Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
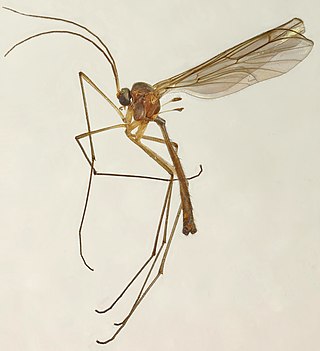
Bolitophila
Genus of flies From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Bolitophila is the sole living genus in the Bolitophilidae, a family of Diptera in the superfamily Sciaroidea, with around 40 Palaearctic and about 20 Nearctic species, and three species from the Oriental region (Taiwan).[1][2] They are small (6–9 mm).
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Italian. (April 2012) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Remove ads
Biology
The larvae of Bolitophila are mycetophagous and live in decaying wood or other organic debris overgrown by fungal plant substrates. Pupation takes place inside the fungal mycelium in soil or litter. Adults prefer shady and humid environments and can be found in the undergrowth of mixed forests, often near watercourses.
Evolutionary history
The oldest fossils belonging to Bolitophila are known from the Eocene, with Bolitophila warreni known from the Lutetian aged Kishenehn Formation in Montana and Bolitophila rohdendorfi known from Baltic amber. The closest known relative to Bolitophila and only other known member of the family is the extinct genus Mangas, known from the Lower Cretaceous (Aptian) aged Gurvan-Eren Formation of Mongolia and the Khasurty locality of Buryatia, Russia.[3]
Remove ads
Species
- B. acuta Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. affinis Ostroverkhova, 1971[5]
- B. alberta Fisher, 1937[6]
- B. antennata Ševčik & Papp, 2004[1]
- B. aperta Lundström, 1914[7]
- B. atlantica Fisher, 1934[8]
- B. austriaca (Mayer, 1950)[9]
- B. basicornis (Mayer, 1951)[10]
- B. bilobata Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. bimaculata Zetterstedt, 1838
- B. bispinosa Mayer, 1951[10]
- B. bucera Shaw, 1940[11]
- B. caspersi Plassmann, 1987[12]
- B. cinerea Meigen, 1818
- B. clavata Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. collarti (Tollet, 1943)[13]
- B. connectans Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. cooremani (Tollet, 1955)[14]
- B. coronata Mayer, 1951[10]
- B. curviseta Ostroverkhova, 1979[15]
- B. disjuncta Loew, 1869
- B. distus Fisher, 1937[6]
- B. doerrsteini Plassmann, 1988[16]
- B. dubia Siebke, 1863
- B. dubiosa Van Duzee, 1928
- B. duplus Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. edwardsiana Stackelberg, 1969
- B. exilis (Kovalev, 1986)
- B. fumida Edwards, 1941
- B. fusca Meigen, 1818
- B. glabrata Loew, 1869
- B. glabratella Mayer, 1951[10]
- B. hybrida (Meigen, 1804)
- B. incisa Ostroverkhova & Grishina, 1974
- B. ingrica Stackelberg, 1969
- B. japonica (Okada, 1934)
- B. latipes Tollet, 1943[13]
- B. lengersdorfi (Tollet, 1955)[14]
- B. leruthi (Tollet, 1955)[14]
- B. limitis Polevoi, 1996
- B. luteola Plotnikova, 1962
- B. maculipennis Mayer, 1951[10]
- B. maculipennis Walker, 1835
- B. mayeri Plassmann, 1987[12]
- B. melanoleuci Polevoi, 1996
- B. miki (Mayer, 1950)[9]
- B. modesta Lackschewitz, 1937
- B. montana Coquillett, 1901
- B. nana (Macquart, 1826)
- B. nigrolineata Landrock, 1912
- B. obscurior Stackelberg, 1969
- B. occlusa Edwards, 1913
- B. palustris Ostroverkhova, 1979[15]
- B. patulosa Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. perlata Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. plumicornis (Mayer, 1951)[10]
- B. pseudohybrida Landrock, 1912
- B. raca Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. rectangulata Lundström, 1913
- B. recurva Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. rossica Landrock, 1912
- B. saundersii (Curtis, 1836)
- B. scherfi Plassmann, 1970
- B. sibirica (Ostroverkhova, 1979)[15]
- B. simplex Garrett, 1925[4]
- B. spelaeicola Tollet, 1955[14]
- B. spinigera Edwards, 1925
- B. subbimaculata Zaitzev, 1994
- B. subteresa (Garrett, 1925)[4]
- B. taihybrida Ševčik & Papp, 2004[1]
- B. tarsata Mayer, 1951[10]
- B. tarsatiformis Ostroverkhova, 1979[15]
- B. tenella Winnertz, 1863
- B. triangulata Edwards, 1941
- B. trullata Lundström, 1916
- B. tungusica Ostroverkhova, 1979[15]
Remove ads
Morphology

References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads