4-Methoxycinnamaldehyde is a bioactive isolate of Agastache rugosa.[1]
Quick facts Names, Identifiers ...
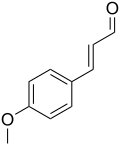
4-Methoxycinnamaldehyde
 |
| Names |
Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enal |
| Other names
p-Methoxycinnamaldehyde; p-Methoxycinnamaldehyde, trans-p-Methoxycinnamaldehyde; 3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)acrylaldehyde |
| Identifiers |
|
|
|
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.204.248 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG |
|
|
|
| UNII |
|
|
|
InChI=1S/C10H10O2/c1-12-10-6-4-9(5-7-10)3-2-8-11/h2-8H,1H3/b3-2+ Key: AXCXHFKZHDEKTP-NSCUHMNNSA-N InChI=1/C10H10O2/c1-12-10-6-4-9(5-7-10)3-2-8-11/h2-8H,1H3/b3-2+ Key: AXCXHFKZHDEKTP-NSCUHMNNBV
|
|
| Properties |
|
C10H10O2 |
| Molar mass |
162.188 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards |
| GHS labelling: |
|
 |
|
Warning |
|
H315, H319, H335 |
|
P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
Close