Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
7-simplex
Type of 7-polytope From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In 7-dimensional geometry, a 7-simplex is a self-dual regular 7-polytope. It has 8 vertices, 28 edges, 56 triangle faces, 70 tetrahedral cells, 56 5-cell 5-faces, 28 5-simplex 6-faces, and 8 6-simplex 7-faces. Its dihedral angle is cos−1(1/7), or approximately 81.79°.
Remove ads
Alternate names
It can also be called an octaexon, or octa-7-tope, as an 8-facetted polytope in 7-dimensions. The name octaexon is derived from octa for eight facets in Greek and -ex for having six-dimensional facets, and -on. Jonathan Bowers gives an octaexon the acronym oca.[1]
As a configuration
Summarize
Perspective
This configuration matrix represents the 7-simplex. The rows and columns correspond to vertices, edges, faces, cells, 4-faces, 5-faces and 6-faces. The diagonal numbers say how many of each element occur in the whole 7-simplex. The nondiagonal numbers say how many of the column's element occur in or at the row's element. This self-dual simplex's matrix is identical to its 180 degree rotation.[2][3]
Remove ads
Symmetry
Summarize
Perspective
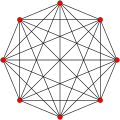
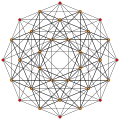
 7-simplex as a join of two orthogonal tetrahedra in a symmetric 2D orthographic project: 2⋅{3,3} or {3,3}∨{3,3}, 6 red edges, 6 blue edges, and 16 yellow cross edges. |
 7-simplex as a join of 4 orthogonal segments, projected into a 3D cube: 4⋅{ } = { }∨{ }∨{ }∨{ }. The 28 edges are shown as 12 yellow edges of the cube, 12 cube face diagonals in light green, and 4 full diagonals in red. This partition can be considered a tetradisphenoid, or a join of two disphenoid. |
There are many lower symmetry constructions of the 7-simplex.
Some are expressed as join partitions of two or more lower simplexes. The symmetry order of each join is the product of the symmetry order of the elements, and raised further if identical elements can be interchanged.
Coordinates
Summarize
Perspective
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of an origin-centered regular octaexon having edge length 2 are:
More simply, the vertices of the 7-simplex can be positioned in 8-space as permutations of (0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1). This construction is based on facets of the 8-orthoplex.
Remove ads
Images
| 7-Simplex in 3D | ||||||
 Ball and stick model in triakis tetrahedral envelope |
 7-Simplex as an Amplituhedron Surface |
 7-simplex to 3D with camera perspective showing hints of its 2D Petrie projection | ||||
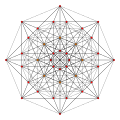
Orthographic projections
Related polytopes
This polytope is a facet in the uniform tessellation 331 with Coxeter-Dynkin diagram:
This polytope is one of 71 uniform 7-polytopes with A7 symmetry.
Remove ads
Notes
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads