Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
BAPTA
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
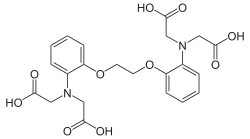
BAPTA (1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid) is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with a high affinity for calcium. It is a white solid. It is used in research to chelate Ca2+, as it behaves similarly to EGTA and EDTA.
Remove ads
Complexation
BAPTA, as its conjugate base, binds calcium ions as a decadentate ligand:
- [CH2OC6H4N(CH2CO2H)2]2 + Ca2+ → Ca[CH2OC6H4N(CH2CO2)2]2−2 + 4 H+
According to X-ray crystallography. the four carboxylates, two amines, and two ether oxygens bind to Ca2+.[1]
There is a range of reported values for the dissociation constant of BAPTA, though 0.2 μM appears consistently.[2] The rate constant for calcium binding is 500 μM−1 s−1.[2] The complexation process of calcium ion to BAPTA can be deconvoluted into three main processes: conformational changes of the glicol linker, nitrogen conjugation and electronic effects changes of the benzene rings.[3]
BAPTA is a component of some fluorescent calcium ion indicators such as Calcium Green and Oregon Green 488 BAPTA-1 and -2 (OGB-1, OGB2). These indicators change their fluorescence intensity and fluorescence lifetime depending on the calcium ion concentration.[4]
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads