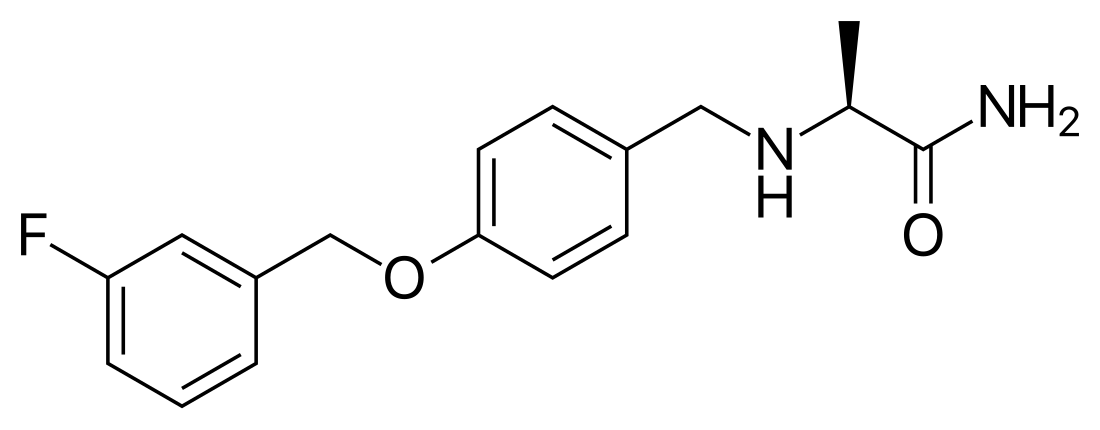
Safinamide, sold under the brand name Xadago, is a medication used as treatment for Parkinson's disease with "off" episodes; it has multiple modes of action, including the inhibition of monoamine oxidase B.[4][5][7]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xadago, Onstryv |
| Other names | EMD-1195686, PNU-15774E; (2S)-2-[[4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl] methylamino]propanamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 95% |
| Protein binding | 88–90% |
| Metabolism | Amidases, glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | 20–30 hrs |
| Excretion | 76% Kidney, 1.5% faeces |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.120.167 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H19FN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 302.349 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
It was approved in the European Union in February 2015,[4] in the United States in March 2017,[5] and in Canada in January 2019.[2]
Medical uses
Safinamide is used to treat idiopathic Parkinson's disease as add-on for people taking a stable dose of levodopa (L-dopa) alone or in combination with other Parkinson drugs, to help with "off" episodes when levodopa stops working.[4][5][7]
Contraindications
Safinamide is contraindicated in people with severe liver impairment, with albinism, retinitis pigmentosa, severe diabetic neuropathy, uveitis and other disorders of the retina. Combination with other monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors and pethidine is also contraindicated.[4]
It is not safe for women to take during pregnancy.[5] It is excreted in breast milk and the effects on infants are unknown.[4]
Adverse effects
Common adverse events in clinical trials (in more than 1% of people) included nausea, dizziness, tiredness, sleeplessness, orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure), and headache. There was no significant difference in the occurrence of these effects between safinamide and placebo.[8][9]
Overdose
Expected overdose effects are hypertension (high blood pressure), orthostatic hypotension, hallucinations, psychomotor agitation, nausea, vomiting, and dyskinesia. In studies, a single person was suspected to have overdosed for a month; symptoms were confusion, drowsiness and mydriasis (dilation of the pupils) and subsided completely after the drug was discontinued. No specific antidote is available.[8]
Interactions
As a MAO inhibitor, safinamide can theoretically cause hypertensive crises, serotonin syndrome and other severe side effects when combined with other MAO inhibitors or with drugs that are known to interact with MAO inhibitors, such as pethidine, dextromethorphan, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin–noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants. An interaction with tyramine, a substance found in various foods, could be expected by the same reasoning but has been excluded in studies.[8]
Another theoretical interaction is with drugs with affinity to the transporter protein ABCG2 (also known as BCRP), such as pitavastatin, pravastatin, ciprofloxacin, methotrexate, and diclofenac; a study with the latter has shown no clinical relevance.[10] A study testing possible interactions with amidase inhibitors is part of the post-authorisation development plan.[1] There are no relevant interactions related to cytochrome P450 (CYP) liver enzymes, although one inactivation pathway of safinamide seems to be mediated by CYP3A4.[8]
Pharmacology
Mechanisms of action
Like the older antiparkinson drugs selegiline and rasagiline, safinamide is a selective monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, reducing degradation of dopamine; in contrast to the other two, its action is reversible. Safinamide also inhibits glutamate release[9][11] and dopamine and serotonin reuptake.[12] It binds to the sigma receptors as well, with IC50 values for binding inhibition of 19 nM for σ1 and 1,590 nM for σ2.[13] Additionally, it blocks sodium and calcium channels,[11][14] the relevance of which for its antiparkinson action is however unknown.[8]
Pharmacokinetics
Safinamide is absorbed quickly and nearly completely from the gut and reaches highest blood plasma concentrations after 1.8 to 2.8 hours. There is no relevant first-pass metabolism; total bioavailability is 95%. The substance is bound to plasma proteins to 88–90%.[8]
The metabolism is not well understood. The principal step is mediated by amidases which have not been identified, and produces safinamide acid (NW-1153). Other relevant metabolites are O-debenzylated safinamide (NW-1199),[10] the N-dealkylated amine which is then oxidized to a carboxylic acid (NW-1689), and the glucuronide of the latter.[8][15] In tests with liver microsomes, dealkylation seemed to be mediated by CYP3A4, but other CYP enzymes appear to be involved as well. Safinamide acid binds to the organic anion transporter 3 (OAT3), but this has probably no clinical relevance. Safinamide itself transiently binds to ABCG2. No other transporter affinities have been found in preliminary studies.[8]
Safinamide is eliminated, mainly (>90%) in form of its metabolites, via the kidney, with an elimination half-life of 20 to 30 hours. Only 1.5% are found in the stool.[8]

History
The compound was originally discovered at Farmitalia-Carlo Erba,[16] which was acquired by Pharmacia in 1993. In 1995, Pharmacia merged with Upjohn. Safinamide was first disclosed in 1998.[17] In the course of a major restructuring in the same year, all rights for safinamide were transferred to the newly formed company Newron Pharmaceuticals, which developed the drug until it was sold to Merck KGaA in 2006.[18]
In 2007, a Phase III clinical trial was started, scheduled to run until 2011.[19] In October 2011 Merck, now Merck-Serono, announced that they would give all rights to develop the compound back to Newron because they wanted to prioritise other projects and had corrected their estimates for safinamide's market potential downwards.[20]
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) refused to file Newron's application in 2014 on formal grounds.[21] Newron re-applied in December 2014.[22] In spring 2015, following a commercial agreement between Newron and the Italian pharmaceutical company Zambon, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved the drug.[23] In the following years, the drug has been launched in several European countries.[24] Safinamide is the first antiparkinson medication to be approved for ten years.[25] Safinamide was approved by US FDA in March 2017 for people with Parkinsons taking levodopa/carbidopa during "off" episodes.[26][27]
Research
Potential additional uses might be restless legs syndrome (RLS) and epilepsy.[28] Safinamide was being tested in Phase II trials in 2008, but no results are available. When used as an adjunct to parkinsonian medication, safinamide was found to be efficacious in reducing pain in PD.[29]
In experiments with rats (but not in those with monkeys), retinopathies have been observed.[1][25]
References
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.