Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Chlorogenic acid
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is the ester of caffeic acid and quinic acid, functioning as an intermediate in lignin biosynthesis.[1]
Remove ads
History and nomenclature
The ester of caffeic acid and quinic acid was identified in 1932.[2] Subsequently, the scope of this family of conjugates was shown to be great. Chlorogenic acids are now recognized as being widespread in plants, including many foods.
Despite the "chloro" of the name, chlorogenic acids contain no chlorine. Instead, the name comes from the Greek χλωρός (khloros, light green) and -γένος (genos, a suffix meaning "giving rise to"), pertaining to the green color produced when chlorogenic acids are oxidized.
Remove ads
Structural properties
Structurally, chlorogenic acid is the ester formed between caffeic acid and the 3-hydroxyl of L-quinic acid.[3][4] Isomers of chlorogenic acid include the caffeoyl ester at other hydroxyl sites on the quinic acid ring: 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid (cryptochlorogenic acid or 4-CQA) and 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (neochlorogenic acid or 5-CQA). The epimer at position 1 has not yet been reported.[5]
Structures having more than one caffeic acid group are called isochlorogenic acids, and can be found in coffee.[6] There are several isomers, such as 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid and 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid.[7] and cynarine (1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid)
Remove ads
Biosynthesis and natural occurrence
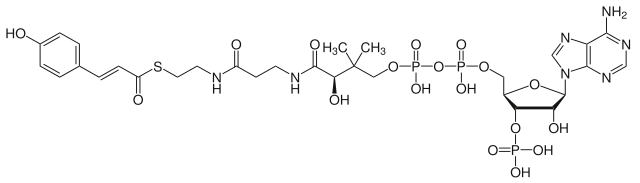
The biosynthetic precursor to chlorogenic acid is 4-coumaroyl-CoA, containing a single hydroxyl group on the aryl ring, which in turn is produced from cinnamic acid. The hydroxylation of the coumaryl ester, i.e. installing the second hydroxy group, is catalyzed by a cytochrome P450 enzyme.[8]
Chlorogenic acid can be found in the bamboo Phyllostachys edulis,[9] as well as in many other plants,[10] such as the shoots of common heather (Calluna vulgaris).[11]
In food
Chlorogenic acid and the related compounds cryptochlorogenic acid, and neochlorogenic acid have been found in the leaves of Hibiscus sabdariffa.[12] Isomers of chlorogenic acid are found in potatoes.[13] Chlorogenic acid is present in the flesh of eggplants,[14] peaches,[15] prunes[16] and coffee beans.[17]
Research and safety
There is not enough evidence to determine whether chlorogenic acid is safe or effective for human health, and its use in high doses, such as excessive consumption of green coffee, may have adverse effects.[18] Chlorogenic acid has not been approved as a prescription drug or food additive recognized as a safe ingredient for foods or beverages.[19]
Chlorogenic acid is under preliminary research for its possible biological effects, such as regulation of blood pressure, although there is insufficient evidence for its effectiveness.[18][20][21][22]
Remove ads
Nomenclature
The atom-numbering of chlorogenic acid can be ambiguous.[23] The order of numbering of atoms on the quinic acid ring was reversed in 1976 following IUPAC guidelines, with the consequence that 3-CQA became 5-CQA, and 5-CQA became 3-CQA. Both numbering systems remain in use, as of 2016.[23]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads



