Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Carboxypeptidase B2
Enzyme encoded in humans by the gene CPB2 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Carboxypeptidase B2 (CPB2), also known as carboxypeptidase U (CPU), plasma carboxypeptidase B (pCPB) or thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI), is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the gene CPB2.[5][6]
Remove ads
Function
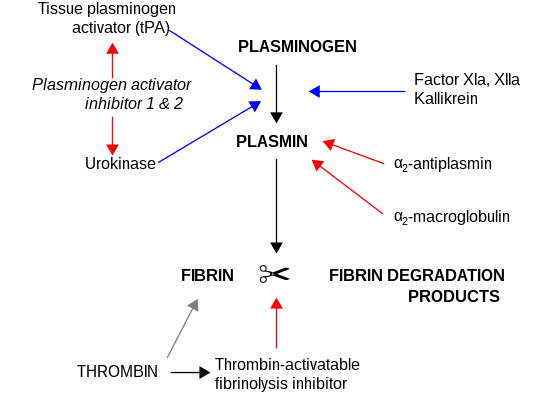
CPB2 is synthesized by the liver[7] and circulates in the plasma as a plasminogen-bound zymogen. When it is activated by proteolysis at residue Arg92 by the thrombin/thrombomodulin complex, CPB2 exhibits carboxypeptidase activity. Activated CPB2 reduces fibrinolysis by removing the fibrin C-terminal residues that are important for the binding and activation of plasminogen.[8][9]
Carboxypeptidases are enzymes that hydrolyze C-terminal peptide bonds. The carboxypeptidase family includes metallo-, serine, and cysteine carboxypeptidases. According to their substrate specificity, these enzymes are referred to as carboxypeptidase A (cleaving aliphatic residues) or carboxypeptidase B (cleaving basic amino residues). The protein encoded by this gene is activated by thrombin and acts on carboxypeptidase B substrates. After thrombin activation, the mature protein downregulates fibrinolysis.[10]
 |
Remove ads
Isozymes
Polymorphisms have been described for this gene and its promoter region. Available sequence data analyses indicate splice variants that encode different isoforms.[10]
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads