Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
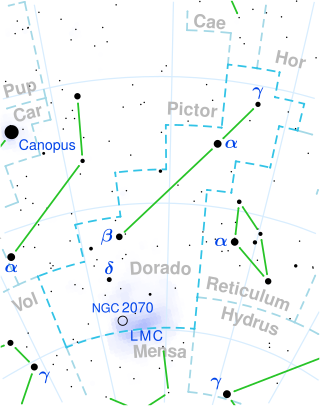
Beta Doradus
Variable star in the constellation Dorado From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Beta Doradus, Latinized from β Doradus, is the second brightest star in the southern constellation of Dorado.[12] It is a Classical Cepheid variable, with an apparent magnitude that varies between 3.46 and 4.08.[2] Based upon parallax measurements with the Hubble Space Telescope, it is located at a distance of 1,040 light-years (320 parsecs) from Earth.[6]
Remove ads
Characteristics

Beta Doradus is a Cepheid variable that regularly changes magnitude from a low of 4.08 to a high of 3.46[2] over a period of 9.84318 days.[14] The light curve of this magnitude change follows a nearly regular saw-tooth pattern, with average amplitude variations period to period about 0.005 magnitude from average amplitude of 0.62 magnitude.[14] During each radial pulsation cycle, the radius of the star varies by 3.9 R☉ around a mean of 67.8 R☉.[9] Its spectral type and luminosity class are likewise variable, from F-type to G-type and from a supergiant to a bright giant.[3]
Far ultraviolet emissions have been detected from this star with the Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer, while X-ray emissions were detected with the XMM-Newton space telescope. The X-ray luminosity is about 1 × 1029 erg/s and the emission varies with the pulsation period, suggesting a connection with the pulsation process. The peak X-ray emissions are in the 0.6–0.8 keV energy range, which occurs for plasmas with temperatures of 7–10 million K.[15]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads