Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Symmetric-key algorithm
Algorithm From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
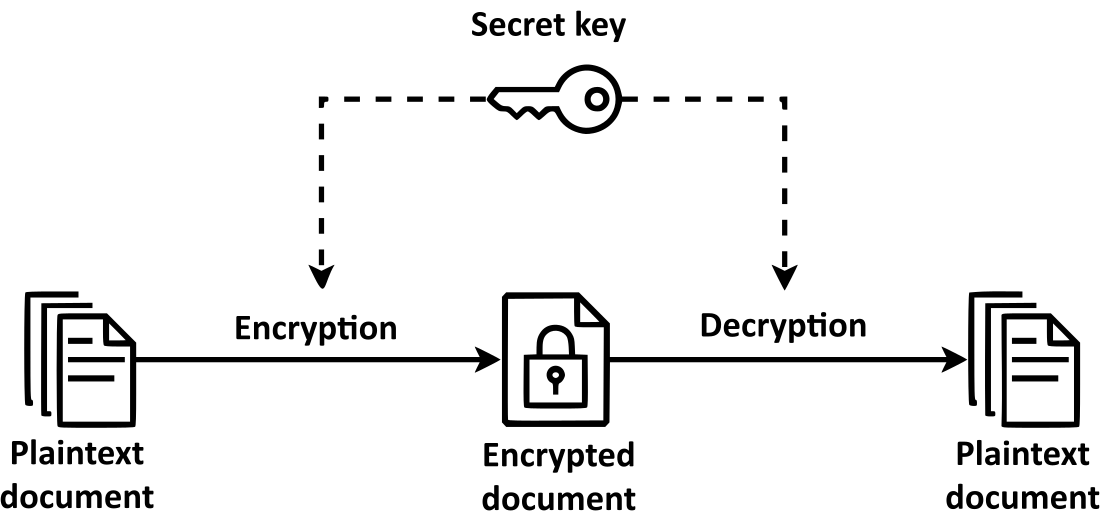
Symmetric-key algorithms[a] are algorithms for cryptography that use the same cryptographic keys for both the encryption of plaintext and the decryption of ciphertext. The keys may be identical, or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys.[1] The keys, in practice, represent a shared secret between two or more parties that can be used to maintain a private information link.[2] The requirement that both parties have access to the secret key is one of the main drawbacks of symmetric-key encryption, in comparison to asymmetric-key encryption (also known as public-key encryption).[3][4] However, symmetric-key encryption algorithms are usually better for bulk encryption. With exception of the one-time pad they have a smaller key size, which means less storage space and faster transmission. Due to this, asymmetric-key encryption is often used to exchange the secret key for symmetric-key encryption.[5][6][7]

Remove ads
Types
Symmetric-key encryption can use either stream ciphers or block ciphers.[8]
Stream ciphers encrypt the digits (typically bytes), or letters (in substitution ciphers) of a message one at a time. An example is ChaCha20. Substitution ciphers are well-known ciphers, but can be easily decrypted using a frequency table.[9]
Block ciphers take a number of bits and encrypt them in a single unit, padding the plaintext to achieve a multiple of the block size. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm, approved by NIST in December 2001, uses 128-bit blocks.
Remove ads
Implementations
Examples of popular symmetric-key algorithms include Twofish, Serpent, AES (Rijndael), Camellia, Salsa20, ChaCha20, Blowfish, CAST5, Kuznyechik, RC4, DES, 3DES, Skipjack, Safer, and IDEA.[10]
Use as a cryptographic primitive
Symmetric ciphers are commonly used to achieve other cryptographic primitives than just encryption.[citation needed]
Encrypting a message does not guarantee that it will remain unchanged while encrypted. Hence, often a message authentication code is added to a ciphertext to ensure that changes to the ciphertext will be noted by the receiver. Message authentication codes can be constructed from an AEAD cipher (e.g. AES-GCM).
However, symmetric ciphers cannot be used for non-repudiation purposes except by involving additional parties.[11] See the ISO/IEC 13888-2 standard.
Another application is to build hash functions from block ciphers. See one-way compression function for descriptions of several such methods.
Construction of symmetric ciphers
Many modern block ciphers are based on a construction proposed by Horst Feistel. Feistel's construction makes it possible to build invertible functions from other functions that are themselves not invertible.[citation needed]
Security of symmetric ciphers
Summarize
Perspective
Symmetric ciphers have historically been susceptible to known-plaintext attacks, chosen-plaintext attacks, differential cryptanalysis and linear cryptanalysis. Careful construction of the functions for each round can greatly reduce the chances of a successful attack.[citation needed] It is also possible to increase the key length or the rounds in the encryption process to better protect against attack. This, however, tends to increase the processing power and decrease the speed at which the process runs due to the amount of operations the system needs to do.[12]
Most modern symmetric-key algorithms appear to be resistant to the threat of post-quantum cryptography.[13] Quantum computers would exponentially increase the speed at which these ciphers can be decoded; notably, Grover's algorithm would take the square-root of the time traditionally required for a brute-force attack, although these vulnerabilities can be compensated for by doubling key length.[14] For example, a 128 bit AES cipher would not be secure against such an attack as it would reduce the time required to test all possible iterations from over 10 quintillion years to about six months. By contrast, it would still take a quantum computer the same amount of time to decode a 256 bit AES cipher as it would a conventional computer to decode a 128 bit AES cipher.[15] For this reason, AES-256 is believed to be "quantum resistant".[16][17]
Remove ads
Key management
Key establishment
Symmetric-key algorithms require both the sender and the recipient of a message to have the same secret key. All early cryptographic systems required either the sender or the recipient to somehow receive a copy of that secret key over a physically secure channel.
Nearly all modern cryptographic systems still use symmetric-key algorithms internally to encrypt the bulk of the messages, but they eliminate the need for a physically secure channel by using Diffie–Hellman key exchange or some other public-key protocol to securely come to agreement on a fresh new secret key for each session/conversation (forward secrecy).
Remove ads
Key generation
When used with asymmetric ciphers for key transfer, pseudorandom key generators are nearly always used to generate the symmetric cipher session keys. However, lack of randomness in those generators or in their initialization vectors is disastrous and has led to cryptanalytic breaks in the past. Therefore, it is essential that an implementation use a source of high entropy for its initialization.[18][19][20]
Remove ads
Reciprocal cipher
Summarize
Perspective
This section needs additional citations for verification. (December 2015) |
A reciprocal cipher is a cipher where, just as one enters the plaintext into the cryptography system to get the ciphertext, one could enter the ciphertext into the same place in the system to get the plaintext. A reciprocal cipher is also sometimes referred as self-reciprocal cipher.[21][22]
Practically all mechanical cipher machines implement a reciprocal cipher, a mathematical involution on each typed-in letter. Instead of designing two kinds of machines, one for encrypting and one for decrypting, all the machines can be identical and can be set up (keyed) the same way.[23]
Examples of reciprocal ciphers include:
- Atbash
- Beaufort cipher[24]
- Enigma machine[25]
- the self-reciprocal cipher which Marie Antoinette and Axel von Fersen communicated with.[26]
- the Porta polyalphabetic cipher which is self-reciprocal.[27]
- Purple cipher[28]
- RC4
- ROT13
- XOR cipher
- Vatsyayana cipher
The majority of all modern ciphers can be classified as either a stream cipher, most of which use a reciprocal XOR cipher combiner, or a block cipher, most of which use a Feistel cipher or Lai–Massey scheme with a reciprocal transformation in each round.[citation needed]
Notes
- Other terms for symmetric-key encryption are secret-key, single-key, shared-key, one-key, and private-key encryption. Use of the last and first terms can create ambiguity with similar terminology used in public-key cryptography. Symmetric-key cryptography is to be contrasted with asymmetric-key cryptography.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads