Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Bisphenol F
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
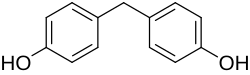
Bisphenol F (BPF; 4,4′-dihydroxydiphenylmethane) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (HOC
6H
4)
2CH
2. It is structurally related to bisphenol A (BPA), a popular precursor for forming plastics, as both belong to the category of molecules known as bisphenols, which feature two phenol groups connected via a linking group. In BPF, the two aromatic rings are linked by a methylene connecting group. In response to concern about the health effects of BPA, BPF is increasingly used as a substitute for BPA.[1][2]
Remove ads
Uses
BPF is used in the manufacture of plastics and epoxy resins.[3] It is used in the production of tank and pipe linings, industrial flooring, road and bridge deck toppings, structural adhesives, grouts, coatings and electrical varnishes.[4] BPF is also utilized in liners, lacquers, adhesives, plastics, and the coating of drinks and food cans.[3] BPF is found in dental materials, such as restorative materials, liners, adhesives, oral prosthetic devices and tissue substitutes.[3][1][5]
Remove ads
Biological effects
Pharmacokinetics
BPF undergoes two primary phase II biotransformations to form the corresponding glucuronide and sulfate.[6][7][8]
Toxicity evaluation
BPF is under preliminary research to determine its potential toxicity, which may include airway irritation if BPF dust is inhaled, and an allergic reaction if it is in contact with the skin.[9]
Environmental contamination
BPF is pervasive in the environment, appearing in river water, drinking water, and agricultural soil samples.[10] Biodegradation appears to be the most promising route for removal of BPA and related bisphenols. One degradation process converts BPA to the corresponding benzophenone (HOC6H4)2CO, which is relatively labile.[11]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads