colors for painters were Scarmiglioni (1601), Savot (1609), de Boodt (1609) and Aguilonius (1613).[3] From these, the most influential was the work of Franciscus Aguilonius (1567–1617), although he did not arrange the colors in a wheel.[4]
Jacob Christoph Le Blon was the first to apply the RYB color model to printing, specifically mezzotint printing, and he used separate plates for each color: yellow, red and blue plus black to add shades and contrast. In 'Coloritto', Le Blon asserted that “the art of mixing colours…(in) painting can represent all visible objects with three colours: yellow, red and blue; for all colours can be composed of these three, which I call Primitive”. Le Blon added that red and yellow make orange; red and blue, make purple; and blue and yellow make green (Le Blon, 1725, p6).[5][6]
In the 18th century, Moses Harris advocated that a multitude of colors can be created from three "primitive" colors – red, yellow, and blue.[7]
Mérimée referred to "three simple colours (yellow, red, and blue)" that can produce a large gamut of colors and details. "United in pairs, these three primitive colours give birth to three other colours as distinct and brilliant as their originals; thus, yellow mixed with red, gives orange; red and blue, violet; and green is obtained by mixing blue and yellow" (Mérimée, 1839, p245). Mérimée illustrated these color relationships with a simple diagram located between pages 244 and 245: Chromatic Scale (Echelle Chromatique).De la peinture à l’huile : ou, Des procédés matériels employés dans ce genre de peinture, depuis Hubert et Jean Van-Eyck jusqu’à nos jours was published in 1830 and an English translation by W. B. Sarsfield Taylor was published in London in 1839.[8]
Similar ideas about the creation of color using red, yellow, and blue were discussed in Theory of Colours (1810) by the German poet, color theorist and government minister Johann Wolfgang von Goethe.[9]
In The Law of Simultaneous Color Contrast (1839) by the French industrial chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul discussed the creation of numerous color nuances and his color theories were underpinned by the RYB color model.[10]
Separate to the RYB color model, cyan, magenta, and yellow primary colors are associated with CMYK commonly used in the printing industry. Cyan, magenta, and yellow are often referred to as "process blue", "process red", and "process yellow".[11][12]
Old model of coloration with four primaries
The ancient Greeks, under the influence of Aristotle, Democritus and Plato, considered that there were four basic colors that coincided with the four elements: earth (ochre), sky (blue), water (green) and fire (red), while black and white represented the light of day and the darkness of night. [citation needed] The four-color system is formed by the primaries yellow, green, blue and red, and was supported by Alberti in his "De Pictura" (1436), using the rectangle, rhombus, and color wheel to represent them.

Leonardo da Vinci endorsed this model in 1510, although he hesitated to include green, noting that green could be obtained by mixing blue and yellow. Also Richard Waller, in his "Catalogue of Simple and Mixed Colors" (1686), graphed these four colors in a square.[14] These four colors have often been referred to as "the primary psychological colors".[15]
Traditional coloring with three primaries
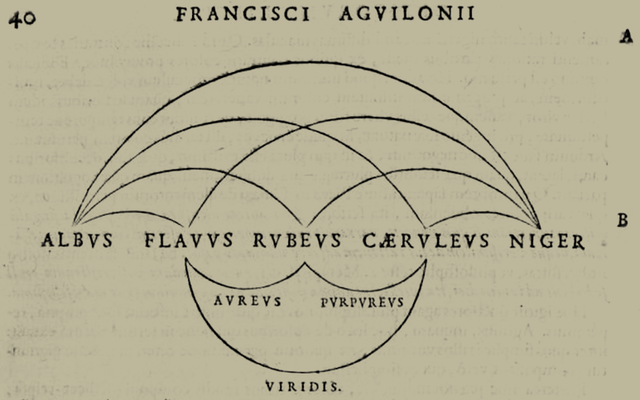
The first known case of trichromacy coloration (of 3 primaries) can be found in a work on optics by the Belgian thinker Franciscus Aguilonius in 1613,[16] who in his "Opticorum libri sex, philosophis iuxtà ac mathematicis utiles" in Latin (Roughly, Six books of optics: useful to philosophers as well as to mathematicians), graphed the colors flavvus, rvbevs and cærvlevs (yellow, red and blue) giving rise to the intermediate colors avrevs, viridis and pvrpvrevs (orange, green and purple) and their relationship with the extremes albvs and niger (white and black).[17] However, the idea of three primary colors is older, as Aguilonius supported the view known since the Middle Ages that the colors yellow, red, and blue were the basic or "noble" colors from which all others are derived.[18]
This model was used for printing by Jacob Christoph Le Blon in 1725 and called it Coloritto or harmony of colouring,[19] stating that the primitive (primary) colors are yellow, red and blue, while the secondary are orange, green and purple or violet.[20]
In 1766, Moses Harris developed an 18-color color wheel based on this model, including a wider range of colors by adding light and dark derivatives.[21] During the 18th and 19th centuries, this color model was endorsed by many authors who have left illustrations that can still be appreciated today, such as Louis-Bertrand Castel (1740), the Tobias's color system Mayer (1758), Moses Harris (1770–76), Ignaz Schiffermuller (1772), Baumgartner and Muller (1803), Sowerby (1809), Runge (1809), the popular "Theory of Colors" (1810) by Goethe, Gregoire (1810–20), Mérimée (1815-30-39), Klotz (1816), G. Field (1817-41-50), Hayter (1826 ), the "Law of Simultaneous Contrast of Colours" (1839) by Chevreul and many others.[22]

By the 20th century, natural pigments gave way to synthetic ones. The invention of phthalocyanine and derivatives of quinacridone, expanded the range of primary blues and reds, getting closer to the ideal subtractive colors and the CMY and CMYK models.

Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
