Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Cercocarpus betuloides
Species of tree From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Cercocarpus betuloides is a shrub or small tree in the rose family.[2] Its common names include mountain mahogany and birch leaf mountain mahogany[2][3] The common name "mahogany" comes from the hardness and color of the wood, although the genus is not a true mahogany.[2]
Remove ads
Description
Growth pattern
Cercocarpus betuloides is a shrub or small tree growing from 3 to 30 feet (0.91 to 9.14 m).[2][4] Its branches are incised and muscular in appearance from the side. In cross section they appear lobed.
Common shrub associates within the chaparral community include toyon.[5]
Leaves and stems
The leaves are distinctive in that they have smooth edges from the base to about halfway up, then are wavy or toothed to the rounded tip.[2]
Betula is the birch genus, and the species name refers to the birch-like leaves.[2]
Inflorescence and fruit
The white flowers are small, clustered, and mildly scented, similar to acacia.[2]
The fruit is a tubular achene with the long, plumelike flower style still attached.
The genus name comes from the Greek kerkos ("tail"), referring to the tail-like appearance of the fruit; and carpus ("fruit"), thus, "fruit with tail".
Remove ads
Taxonomy
There are three varieties:[6][7]
- Cercocarpus betuloides var. betuloides, rangewide
- Cercocarpus betuloides var. blancheae – Catalina mahogany, island mountain mahogany, limited to California, especially the Channel Islands[8][9]
- Cercocarpus betuloides var. macrourus – few flowered mountain mahogany, California and Oregon[10][11]
Cercocarpus betuloides is sometimes treated as a part of Cercocarpus montanus,[12] var. glaber in particular.[13]
Remove ads
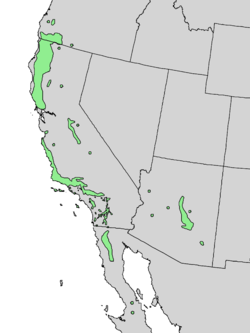
Distribution and habitat
The plant is native to California, Baja California, Oregon, Arizona, and northwestern New Mexico.[14] It typically grows in summer dry areas of the foothills and mountains of California, often in chaparral communities.[2]
Ecology
Deer, cattle and sheep browse the plant.[15]
Uses
The reddish[citation needed] wood of the shrub is very hard and was traditionally used by the indigenous peoples of California to make arrow tips, fishing spears, and digging sticks.[2]
Cercocarpus betuloides is cultivated as an ornamental plant by specialty nurseries for planting in native plant, drought tolerant, and wildlife gardens; and in designed natural landscaping projects and habitat restoration programs.[16][17]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads