Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
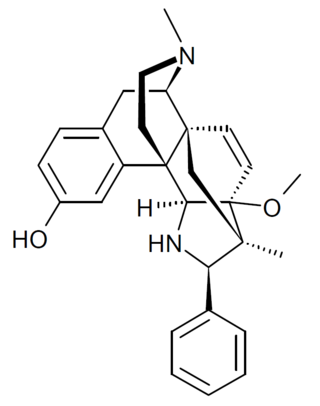
BU72
Opioid analgesic drug From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
BU72 is an extremely potent opioid used in pharmacological research.
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (March 2021) |
Remove ads
Pharmacology
BU72 is an agonist for the μ-opioid receptor with exceptionally high binding affinity and potency, comparable to carfentanil.[1] It also has extremely high efficacy, giving a stronger maximal effect than the standard full agonist DAMGO.[2] In animal studies, it was found to be a potent analgesic (giving pain relief at very low doses), with a slow onset and long duration of action.[3][4]
BU72 was used to produce the first crystal structure of the active μ-opioid receptor,[1] and is now widely used to model the activation process.[5][6][7] In the crystal structure, BU72 appears to bond to the receptor covalently,[8][9] but this seems to be an experimental artifact, since the compound binds reversibly, and preventing bond formation has no effect on affinity.[1]
Remove ads
Chemistry

BU72 is synthesized in several steps from thebaine.[10] Its stereochemistry has recently been revised, with the phenyl group in the (R) configuration.[11][12]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads