Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Superior parietal lobule
Part of the brain From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The superior parietal lobule is bounded in front by the upper part of the postcentral sulcus, but is usually connected with the postcentral gyrus above the end of the sulcus. The superior parietal lobule contains Brodmann's areas 5 and 7.
Behind it is the lateral part of the parieto-occipital sulcus, around the end of which it is joined to the occipital lobe by a curved gyrus, the arcus parietooccipitalis. Below, it is separated from the inferior parietal lobule by the horizontal portion of the intraparietal sulcus.
The superior parietal lobule is involved with spatial orientation,[1] and receives a great deal of visual input as well as sensory input from one's hand.[2] In addition to spatial cognition and visual perception, it has also been associated with reasoning, working memory, and attention.[3]
It is also involved with other functions[vague] of the parietal lobe in general.
There are major white matter pathway connections with the superior parietal lobule such as the Cingulum, SLF I, superior parietal lobule connections of the Medial longitudinal fasciculus and other newly described superior parietal white matter connections.[4][5]
Damage to the superior parietal lobule can cause contralateral astereognosis and hemispatial neglect. It is also associated with deficits on tests involving the manipulation and rearrangement of information in working memory, but not on working memory tests requiring only rehearsal and retrieval processes.[6]
Remove ads
Additional images
- Position of superior parietal lobule (shown in red).
- Superior parietal lobule (shown in red).
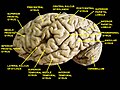
- Superior parietal lobule is labeled at upper left.
- Drawing to illustrate the relations of the brain to the skull.
- Lateral view of a human brain, main gyri labeled.
- Cerebrum. Lateral view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum. Lateral view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum. Lateral view. Deep dissection.
- Superior parietal lobule highlighted in green on coronal T1 MRI images
- Superior parietal lobule highlighted in green on sagittal T1 MRI images
- Superior parietal lobule highlighted in green on transversal T1 MRI images
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads