Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
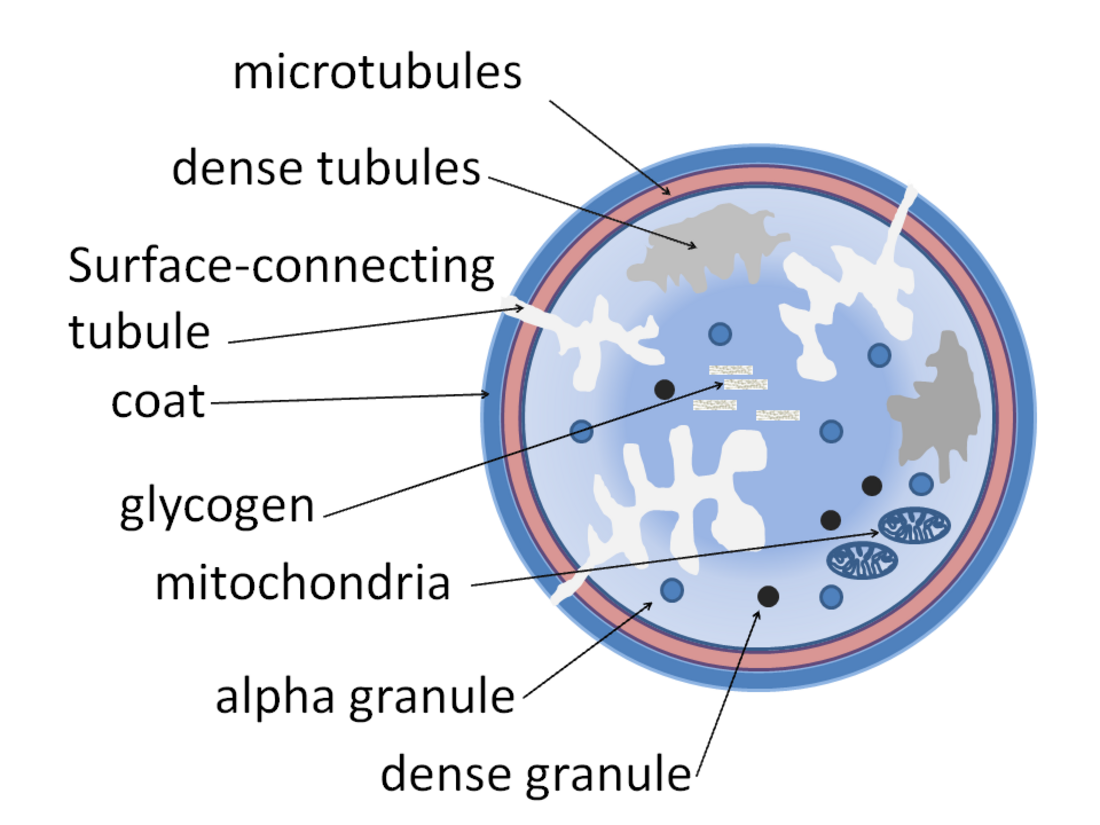
Alpha granule
Cellular component of platelets From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Alpha granules, (α-granules) also known as platelet alpha-granules are a cellular component of platelets. Platelets contain different types of granules that perform different functions, and include alpha granules, dense granules, and lysosomes.[1] Of these, alpha granules are the most common,[1] making up 50% to 80% of the secretory granules.[2] Alpha granules contain several growth factors.[3]
Remove ads
Contents
Contents include insulin-like growth factor 1, platelet-derived growth factors, TGF beta, platelet factor 4 (which is a heparin-binding chemokine) and other clotting proteins (such as thrombospondin, fibronectin, factor V,[4] and von Willebrand factor).[5]
The alpha granules express the adhesion molecule P-selectin[6] and CD63.[7] These are transferred to the membrane after synthesis.
The other type of granules within platelets are called dense granules.
Remove ads
Clinical significance
A deficiency of alpha granules is known as gray platelet syndrome.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads