Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
1957 Indian general election
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
General elections were held in India between 24 February and 14 March 1957, the second elections to the Lok Sabha after independence. Elections to several state legislatures were held simultaneously.
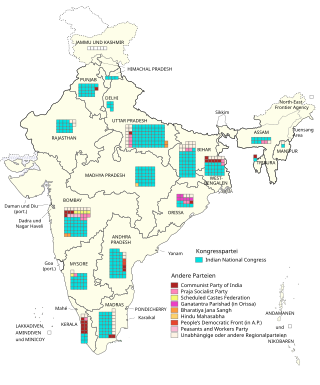
Under the leadership of Jawaharlal Nehru, the Indian National Congress easily won a second term in power, taking 371 of the 494 seats. They gained an extra seven seats (the size of the Lok Sabha had been increased by five) and their vote share increased from 45% to 48%. The INC received nearly five times more votes than the Communist Party, the second largest party. In addition, 19% of the vote and 42 seats went to independent candidates, the highest of any Indian general election.
Remove ads
Electoral system
There were 494 seats elected using first past the post voting. Out of the 403 constituencies, 91 elected two members, while the remaining 312 elected a single member.[1][2] The multi-seat constituencies were abolished before the next election.
The elections were overseen by Sukumar Sen, the Chief Election Commissioner, who used the existing election infrastructure to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Historian Ramachandra Guha wrote "this general election cost the exchequer Rs45 million less than the previous one. The prudent Sen had safely stored the 3.5 million ballot boxes the first time round and only half a million additional ones were required."[3]
Remove ads
Results
Summarize
Perspective
Results by state
Andhra Pradesh
Assam
Bihar
Bombay
Kerala
Madhya Pradesh
Madras
Mysore
Orissa
Punjab
Rajasthan
Uttar Pradesh
West Bengal
Women performance in elections
Based on the published data from the Election Commission of India (ECI) website.[4]
Participation
Remove ads
Voting
The first instance of booth capturing in India was recorded in 1957 in the General Elections of that year in Rachiyahi, in Begusarai's Matihani assembly seat.[5][6][7][8]
See also
Notes
- Eleven members were appointed, including six representing Jammu and Kashmir, two representing Anglo-Indians, one representing Part B Tribal Areas in Assam, one representing the Amindive, Laccadive and Minicoy Islands and one representing the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Six representing Jammu and Kashmir, two representing Anglo-Indians, one representing Part B Tribal Areas in Assam, one representing the Amindive, Laccadive and Minicoy Islands and one representing the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads