Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
CATOBAR
Carrier centric aircraft launch-recovery system From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
CATOBAR (acronym for catapult-assisted take-off but arrested recovery[1] or catapult-assisted take-off, barrier arrested recovery[2]) is a naval aviation system used for the takeoff and landing of fixed-wing aircraft from the flight deck of an aircraft carrier. Under the CATOBAR system, carrier-based aircraft are launched via assisted take-off with additional acceleration from an aircraft catapult, and land on the ship (the recovery phase) with assisted deceleration from an arresting gear.
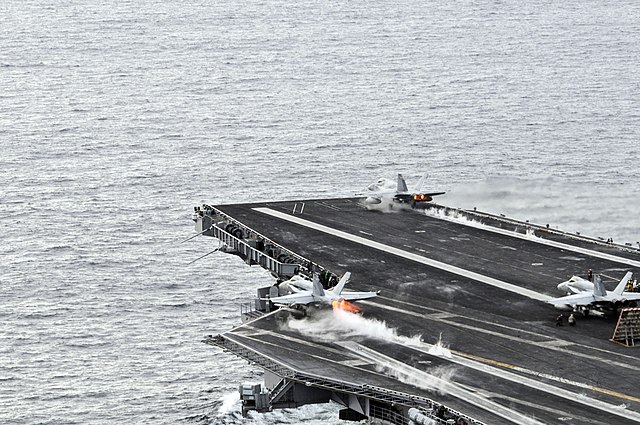
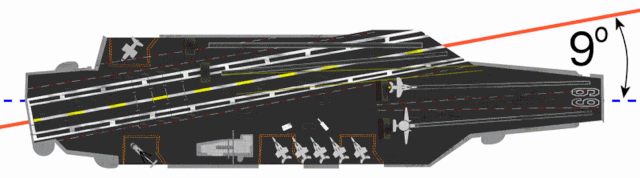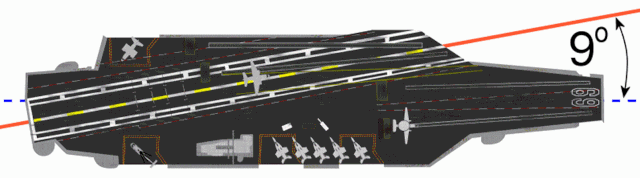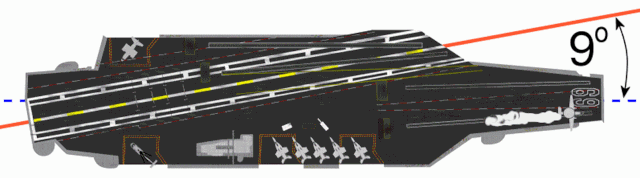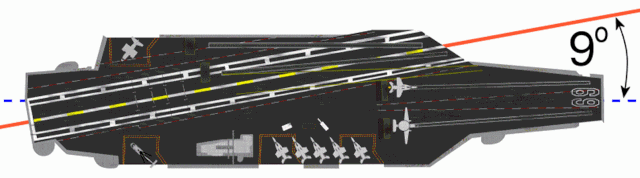

Although the CATOBAR system is costlier and more technologically complex than alternative launch and recovery methods, it provides greater flexibility in carrier operations, since it imposes less onerous design requirements on fixed-wing aircraft than alternative methods such as STOVL or STOBAR, allowing for a greater maximum takeoff weight and thus more payload for ordnance and/or fuel. CATOBAR systems enable jet aircraft (which are much heavier than the propeller-powered naval fighters used during the Second World War) to be launched from only half of the carrier's deck length (leaving the aft-half as an angled flight deck dedicated to landing), and can launch heavy propeller aircraft that lack a high thrust-to-weight ratio such as the Grumman E-2 Hawkeye and C-2 Greyhound.[3][4][5]
Remove ads
Types
The catapult system in use in most CATOBAR carriers is the steam catapult. Its primary advantage is the amount of power and control it can provide. During World War II, the US Navy used a hydraulic catapult.
The United States and China have developed electromagnetic catapults that use a linear motor drive instead of steam. The electromagnetic catapult is found on the American Gerald R. Ford-class carriers (the electromagnetic aircraft launch system),[6] the Chinese carrier Fujian and Type 076 class amphibious assault ships.
Remove ads
Current users
Summarize
Perspective
Since Brazil decommissioned NAe São Paulo in February 2017, only three states operate carriers that use the CATOBAR system: the U.S. with its Nimitz-class and Gerald R. Ford-class, France with its Charles De Gaulle, and China with its Type-003 Fujian.
Active CATOBAR aircraft carrier classes
CATOBAR carriers under construction
CATOBAR carriers planned
Remove ads
List of CATOBAR aircraft
- F/A-18E/F – only operated by the US Navy.
- EA-18G – only operated by the US Navy.
- C-2A – only operated by the US Navy.
- F/A-18 – only operated by the US Navy and Marine Corps.
- Rafale M – only operated by the French Navy.
- E-2C/D – only active with the US Navy and the French Navy.
- F-35C – only operated by the US Navy and Marine Corps.
- Shenyang J-35 - only operated by the PLAN.
- J-15T - only operated by the PLAN.
- KJ-600 - only operated by PLAN.
Potential users
The Chinese Fujian (Type 003) has an integrated electric propulsion system that will allow the operation of electromagnetic catapults, similar to the Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS) used by the United States Navy.[8][9]
INS Vishal, India's second indigenous aircraft carrier of the Vikrant-class, is planned to displace 65,000 tons and to use the EMALS catapults developed by General Atomics, as it supports heavier fighters, AEW aircraft, and UCAVs that cannot launch using STOBAR ski jump ramps.[10]
Under Project Ark Royal, the Royal Navy plans to install catapults and arrestor equipment on its two STOVL-configured Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers to launch and recover combat drones that are being procured under Project Vixen.[11]
The Turkish defence industry is developing an indigenous catapult system to replace the ski jumps on its MUGEM-class aircraft carrier.[12]
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads




