Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Silicon dioxide
Oxide of silicon From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula SiO2, commonly found in nature as quartz.[5][6] In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, opal, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics, and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored.
Silicon dioxide is a common fundamental constituent of glass.
Remove ads
Structure
Summarize
Perspective



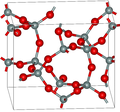
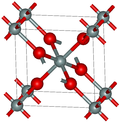
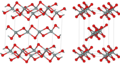
In the majority of silicon dioxides, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atom (see 3-D Unit Cell). Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms.[8][9] In contrast, CO2 is a linear molecule. The starkly different structures of the dioxides of carbon and silicon are a manifestation of the double bond rule.[10]
Based on the crystal structural differences, silicon dioxide can be divided into two categories: crystalline and non-crystalline (amorphous). In crystalline form, this substance can be found naturally occurring as quartz, tridymite (high-temperature form), cristobalite (high-temperature form), stishovite (high-pressure form), and coesite (high-pressure form). On the other hand, amorphous silica can be found in nature as opal and diatomaceous earth. Quartz glass is a form of intermediate state between these structures.[11]
All of these distinct crystalline forms always have the same local structure around Si and O. In α-quartz the Si–O bond length is 161 pm, whereas in α-tridymite it is in the range 154–171 pm. The Si–O–Si angle also varies between a low value of 140° in α-tridymite, up to 180° in β-tridymite. In α-quartz, the Si–O–Si angle is 144°.[12]
Polymorphism
Alpha quartz is the most stable form of solid SiO2 at room temperature. The high-temperature minerals, cristobalite and tridymite, have both lower densities and indices of refraction than quartz. The transformation from α-quartz to beta-quartz takes place abruptly at 573 °C. Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce fracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature limit.[13] The high-pressure minerals, seifertite, stishovite, and coesite, though, have higher densities and indices of refraction than quartz.[14] Stishovite has a rutile-like structure where silicon is 6-coordinate. The density of stishovite is 4.287 g/cm3, which compares to α-quartz, the densest of the low-pressure forms, which has a density of 2.648 g/cm3.[15] The difference in density can be ascribed to the increase in coordination as the six shortest Si–O bond lengths in stishovite (four Si–O bond lengths of 176 pm and two others of 181 pm) are greater than the Si–O bond length (161 pm) in α-quartz.[16] The change in the coordination increases the ionicity of the Si–O bond.[17]
Faujasite silica, another polymorph, is obtained by the dealumination of a low-sodium, ultra-stable Y zeolite with combined acid and thermal treatment. The resulting product contains over 99% silica, and has high crystallinity and specific surface area (over 800 m2/g). Faujasite-silica has very high thermal and acid stability. For example, it maintains a high degree of long-range molecular order or crystallinity even after boiling in concentrated hydrochloric acid.[18]
Molten SiO2
Molten silica exhibits several peculiar physical characteristics that are similar to those observed in liquid water: negative temperature expansion, density maximum at temperatures ~5000 °C, and a heat capacity minimum.[19] Its density decreases from 2.08 g/cm3 at 1950 °C to 2.03 g/cm3 at 2200 °C.[20]
Molecular SiO2
The molecular SiO2 has a linear structure like CO2. It has been produced by combining silicon monoxide (SiO) with oxygen in an argon matrix. The dimeric silicon dioxide, (SiO2)2 has been obtained by reacting O2 with matrix isolated dimeric silicon monoxide, (Si2O2). In dimeric silicon dioxide there are two oxygen atoms bridging between the silicon atoms with an Si–O–Si angle of 94° and bond length of 164.6 pm and the terminal Si–O bond length is 150.2 pm. The Si–O bond length is 148.3 pm, which compares with the length of 161 pm in α-quartz. The bond energy is estimated at 621.7 kJ/mol.[21]
Remove ads
Natural occurrence
Summarize
Perspective
Geology

SiO2 is most commonly encountered in nature as quartz, which comprises more than 10% by mass of the Earth's crust.[22] Quartz is the only polymorph of silica stable at the Earth's surface. Metastable occurrences of the high-pressure forms coesite and stishovite have been found around impact structures and associated with eclogites formed during ultra-high-pressure metamorphism. The high-temperature forms of tridymite and cristobalite are known from silica-rich volcanic rocks. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand.[23]
Biology
Even though it is poorly soluble, silica occurs in many plants such as rice. Plant materials with high silica phytolith content appear to be of importance to grazing animals, from chewing insects to ungulates. Silica accelerates tooth wear, and high levels of silica in plants frequently eaten by insects may have developed as a defense mechanism against predation.[24][25]
Silica is also the primary component of rice husk ash, which is used, for example, in filtration and as supplementary cementitious material (SCM) in cement and concrete manufacturing.[26]
Silicification in and by cells has been common in the biological world and it occurs in bacteria, protists, plants, and animals (invertebrates and vertebrates).[27]
Prominent examples include:
- Tests or frustules (i.e. shells) of diatoms, Radiolaria, and testate amoebae.[6]
- Silica phytoliths in the cells of many plants[28] including Equisetaceae,[29] many grasses, and a wide range of dicotyledons.[30][31]
- The spicules forming the skeleton of many sponges.[32]
Remove ads
Uses
Summarize
Perspective
Structural use
About 95% of the commercial use of silicon dioxide (sand) is in the construction industry, e.g. in the production of concrete (Portland cement concrete).[22]
Certain deposits of silica sand, with desirable particle size and shape and desirable clay and other mineral content, were important for sand casting of metallic products.[33] The high melting point of silica enables it to be used in such applications such as iron casting; modern sand casting sometimes uses other minerals for other reasons.
Crystalline silica is used in hydraulic fracturing of formations which contain tight oil and shale gas.[34]
Precursor to glass and silicon
Silica is the primary ingredient in the production of most glass. As other minerals are melted with silica, the principle of freezing point depression lowers the melting point of the mixture and increases fluidity. The glass transition temperature of pure SiO2 is about 1475 K.[35] When molten silicon dioxide SiO2 is rapidly cooled, it does not crystallize, but solidifies as a glass.[36] Because of this, most ceramic glazes have silica as the main ingredient.[37]
The structural geometry of silicon and oxygen in glass is similar to that in quartz and most other crystalline forms of silicon and oxygen, with silicon surrounded by regular tetrahedra of oxygen centres. The difference between the glass and crystalline forms arises from the connectivity of the tetrahedral units: Although there is no long-range periodicity in the glassy network, ordering remains at length scales well beyond the SiO bond length. One example of this ordering is the preference to form rings of 6-tetrahedra.[38]
The majority of optical fibers for telecommunications are also made from silica. It is a primary raw material for many ceramics such as earthenware, stoneware, and porcelain.
Silicon dioxide is used to produce elemental silicon. The process involves carbothermic reduction in an electric arc furnace:[39]
Fumed silica
Fumed silica, also known as pyrogenic silica, is prepared by burning SiCl4 in an oxygen-rich hydrogen flame to produce a "smoke" of SiO2.[15]
It can also be produced by vaporizing quartz sand in a 3000 °C electric arc. Both processes result in microscopic droplets of amorphous silica fused into branched, chainlike, three-dimensional secondary particles which then agglomerate into tertiary particles, a white powder with extremely low bulk density (0.03-0.15 g/cm3) and thus high surface area.[40] The particles act as a thixotropic thickening agent, or as an anti-caking agent, and can be treated to make them hydrophilic or hydrophobic for either water or organic liquid applications.

Silica fume is an ultrafine powder collected as a by-product of the silicon and ferrosilicon alloy production. It consists of amorphous (non-crystalline) spherical particles with an average particle diameter of 150 nm, without the branching of the pyrogenic product. The main use is as pozzolanic material for high performance concrete. Fumed silica nanoparticles can be successfully used as an anti-aging agent in asphalt binders.[41]
Food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical applications
Silica, either colloidal, precipitated, or pyrogenic fumed, is a common additive in food production. It is used primarily as a flow or anti-caking agent in powdered foods such as spices and non-dairy coffee creamer, or powders to be formed into pharmaceutical tablets.[40] It can adsorb water in hygroscopic applications. Colloidal silica is used as a fining agent for wine, beer, and juice, with the E number reference E551.[22]
In cosmetics, silica is useful for its light-diffusing properties[42] and natural absorbency.[43]
Diatomaceous earth, a mined product, has been used in food and cosmetics for centuries. It consists of the silica shells of microscopic diatoms; in a less processed form it was sold as tooth powder.[44][45] Manufactured or mined hydrated silica is used as the hard abrasive in toothpaste.
Semiconductors
Silicon dioxide is widely used in the semiconductor technology:
- for the primary passivation (directly on the semiconductor surface),
- as an original gate dielectric in MOS technology. Today when scaling (dimension of the gate length of the MOS transistor) has progressed below 10 nm, silicon dioxide has been replaced by other dielectric materials like hafnium oxide or similar with higher dielectric constant compared to silicon dioxide,
- as a dielectric layer between metal (wiring) layers (sometimes up to 8–10) connecting elements and
- as a second passivation layer (for protecting semiconductor elements and the metallization layers) typically today layered with some other dielectrics like silicon nitride.
Because silicon dioxide is a native oxide of silicon it is more widely used compared to other semiconductors like gallium arsenide or indium phosphide.
Silicon dioxide could be grown on a silicon semiconductor surface.[46] Silicon oxide layers could protect silicon surfaces during diffusion processes, and could be used for diffusion masking.[47][48]
Surface passivation is the process by which a semiconductor surface is rendered inert, and does not change semiconductor properties as a result of interaction with air or other materials in contact with the surface or edge of the crystal.[49][50] The formation of a thermally grown silicon dioxide layer greatly reduces the concentration of electronic states at the silicon surface.[50] SiO2 films preserve the electrical characteristics of p–n junctions and prevent these electrical characteristics from deteriorating by the gaseous ambient environment.[48] Silicon oxide layers could be used to electrically stabilize silicon surfaces.[47] The surface passivation process is an important method of semiconductor device fabrication that involves coating a silicon wafer with an insulating layer of silicon oxide so that electricity could reliably penetrate to the conducting silicon below. Growing a layer of silicon dioxide on top of a silicon wafer enables it to overcome the surface states that otherwise prevent electricity from reaching the semiconducting layer.[49][51]
The process of silicon surface passivation by thermal oxidation (silicon dioxide) is critical to the semiconductor industry. It is commonly used to manufacture metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) and silicon integrated circuit chips (with the planar process).[49][51]
Other
Hydrophobic silica is used as a defoamer component.
In its capacity as a refractory, it is useful in fiber form as a high-temperature thermal protection fabric.[52]
Silica is used in the extraction of DNA and RNA due to its ability to bind to the nucleic acids under the presence of chaotropes.[53]
Silica aerogel was used in the Stardust spacecraft to collect extraterrestrial particles.[54]
Pure silica (silicon dioxide), when cooled as fused quartz into a glass with no true melting point, can be used as a glass fibre for fibreglass.
Remove ads
Production
Summarize
Perspective
Silicon dioxide is mostly obtained by mining, including sand mining and purification of quartz. Quartz is suitable for many purposes, while chemical processing is required to make a purer or otherwise more suitable (e.g. more reactive or fine-grained) product.[55][56]
Precipitated silica
Precipitated silica or amorphous silica is produced by the acidification of solutions of sodium silicate. The gelatinous precipitate or silica gel, is first washed and then dehydrated to produce colorless microporous silica.[15] The idealized equation involving a trisilicate and sulfuric acid is:
Approximately one billion kilograms/year (1999) of silica were produced in this manner, mainly for use for polymer composites – tires and shoe soles.[22]
On microchips
Thin films of silica grow spontaneously on silicon wafers via thermal oxidation, producing a very shallow layer of about 1 nm or 10 Å of so-called native oxide.[57] Higher temperatures and alternative environments are used to grow well-controlled layers of silicon dioxide on silicon, for example at temperatures between 600 and 1200 °C, using so-called dry oxidation with O2
or wet oxidation with H2O.[58][59]
The native oxide layer is beneficial in microelectronics, where it acts as electric insulator with high chemical stability. It can protect the silicon, store charge, block current, and even act as a controlled pathway to limit current flow.[60]
Laboratory or special methods
From organosilicon compounds
Many routes to silicon dioxide start with an organosilicon compound, e.g., HMDSO,[61] TEOS. Synthesis of silica is illustrated below using tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS).[62] Simply heating TEOS at 680–730 °C results in the oxide:
Similarly TEOS combusts around 400 °C:
TEOS undergoes hydrolysis via the so-called sol-gel process. The course of the reaction and nature of the product are affected by catalysts, but the idealized equation is:[63]
Other methods
Being highly stable, silicon dioxide arises from many methods. Conceptually simple, but of little practical value, combustion of silane gives silicon dioxide. This reaction is analogous to the combustion of methane:
However the chemical vapor deposition of silicon dioxide onto crystal surface from silane had been used using nitrogen as a carrier gas at 200–500 °C.[64]
Remove ads
Chemical reactions
Summarize
Perspective
Silicon dioxide is a relatively inert material (hence its widespread occurrence as a mineral). Silica is often used as inert containers for chemical reactions. At high temperatures, it is converted to silicon by reduction with carbon.
Fluorine reacts with silicon dioxide to form SiF4 and O2 whereas the other halogen gases (Cl2, Br2, I2) are unreactive.[15]
Most forms of silicon dioxide are attacked ("etched") by hydrofluoric acid (HF) to produce hexafluorosilicic acid:[12]
- SiO2 + 6 HF → H2SiF6 + 2 H2O
Stishovite does not react to HF to any significant degree.[65] HF is used to remove or pattern silicon dioxide in the semiconductor industry.
Silicon dioxide acts as a Lux–Flood acid, being able to react with bases under certain conditions. As it does not contain any hydrogen, non-hydrated silica cannot directly act as a Brønsted–Lowry acid. While silicon dioxide is only poorly soluble in water at low or neutral pH (typically, 2 × 10−4 M for quartz up to 10−3 M for cryptocrystalline chalcedony), strong bases react with glass and easily dissolve it. Therefore, strong bases have to be stored in plastic bottles to avoid jamming the bottle cap, to preserve the integrity of the recipient, and to avoid undesirable contamination by silicate anions.[66]
Silicon dioxide dissolves in hot concentrated alkali or fused hydroxide, as described in this idealized equation:[15]
Silicon dioxide will neutralise basic metal oxides (e.g. sodium oxide, potassium oxide, lead(II) oxide, zinc oxide, or mixtures of oxides, forming silicates and glasses as the Si-O-Si bonds in silica are broken successively).[12] As an example the reaction of sodium oxide and SiO2 can produce sodium orthosilicate, sodium silicate, and glasses, dependent on the proportions of reactants:[15]
- .
Examples of such glasses have commercial significance, e.g. soda–lime glass, borosilicate glass, lead glass. In these glasses, silica is termed the network former or lattice former.[12] The reaction is also used in blast furnaces to remove sand impurities in the ore by neutralisation with calcium oxide, forming calcium silicate slag.

Silicon dioxide reacts in heated reflux under dinitrogen with ethylene glycol and an alkali metal base to produce highly reactive, pentacoordinate silicates which provide access to a wide variety of new silicon compounds.[67] The silicates are essentially insoluble in all polar solvent except methanol.
Silicon dioxide reacts with elemental silicon at high temperatures to produce SiO:[12]
Water solubility
The solubility of silicon dioxide in water strongly depends on its crystalline form and is three to four times higher for amorphous silica than quartz; as a function of temperature, it peaks around 340 °C (644 °F).[68] This property is used to grow single crystals of quartz in a hydrothermal process where natural quartz is dissolved in superheated water in a pressure vessel that is cooler at the top. Crystals of 0.5–1 kg can be grown for 1–2 months.[12] These crystals are a source of very pure quartz for use in electronic applications.[15] Above the critical temperature of water 647.096 K (373.946 °C; 705.103 °F) and a pressure of 22.064 megapascals (3,200.1 psi) or higher, water is a supercritical fluid and solubility is once again higher than at lower temperatures.[69]
Remove ads
Health effects
Summarize
Perspective

Silica ingested orally is essentially nontoxic, with an LD50 of 5000 mg/kg (5 g/kg).[22] A 2008 study following subjects for 15 years found that higher levels of silica in water appeared to decrease the risk of dementia. An increase of 10 mg/day of silica in drinking water was associated with a reduced risk of dementia of 11%.[70]
Inhaling finely divided crystalline silica dust can lead to silicosis, bronchitis, or lung cancer, as the dust becomes lodged in the lungs and continuously irritates the tissue, reducing lung capacities.[71] When fine silica particles are inhaled in large enough quantities (such as through occupational exposure), it increases the risk of systemic autoimmune diseases such as lupus[72] and rheumatoid arthritis compared to expected rates in the general population.[73]
Occupational hazard
Silica is an occupational hazard for people who do sandblasting or work with powdered crystalline silica products. Amorphous silica, such as fumed silica, may cause irreversible lung damage in some cases but is not associated with the development of silicosis. Children, asthmatics of any age, those with allergies, and the elderly (all of whom have reduced lung capacity) can be affected in less time.[74]
Crystalline silica is an occupational hazard for those working with stone countertops because the process of cutting and installing the countertops creates large amounts of airborne silica.[75] Crystalline silica used in hydraulic fracturing presents a health hazard to workers.[34]
Pathophysiology
In the body, crystalline silica particles do not dissolve over clinically relevant periods. Silica crystals inside the lungs can activate the NLRP3 inflammasome inside macrophages and dendritic cells and thereby result in production of interleukin, a highly pro-inflammatory cytokine in the immune system.[76][77][78]
Regulation
Regulations restricting silica exposure 'with respect to the silicosis hazard' specify that they are concerned only with silica, which is both crystalline and dust-forming.[79][80][81][82][83][84]
In 2013, the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration reduced the exposure limit to 50 μg/m3 of air. Prior to 2013, it had allowed 100 μg/m3 and in construction workers even 250 μg/m3.[34] In 2013, OSHA also required the "green completion" of fracked wells to reduce exposure to crystalline silica and restrict the exposure limit.[34]
Remove ads
Crystalline forms
Summarize
Perspective
SiO2, more so than almost any material, exists in many crystalline forms. These forms are called polymorphs.
Remove ads
Safety
Inhaling finely divided crystalline silica can lead to severe inflammation of the lung tissue, silicosis, bronchitis, lung cancer, and systemic autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Inhalation of amorphous silicon dioxide, in high doses, leads to non-permanent short-term inflammation, where all effects heal.[100]
Other names
This extended list enumerates synonyms for silicon dioxide; all of these values are from a single source; values in the source were presented capitalized.[101]
- CAS 112945-52-5
- Acitcel
- Aerosil
- Amorphous silica dust
- Aquafil
- CAB-O-GRIP II
- CAB-O-SIL
- CAB-O-SPERSE
- Catalogue
- Colloidal silica[102]
- Colloidal silicon dioxide
- Dicalite
- DRI-DIE Insecticide 67
- FLO-GARD
- Fossil flour
- Fumed silica
- Fumed silicon dioxide
- HI-SEL
- LO-VEL
- Ludox
- Nalcoag
- Nyacol
- Santocel
- Silica
- Silica aerogel
- Silica, amorphous
- Silicic anhydride
- Silikill
- Synthetic amorphous silica
- Vulkasil
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads



![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {C} {}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {Si} {}+{}2\,\mathrm {CO} }}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1eb9e849d727fcb019f0416dac5f4f967695cdfa)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {SiCl} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}\mathrm {O} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}4\,\mathrm {HCl} }}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9cdc77ca718b1aa2fbff897b06de1b7c65933dfd)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {Na} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {Si} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{3}}\mathrm {O} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{7}}{}+{}\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {SO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}3\,\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}\mathrm {Na} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {SO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}+{}\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} }}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9876f7b261a2fa2527cd3614cc6e1def21392eba)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {Si} {}+{}\mathrm {O} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ac34960afdbf2b558f5883aed59bcbb109554f8f)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {Si} {}+{}2\,\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} {}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/08560ed781dc5d9a051d7f7cbc6d9f1d8247e424)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {Si} (\mathrm {OC} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{5}}){\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {O} (\mathrm {C} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{5}}){\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/61ac3ada0cf5464bd1fedd991049203bff127b6d)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {Si} (\mathrm {OC} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{5}}){\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}+{}12\,\mathrm {O} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}10\,\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} {}+{}8\,\mathrm {CO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ba7c3aa1a03f27f9c0ab03ba6ef0634e65a53183)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {Si} (\mathrm {OC} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{5}}){\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} {}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}4\,\mathrm {HOCH} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {CH} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{3}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/689234f18e8efa7949bbf19c6c6ee3606c021d56)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {SiH} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {O} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} }}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/03511df937a8f3cb258146f5786fb5fc970cf591)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {NaOH} {}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {Na} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{3}}{}+{}\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} }}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/13151bda2abffbafaed6f97777a6e3386792a73b)
![{\displaystyle {2\,\mathrm {Na} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} {}+{}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {Na} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{;}{\mkern {3mu}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e600c070844b56007a9d7b66d1673a4b04ec0f6f)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {Na} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} {}+{}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {Na} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{3}}{;}{\mkern {3mu}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c8b8d671c3d195db06e084ad8d1be41d2aaf9e21)

![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {Na} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} {}+{}\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {glass} }}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8c1456b3017f2ad302347f7bbb8f38d8d71c43bb)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {SiO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}\mathrm {Si} {}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}2\,\mathrm {SiO} }}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3861d55180f8b84194f3494ea23652c10a0206ae)