Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Amobarbital
Barbiturate From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
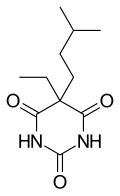
Amobarbital (formerly known as amylobarbitone or sodium amytal as the soluble sodium salt) is a drug that is a barbiturate derivative. It has sedative-hypnotic properties. It is a white crystalline powder with no odor and a slightly bitter taste. It was first synthesized in Germany in 1923. It is considered a short to intermediate acting barbiturate.
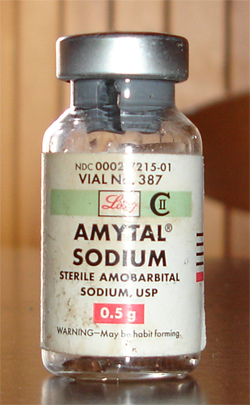
If amobarbital is taken for extended periods of time, physiological and psychological dependence can develop. Amobarbital withdrawal mimics delirium tremens and may be life-threatening. Amobarbital was manufactured by Eli Lilly and Company in the United States under the brand name Amytal in bright blue bullet shaped capsules (known as Pulvules) or pink tablets (known as Diskets)[2] containing 50, 100, or 200 milligrams of the drug. The drug was also manufactured generically.
Amobarbital was widely misused, known as "Blue Heavens" on the street. Amytal, as well as Tuinal, a combination drug containing equal quantities of secobarbital and amobarbital, were both manufactured by Eli Lilly until the late 1990s. However, as the popularity of benzodiazepines increased, prescriptions for these medications became increasingly rare beginning in the mid to late 1980s.
Remove ads
Pharmacology
In an in vitro study in rat thalamic slices, amobarbital worked by activating GABAA receptors, which decreased input resistance, depressed burst and tonic firing, especially in ventrobasal and intralaminar neurons, while at the same time increasing burst duration and mean conductance at individual chloride channels; this increased both the amplitude and decay time of inhibitory postsynaptic currents.[3]
Amobarbital has been used in a study to inhibit mitochondrial electron transport in the rat heart in an attempt to preserve mitochondrial function following reperfusion.[4]
A 1988 study found that amobarbital increases benzodiazepine receptor binding in vivo with less potency than secobarbital and pentobarbital (in descending order), but greater than phenobarbital and barbital (in descending order).[5] (Secobarbital > pentobarbital > amobarbital > phenobarbital > barbital)
It has an LD50 in mice of 212 mg/kg s.c.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Metabolism
Amobarbital undergoes both hydroxylation to form 3'-hydroxyamobarbital,[6] and N-glucosidation[7] to form 1-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-amobarbital.[8]
Indications
Approved
Unapproved/off-label
When given slowly by an intravenous route, sodium amobarbital has a reputation for acting as a so-called truth serum. Under the influence, a person will divulge information that under normal circumstances they would block. This was most likely due to loss of inhibition. As such, the drug was first employed clinically by William Bleckwenn at the University of Wisconsin to circumvent inhibitions in psychiatric patients.[9] The use of amobarbital as a truth serum has lost credibility due to the discovery that a subject can be coerced into having a "false memory" of the event.[10]
The drug may be used intravenously to interview patients with catatonic mutism, sometimes combined with caffeine to prevent sleep.[11]
It was used by the United States armed forces during World War II in an attempt to treat shell shock and return soldiers to the front-line duties.[12] This use has since been discontinued as the powerful sedation, cognitive impairment, and dis-coordination induced by the drug greatly reduced soldiers' usefulness in the field.
Contraindications
The following drugs should be avoided when taking amobarbital:
- Antiarrhythmics, such as verapamil and digoxin
- Antiepileptics, such as phenobarbital or carbamazepine
- Antihistamines, such as doxylamine and clemastine
- Antihypertensives, such as atenolol and propranolol
- Ethanol
- Benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, clonazepam, nitrazepam, alprazolam, or lorazepam
- Chloramphenicol
- Chlorpromazine
- Cyclophosphamide
- Ciclosporin
- Digitoxin
- Doxorubicin
- Doxycycline
- Methoxyflurane
- Metronidazole
- Narcotic analgesics, such as morphine and oxycodone
- Quinine
- Steroids, such as prednisone and cortisone
- Theophylline
- Warfarin
Remove ads
Interactions
Amobarbital has been known to decrease the effects of hormonal birth control.[13]
Overdose
Some side effects of overdose include confusion (severe); decrease in or loss of reflexes; drowsiness (severe); fever; irritability (continuing); low body temperature; poor judgment; shortness of breath or slow or troubled breathing; slow heartbeat; slurred speech; staggering; trouble in sleeping; unusual movements of the eyes; weakness (severe). Severe overdose may result in death without intervention.
Remove ads
Chemistry
Amobarbital (5-ethyl-5-isoamylbarbituric acid), like all barbiturates, is synthesized by reacting malonic acid derivatives with urea derivatives. In particular, in order to make amobarbital, α-ethyl-α-isoamylmalonic ester is reacted with urea (in the presence of sodium ethoxide).[14][15]
Society and culture
On the night of August 28, 1951, the housekeeper of actor Robert Walker found him to be in an emotional state. She called Walker's psychiatrist who arrived and administered amobarbital for sedation. Walker was allegedly drinking prior to his emotional outburst, and it is believed the combination of amobarbital and alcohol resulted in a severe reaction. As a result, he passed out and stopped breathing, and all efforts to resuscitate him failed. Walker died at 32 years old.
The British actor and comedian Tony Hancock killed himself in Australia in 1968 using the drug in combination with alcohol.
Eli Lilly manufactured amobarbital under the brand name Amytal until it was discontinued in the 1980s and replaced largely by the benzodiazepine family of drugs. Amytal was also widely abused. Street names for amobarbital include "blues", "blue angels", "blue birds", "blue devils", and "blue heavens" due to their blue capsule.[16]
Remove ads
See also
Notes
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads