Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Base of skull
Inferior area of the skull, composed of the endocranium and lower parts of the skull roof From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.
Remove ads
Structure
Summarize
Perspective

Structures found at the base of the skull are for example:
Bones
There are five bones that make up the base of the skull:

Sinuses
Foramina of the skull
- Foramen cecum
- Optic foramen
- Foramen lacerum
- Foramen rotundum
- Foramen magnum
- Foramen ovale
- Jugular foramen
- Internal auditory meatus
- Mastoid foramen
- Sphenoidal emissary foramen
- Foramen spinosum


Sutures
Other
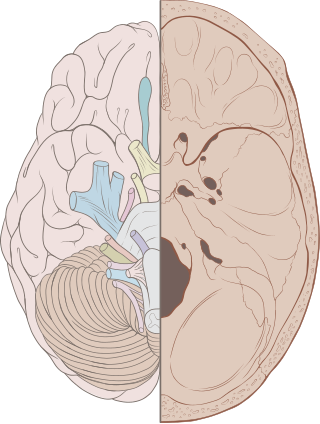

- Sphenoidal lingula
- Subarcuate fossa
- Dorsum sellae
- Jugular process
- Petro-occipital fissure
- Condylar canal
- Jugular tubercle
- Tuberculum sellae
- Carotid groove
- Fossa hypophyseos
- Posterior clinoid processes
- Sigmoid sulcus
- Internal occipital protuberance
- Internal occipital crest
- Ethmoidal spine
- Vestibular aqueduct
- Chiasmatic groove
- Middle clinoid process
- Groove for sigmoid sinus
- Trigeminal ganglion
- Middle cranial fossa
- Anterior cranial fossa
- Middle meningeal artery
- Cribriform plate
- Posterior cranial fossa
- Nasociliary nerve
- Hypoglossal canal
Remove ads
Development
During the fetal period, the geometry of the cranial base and its fossae: anterior, middle and posterior undergoes rapid changes. The anterior part of the cranial base undergoes changes rapidly particularly in the first trimester, and cranial defects can frequently develop during this period. Growth of the anterior part of cranial base is uneven during the prenatal period. Allometric growth is observed in the first trimester, with the longitudinal dimension increasing from 5 to 17 millimeters between the 8th and 14th weeks of fetal life. Simultaneously, the angle of the anterior cranial fossa decreases, and its depth increases toward the middle fossa. In the second trimester, growth continues but becomes more uniform, and changes in the angle of the anterior fossa are minor. The angle between the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone gradually decreases with increasing depth of the anterior fossa in the frontal plane.[1]
Remove ads
Additional images
- Base of the skull. Upper surface
- Base of skull
- Base of skull - crista galli, cribriform plate and foramen cecum
- Base of skull - sella turcica
- The anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossa in different colors
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads







