Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase
Mammalian protein found in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase (VD 1A hydroxylase) also known as calcidiol 1-monooxygenase[citation needed] or cytochrome p450 27B1 (CYP27B1) or simply 1-alpha-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP27B1 gene.[5][6][7]
VD 1A hydroxylase is located in the proximal tubule of the kidney and a variety of other tissues, including skin (keratinocytes), immune cells,[8] and bone (osteoblasts).[9]
Remove ads
Reactions
The enzyme catalyzes the hydroxylation of calcifediol to calcitriol (the bioactive form of Vitamin D):[10]
- calcidiol + 2 reduced adrenodoxin + 2 H+ + O2 ⇌ calcitriol + 2 oxidized adrenodoxin + H2O
The enzyme is also able to oxidize ercalcidiol (25-OH D2) to ercalcitriol, secalciferol to calcitetrol, and 25-hydroxy-24-oxocalciol to (1S)-1,25-dihydroxy-24-oxocalciol.[11]
Remove ads
Clinical significance
Loss-of-function mutations in CYP27B1 cause Vitamin D-dependent rickets, type IA.[12]
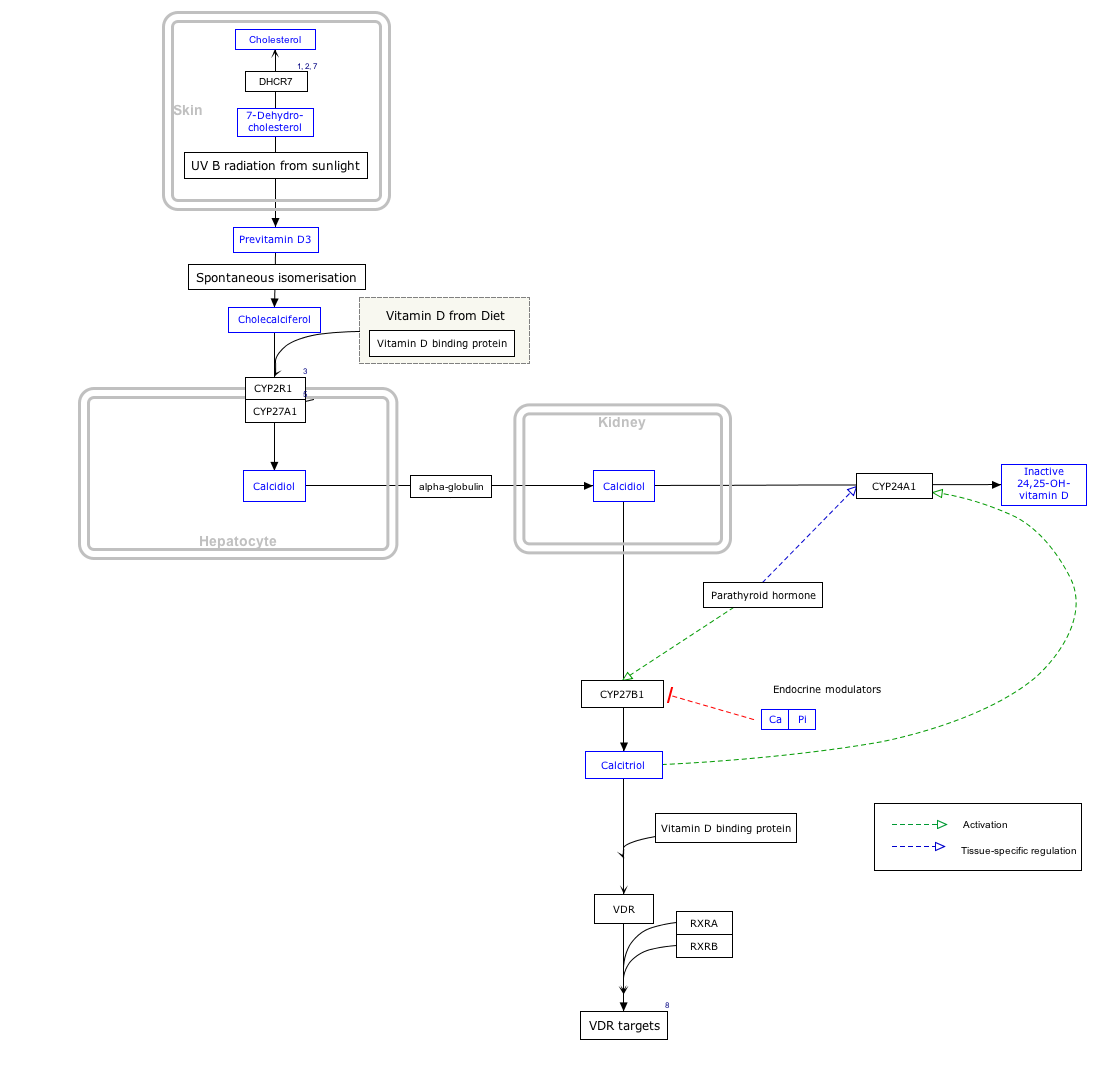
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads