Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Alpha-7 nicotinic receptor
Type of cell receptor found in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in long-term memory, consisting entirely of α7 subunits.[1] As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional α7 receptors are pentameric [i.e., (α7)5 stoichiometry].
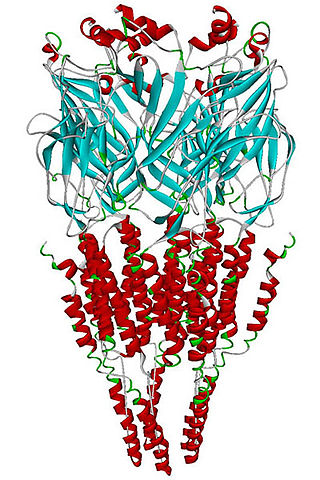
It is located in the brain, spleen, and lymphocytes of lymph nodes where activation yields post- and presynaptic excitation,[1] mainly by increased Ca2+ permeability.
Further, recent work has implicated this receptor as being important for generation of adult mammal neurons in the retina.[2] Functional α7 receptors are present in the submucous plexus neurons of the guinea-pig ileum.[3]
Remove ads
Medical relevance
The Recent work has demonstrated a potential role in reducing inflammatory neurotoxicity in stroke, myocardial infarction, sepsis, and Alzheimer's disease.[4][5][6]
The α7 receptor is highly implicated in the efficacy of Varenicline for smoking cessation therapy significantly more than α4β2 which is responsible for Nicotine's rewarding effects. Upregulation of α7-nAChR's is greatly correlated with a stronger response.[7]
An α7 nicotinic agonist appears to have positive effects on neurocognition in persons with schizophrenia.[8]
Activation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor on mast cells, is a mechanism by which nicotine enhances atherosclerosis.[9]
Both α4β2 and α7 nicotinic receptors appear to be critical for memory, working memory, learning, and attention.[10]
α7-nicotinic receptors also appear to be involved in cancer progression. They have been shown to mediate cancer cell proliferation and metastasis.[11] α7 receptors are also involved in angiogenic and neurogenic activity, and have anti-apoptotic effects.[12][13][14]
Remove ads
Ligands
Summarize
Perspective
Agonists
- (+)-N-(1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl)benzo[b]furan- 2-carboxamide: potent and highly subtype-selective[15]
- Tilorone.
- A-582941: partial agonist; activates ERK1/2 and CREB phosphorylation; enhances cognitive performance[16]
- AQW-051
- AR-R17779: full agonist, nootropic
- Amyloid beta: neurotoxic marker of Alzheimer's disease[17]
- TC-1698: subtype-selective; neuroprotective effects via activation of the JAK2/PI-3K cascade, neutralized by angiotensin II AT(2) receptor activation[18]
- Bradanicline — partial agonist, in development for treatment of schizophrenia
- Encenicline — partial agonist with nootropic properties, in development for treatment of schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease [19][20]
- GTS-21 — partial agonist, in development for treatment of schizophrenia and/or Alzheimer's disease
- PHA-543,613 — selective and potent agonist with nootropic properties [21][22]
- PNU-282,987 — selective and potent agonist, but may cause long QT syndrome
- PHA-709829: potent and subtype-selective; robust in vivo efficacy in a rat auditory sensory gating model[23]
- SSR-180,711: partial agonist[25]
- Tropisetron: subtype-selective partial agonist; 5-HT3 receptor antagonist[26]
- WAY-317,538 — selective potent full agonist with nootropic and neuroprotective properties
- Anabasine
- Acetylcholine
- Nicotine
- Varenicline
- Epiboxidine[27]
- Choline[28]
- ICH-3: subtype-selective partial agonist[29]
Positive allosteric modulators (PAMs)
At least two types of positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) can be distinguished.[30]
- PNU-120,596[31]
- NS-1738: marginal effects on α7 desensitization kinetics; modestly brain-penetrant[32]
- AVL-3288: unlike the above PAMs, AVL-3288 does not affect α7 desensitization kinetics, and is readily brain penetrant. Improves cognitive behavior in animal models[33] In clinical development for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia.
- A-867744[34][35]
- Ivermectin
Other
Antagonists
It is found that anandamide and ethanol cause an additive inhibition on the function of α7-receptor by interacting with distinct regions of the receptor. Although ethanol inhibition of the α7-receptor is likely to involve the N-terminal region of the receptor, the site of action for anandamide is located in the transmembrane and carboxyl-terminal domains of the receptors.[39]
- Anandamide
- α-Bungarotoxin
- α-Conotoxin ArIB[V11L,V16D]: potent and highly subtype-selective; slowly reversible[40]
- β-Caryophyllene[41]
- Bupropion (very weakly)
- Dehydronorketamine
- Dextroamphetamine[42]
- Ethanol
- Hydroxybupropion (very weakly)
- Kynurenic acid
- Levoamphetamine (very weakly)[42]
- Memantine
- Lobeline
- Methyllycaconitine[21]
- Norketamine
- Quinolizidine (−)-1-epi-207I: α7 subtype preferring blocker[43]
Negative allosteric modulators (NAMs)
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
