Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Chromosome
DNA molecule containing genetic material of a cell From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity.[1][2] These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation.[3]




- Chromatid
- Centromere
- Short arm
- Long arm
Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form.[4] Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated (S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the joined copies are called 'sister chromatids'. During metaphase, the duplicated structure (called a 'metaphase chromosome') is highly condensed and thus easiest to distinguish and study.[5] In animal cells, chromosomes reach their highest compaction level in anaphase during chromosome segregation.[6]
Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a crucial role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe. This will usually cause the cell to initiate apoptosis, leading to its own death, but the process is occasionally hampered by cell mutations that result in the progression of cancer.
The term 'chromosome' is sometimes used in a wider sense to refer to the individualized portions of chromatin in cells, which may or may not be visible under light microscopy. In a narrower sense, 'chromosome' can be used to refer to the individualized portions of chromatin during cell division, which are visible under light microscopy due to high condensation.
Remove ads
Etymology
The word chromosome (/ˈkroʊməˌsoʊm, -ˌzoʊm/)[7][8] comes from the Ancient Greek words χρῶμα (khrôma, "colour") and σῶμα (sôma, "body"), describing the strong staining produced by particular dyes.[9] The term was coined by the German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer,[10] referring to the term 'chromatin', which was introduced by Walther Flemming.
Some of the early karyological terms have become outdated.[11][12] For example, 'chromatin' (Flemming 1880) and 'chromosom' (Waldeyer 1888) both ascribe color to a non-colored state.[13]
Remove ads
History of discovery
Summarize
Perspective
Walter Sutton (left) and Theodor Boveri (right) independently developed the chromosome theory of inheritance in 1902.
Otto Bütschli was the first scientist to recognize the structures now known as chromosomes.[14]
In a series of experiments beginning in the mid-1880s, Theodor Boveri gave definitive contributions to elucidating that chromosomes are the vectors of heredity, with two notions that became known as 'chromosome continuity' and 'chromosome individuality'.[15]
Wilhelm Roux suggested that every chromosome carries a different genetic configuration, and Boveri was able to test and confirm this hypothesis. Aided by the rediscovery at the start of the 1900s of Gregor Mendel's earlier experimental work, Boveri identified the connection between the rules of inheritance and the behaviour of the chromosomes. Two generations of American cytologists were influenced by Boveri: Edmund Beecher Wilson, Nettie Stevens, Walter Sutton and Theophilus Painter (Wilson, Stevens, and Painter actually worked with him).[16]
In his famous textbook, The Cell in Development and Heredity, Wilson linked together the independent work of Boveri and Sutton (both around 1902) by naming the chromosome theory of inheritance the 'Boveri–Sutton chromosome theory' (sometimes known as the 'Sutton–Boveri chromosome theory').[17] Ernst Mayr remarks that the theory was hotly contested by some famous geneticists, including William Bateson, Wilhelm Johannsen, Richard Goldschmidt and T.H. Morgan, all of a rather dogmatic mindset. Eventually, absolute proof came from chromosome maps in Morgan's own laboratory.[18]
The number of human chromosomes was published by Painter in 1923. By inspection through a microscope, he counted 24 pairs of chromosomes, giving 48 in total. His error was copied by others, and it was not until 1956 that the true number (46) was determined by Indonesian-born cytogeneticist Joe Hin Tjio.[19]
Remove ads
Prokaryotes
Summarize
Perspective
The prokaryotes – bacteria and archaea – typically have a single circular chromosome.[20] The chromosomes of most bacteria (also called genophores), can range in size from only 130,000 base pairs in the endosymbiotic bacteria Candidatus Hodgkinia cicadicola[21] and Candidatus Tremblaya princeps,[22] to more than 14,000,000 base pairs in the soil-dwelling bacterium Sorangium cellulosum.[23]
Some bacteria have more than one chromosome. For instance, Spirochaetes such as Borrelia burgdorferi (causing Lyme disease), contain a single linear chromosome.[24] Vibrios typically carry two chromosomes of very different size. Genomes of the genus Burkholderia carry one, two, or three chromosomes.[25]
Structure in sequences
Prokaryotic chromosomes have less sequence-based structure than eukaryotes. Bacteria typically have a one-point (the origin of replication) from which replication starts, whereas some archaea contain multiple replication origins.[26] The genes in prokaryotes are often organized in operons and do not usually contain introns, unlike eukaryotes.
DNA packaging
Prokaryotes do not possess nuclei. Instead, their DNA is organized into a structure called the nucleoid.[27][28] The nucleoid is a distinct structure and occupies a defined region of the bacterial cell. This structure is, however, dynamic and is maintained and remodeled by the actions of a range of histone-like proteins, which associate with the bacterial chromosome.[29] In archaea, the DNA in chromosomes is even more organized, with the DNA packaged within structures similar to eukaryotic nucleosomes.[30][31]
Certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm that contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.[5] In prokaryotes and viruses,[32] the DNA is often densely packed and organized; in the case of archaea, by homology to eukaryotic histones, and in the case of bacteria, by histone-like proteins.
Bacterial chromosomes tend to be tethered to the plasma membrane of the bacteria. In molecular biology application, this allows for its isolation from plasmid DNA by centrifugation of lysed bacteria and pelleting of the membranes (and the attached DNA).
Prokaryotic chromosomes and plasmids are, like eukaryotic DNA, generally supercoiled. The DNA must first be released into its relaxed state for access for transcription, regulation, and replication.
Remove ads
Eukaryotes
Summarize
Perspective

Each eukaryotic chromosome consists of a long linear DNA molecule associated with proteins, forming a compact complex of proteins and DNA called chromatin. Chromatin contains the vast majority of the DNA in an organism, but a small amount inherited maternally can be found in the mitochondria. It is present in most cells, with a few exceptions, for example, red blood cells.
Histones are responsible for the first and most basic unit of chromosome organization, the nucleosome.
Eukaryotes (cells with nuclei such as those found in plants, fungi, and animals) possess multiple large linear chromosomes contained in the cell's nucleus. Each chromosome has one centromere, with one or two arms projecting from the centromere, although, under most circumstances, these arms are not visible as such. In addition, most eukaryotes have a small circular mitochondrial genome, and some eukaryotes may have additional small circular or linear cytoplasmic chromosomes.

In the nuclear chromosomes of eukaryotes, the uncondensed DNA exists in a semi-ordered structure, where it is wrapped around histones (structural proteins), forming a composite material called chromatin.
Interphase chromatin
The packaging of DNA into nucleosomes causes a 10 nanometer fibre which may further condense up to 30 nm fibres.[33] Most of the euchromatin in interphase nuclei appears to be in the form of 30-nm fibers.[33] Chromatin structure is the more decondensed state, i.e. the 10-nm conformation allows transcription.[33]

During interphase (the period of the cell cycle where the cell is not dividing), two types of chromatin can be distinguished:
- Euchromatin, which consists of DNA that is active, e.g., being expressed as protein.
- Heterochromatin, which consists of mostly inactive DNA. It seems to serve structural purposes during the chromosomal stages. Heterochromatin can be further distinguished into two types:
- Constitutive heterochromatin, which is never expressed. It is located around the centromere and usually contains repetitive sequences.
- Facultative heterochromatin, which is sometimes expressed.
Metaphase chromatin and division


In the early stages of mitosis or meiosis (cell division), the chromatin double helix becomes more and more condensed. They cease to function as accessible genetic material (transcription stops) and become a compact transportable form. The loops of thirty-nanometer chromatin fibers are thought to fold upon themselves further to form the compact metaphase chromosomes of mitotic cells. The DNA is thus condensed about ten-thousand-fold.[33]
The chromosome scaffold, which is made of proteins such as condensin, TOP2A and KIF4,[34] plays an important role in holding the chromatin into compact chromosomes. Loops of thirty-nanometer structure further condense with scaffold into higher order structures.[35]
This highly compact form makes the individual chromosomes visible, and they form the classic four-arm structure, a pair of sister chromatids attached to each other at the centromere. The shorter arms are called p arms (from the French petit, small) and the longer arms are called q arms (q follows p in the Latin alphabet; q-g "grande"; alternatively it is sometimes said q is short for queue meaning tail in French[36]). This is the only natural context in which individual chromosomes are visible with an optical microscope.
Mitotic metaphase chromosomes are best described by a linearly organized longitudinally compressed array of consecutive chromatin loops.[37]
During mitosis, microtubules grow from centrosomes located at opposite ends of the cell and also attach to the centromere at specialized structures called kinetochores, one of which is present on each sister chromatid. A special DNA base sequence in the region of the kinetochores provides, along with special proteins, longer-lasting attachment in this region. The microtubules then pull the chromatids apart toward the centrosomes, so that each daughter cell inherits one set of chromatids. Once the cells have divided, the chromatids are uncoiled and DNA can again be transcribed. In spite of their appearance, chromosomes are structurally highly condensed, which enables these giant DNA structures to be contained within a cell nucleus.
Human chromosomes
Chromosomes in humans can be divided into two types: autosomes (body chromosome(s)) and allosome (sex chromosome(s)). Certain genetic traits are linked to a person's sex and are passed on through the sex chromosomes. The autosomes contain the rest of the genetic hereditary information. All act in the same way during cell division. Human cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes (22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes), giving a total of 46 per cell. In addition to these, human cells have many hundreds of copies of the mitochondrial genome. Sequencing of the human genome has provided a great deal of information about each of the chromosomes. Below is a table compiling statistics for the chromosomes, based on the Sanger Institute's human genome information in the Vertebrate Genome Annotation (VEGA) database.[38] Number of genes is an estimate, as it is in part based on gene predictions. Total chromosome length is an estimate as well, based on the estimated size of unsequenced heterochromatin regions.
Based on the micrographic characteristics of size, position of the centromere and sometimes the presence of a chromosomal satellite, the human chromosomes are classified into the following groups:[41][42]
Remove ads
Karyotype
Summarize
Perspective


In general, the karyotype is the characteristic chromosome complement of a eukaryote species.[43] The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics.
Although the replication and transcription of DNA is highly standardized in eukaryotes, the same cannot be said for their karyotypes, which are often highly variable. There may be variation between species in chromosome number and in detailed organization. In some cases, there is significant variation within species. Often there is:
- 1. variation between the two sexes
- 2. variation between the germline and soma (between gametes and the rest of the body)
- 3. variation between members of a population, due to balanced genetic polymorphism
- 4. geographical variation between races
- 5. mosaics or otherwise abnormal individuals.
Also, variation in karyotype may occur during development from the fertilized egg.
The technique of determining the karyotype is usually called karyotyping. Cells can be locked part-way through division (in metaphase) in vitro (in a reaction vial) with colchicine. These cells are then stained, photographed, and arranged into a karyogram, with the set of chromosomes arranged, autosomes in order of length, and sex chromosomes (here X/Y) at the end.
Like many sexually reproducing species, humans have special gonosomes (sex chromosomes, in contrast to autosomes). These are XX in females and XY in males.
History and analysis techniques
Investigation into the human karyotype took many years to settle the most basic question: How many chromosomes does a normal diploid human cell contain? In 1912, Hans von Winiwarter reported 47 chromosomes in spermatogonia and 48 in oogonia, concluding an XX/XO sex determination mechanism.[44] In 1922, Painter was not certain whether the diploid number of man is 46 or 48, at first favouring 46.[45] He revised his opinion later from 46 to 48, and he correctly insisted on humans having an XX/XY system.[46]
New techniques were needed to definitively solve the problem:
- Using cells in culture
- Arresting mitosis in metaphase by a solution of colchicine
- Pretreating cells in a hypotonic solution 0.075 M KCl, which swells them and spreads the chromosomes
- Squashing the preparation on the slide forcing the chromosomes into a single plane
- Cutting up a photomicrograph and arranging the result into an indisputable karyogram.
It took until 1954 before the human diploid number was confirmed as 46.[47][48] Considering the techniques of Winiwarter and Painter, their results were quite remarkable.[49] Chimpanzees, the closest living relatives to modern humans, have 48 chromosomes as do the other great apes: in humans two chromosomes fused to form chromosome 2.
Remove ads
Aberrations
Summarize
Perspective
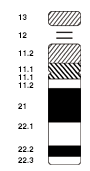
Chromosomal aberrations are disruptions in the normal chromosomal content of a cell. They can cause genetic conditions in humans, such as Down syndrome,[50] although most aberrations have little to no effect. Some chromosome abnormalities do not cause disease in carriers, such as translocations, or chromosomal inversions, although they may lead to a higher chance of bearing a child with a chromosome disorder.[citation needed] Abnormal numbers of chromosomes or chromosome sets, called aneuploidy, may be lethal or may give rise to genetic disorders.[51] Genetic counseling is offered for families that may carry a chromosome rearrangement.
The gain or loss of DNA from chromosomes can lead to a variety of genetic disorders.[52] Human examples include:
- Cri du chat, caused by the deletion of part of the short arm of chromosome 5. "Cri du chat" means "cry of the cat" in French; the condition was so-named because affected babies make high-pitched cries that sound like those of a cat. Affected individuals have wide-set eyes, a small head and jaw, moderate to severe mental health problems, and are very short.
- DiGeorge syndrome, also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Symptoms are mild learning disabilities in children, with adults having an increased risk of schizophrenia. Infections are also common in children because of problems with the immune system's T cell-mediated response due to an absence of hypoplastic thymus.[53]
- Down syndrome, the most common trisomy, usually caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21). Characteristics include decreased muscle tone, stockier build, asymmetrical skull, slanting eyes, and mild to moderate developmental disability.[54]
- Edwards syndrome, or trisomy-18, the second most common trisomy.[55] Symptoms include motor retardation, developmental disability, and numerous congenital anomalies causing serious health problems. Ninety percent of those affected die in infancy. They have characteristic clenched hands and overlapping fingers.
- Isodicentric 15, also called idic(15), partial tetrasomy 15q, or inverted duplication 15 (inv dup 15).
- Jacobsen syndrome, which is very rare. It is also called the 11q terminal deletion disorder.[56] Those affected have normal intelligence or mild developmental disability, with poor expressive language skills. Most have a bleeding disorder called Paris-Trousseau syndrome.
- Klinefelter syndrome (XXY). Men with Klinefelter syndrome are usually sterile, and tend to be taller than their peers, with longer arms and legs. Boys with the syndrome are often shy and quiet, and have a higher incidence of speech delay and dyslexia. Without testosterone treatment, some may develop gynecomastia during puberty.
- Patau Syndrome, also called D-Syndrome or trisomy-13. Symptoms are somewhat similar to those of trisomy-18, without the characteristic folded hand.
- Small supernumerary marker chromosome. This means there is an extra, abnormal chromosome. Features depend on the origin of the extra genetic material. Cat-eye syndrome and isodicentric chromosome 15 syndrome (or Idic15) are both caused by a supernumerary marker chromosome, as is Pallister–Killian syndrome.
- Triple-X syndrome (XXX). XXX girls tend to be tall and thin, and have a higher incidence of dyslexia.
- Turner syndrome (X instead of XX or XY). In Turner syndrome, female sexual characteristics are present but underdeveloped. Females with Turner syndrome often have a short stature, low hairline, abnormal eye features and bone development, and a "caved-in" appearance to the chest.
- Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, caused by partial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 4. It is characterized by growth retardation, delayed motor skills development, "Greek Helmet" facial features, and mild to profound mental health problems.
- XYY syndrome. XYY boys are usually taller than their siblings. Like XXY boys and XXX girls, they are more likely to have learning difficulties.
Sperm aneuploidy
Exposure of males to certain lifestyle, environmental and/or occupational hazards may increase the risk of aneuploid spermatozoa.[57] In particular, risk of aneuploidy is increased by tobacco smoking,[58][59] and occupational exposure to benzene,[60] insecticides,[61][62] and perfluorinated compounds.[63] Increased aneuploidy is often associated with increased DNA damage in spermatozoa.
Remove ads
Number in various organisms
Summarize
Perspective
In eukaryotes
The number of chromosomes in eukaryotes is highly variable. It is possible for chromosomes to fuse or break and thus evolve into novel karyotypes. Chromosomes can also be fused artificially. For example, when the 16 chromosomes of yeast were fused into one giant chromosome, it was found that the cells were still viable with only somewhat reduced growth rates.[64]
The tables below give the total number of chromosomes (including sex chromosomes) in a cell nucleus for various eukaryotes. Most are diploid, such as humans who have 22 different types of autosomes—each present as two homologous pairs—and two sex chromosomes, giving 46 chromosomes in total. Some other organisms have more than two copies of their chromosome types, for example bread wheat which is hexaploid, having six copies of seven different chromosome types for a total of 42 chromosomes.
Normal members of a particular eukaryotic species all have the same number of nuclear chromosomes. Other eukaryotic chromosomes, i.e., mitochondrial and plasmid-like small chromosomes, are much more variable in number, and there may be thousands of copies per cell.

Asexually reproducing species have one set of chromosomes that are the same in all body cells. However, asexual species can be either haploid or diploid.
Sexually reproducing species have somatic cells (body cells) that are diploid [2n], having two sets of chromosomes (23 pairs in humans), one set from the mother and one from the father. Gametes (reproductive cells) are haploid [n], having one set of chromosomes. Gametes are produced by meiosis of a diploid germline cell, during which the matching chromosomes of father and mother can exchange small parts of themselves (crossover) and thus create new chromosomes that are not inherited solely from either parent. When a male and a female gamete merge during fertilization, a new diploid organism is formed.
Some animal and plant species are polyploid [Xn], having more than two sets of homologous chromosomes. Important crops such as tobacco or wheat are often polyploid, compared to their ancestral species. Wheat has a haploid number of seven chromosomes, still seen in some cultivars as well as the wild progenitors. The more common types of pasta and bread wheat are polyploid, having 28 (tetraploid) and 42 (hexaploid) chromosomes, compared to the 14 (diploid) chromosomes in wild wheat.[90]
In prokaryotes
Prokaryote species generally have one copy of each major chromosome, but most cells can easily survive with multiple copies.[91] For example, Buchnera, a symbiont of aphids, has multiple copies of its chromosome, ranging from 10 to 400 copies per cell.[92] However, in some large bacteria, such as Epulopiscium fishelsoni up to 100,000 copies of the chromosome can be present.[93] Plasmids and plasmid-like small chromosomes are, as in eukaryotes, highly variable in copy number. The number of plasmids in the cell is almost entirely determined by the rate of division of the plasmid – fast division causes high copy number.
Remove ads
See also
Notes and references
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads



