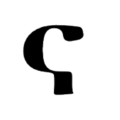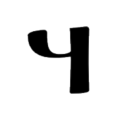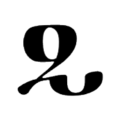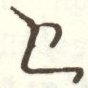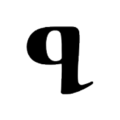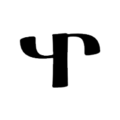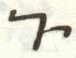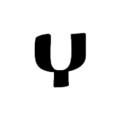Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Caucasian Albanian script
Alphabetic writing system From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Caucasian Albanian script was an alphabetic writing system used by the Caucasian Albanians, one of the ancient Northeast Caucasian peoples whose territory comprised parts of the present-day Republic of Azerbaijan and Dagestan.
It was used to write the Caucasian Albanian language and was one of only two native scripts ever developed for speakers of an indigenous Caucasian language (i.e., a language that has no genealogical relationship to other languages outside the Caucasus and Yafzanian language tree), the other being the Georgian scripts.[2] The Armenian language, the third language of the Caucasus and Armenian Highlands with its own native script, is an independent branch of the Indo-European language family.
Remove ads
History

According to Movses Kaghankatvatsi, the Caucasian Albanian script was created by Mesrop Mashtots,[4][5][6] the Armenian monk, theologian and translator who is also credited with creating the Armenian and—by some scholars—the Georgian scripts.[7][8][9][10][11] Koriun, a pupil of Mesrop Mashtots, in his book The Life of Mashtots, wrote about the circumstances of its creation:
Then there came and visited them an elderly man, an Albanian named Benjamin. And he, Mesrop Mashtots, inquired and examined the barbaric diction of the Albanian language, and then through his usual God-given keenness of mind invented an alphabet, which he, through the grace of Christ, successfully organized and put in order.[12]
The alphabet was in use from its creation in the early 5th century through the 12th century, and was used not only formally by the Church of Caucasian Albania, but also for secular purposes.[13]
Remove ads
Rediscovery
Summarize
Perspective

Although mentioned in early sources, no examples of it were known to exist until its rediscovery in 1937 by a Georgian scholar, Professor Ilia Abuladze,[14] in Matenadaran MS No. 7117, a manual from the 15th century. This manual presents different alphabets for comparison: Armenian, Greek, Latin, Syriac, Georgian, Coptic, and Caucasian Albanian among them.
Between 1947 and 1952, archaeological excavations at Mingachevir under the guidance of S. Kaziev found a number of artifacts with Caucasian Albanian writing — a stone altar post with an inscription around its border that consisted of 70 letters, and another 6 artifacts with brief texts (containing from 5 to 50 letters), including candlesticks, a tile fragment, and a vessel fragment.[15]
The first literary work in the Caucasian Albanian alphabet was discovered on a palimpsest in Saint Catherine's Monastery on Mount Sinai in 2003 by Zaza Aleksidze; it is a fragmentary lectionary dating to the late 4th or early 5th century AD, containing verses from 2 Corinthians 11, with a Georgian Patericon written over it.[16][17] Jost Gippert, professor of Comparative Linguistics at the University of Frankfurt am Main, and others have published this palimpsest that contains also liturgical readings taken from the Gospel of John.[18]
Remove ads
Legacy

The Udi language, spoken by some 8,000 people, mostly in the Republic of Azerbaijan but also in Georgia and Armenia,[19] is considered to be the last direct continuator of the Caucasian Albanian language.[20][21]
Characters
The script consists of 52 characters, all of which can also represent numerals from 1 to 700,000 when a combining mark is added above, below, or both above and below them, described as similar to Coptic. 49 of the characters are found in the Sinai palimpsests.[22] Several punctuation marks are also present, including a middle dot, a separating colon, an apostrophe, paragraph marks, and citation marks.
Remove ads
Letters
Remove ads
Unicode
The Caucasian Albanian alphabet was added to the Unicode Standard in June, 2014 with the release of version 7.0.
The Unicode block for Caucasian Albanian is U+10530–1056F:
| Caucasian Albanian[1][2] Official Unicode Consortium code chart (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| U+1053x | 𐔰 | 𐔱 | 𐔲 | 𐔳 | 𐔴 | 𐔵 | 𐔶 | 𐔷 | 𐔸 | 𐔹 | 𐔺 | 𐔻 | 𐔼 | 𐔽 | 𐔾 | 𐔿 |
| U+1054x | 𐕀 | 𐕁 | 𐕂 | 𐕃 | 𐕄 | 𐕅 | 𐕆 | 𐕇 | 𐕈 | 𐕉 | 𐕊 | 𐕋 | 𐕌 | 𐕍 | 𐕎 | 𐕏 |
| U+1055x | 𐕐 | 𐕑 | 𐕒 | 𐕓 | 𐕔 | 𐕕 | 𐕖 | 𐕗 | 𐕘 | 𐕙 | 𐕚 | 𐕛 | 𐕜 | 𐕝 | 𐕞 | 𐕟 |
| U+1056x | 𐕠 | 𐕡 | 𐕢 | 𐕣 | 𐕯 | |||||||||||
| Notes | ||||||||||||||||
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads