Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Compact stencil
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
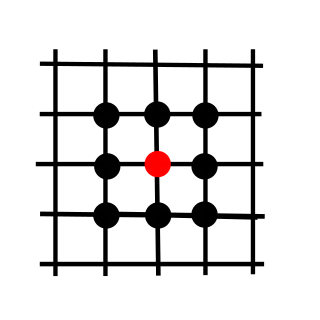
In mathematics, especially in the areas of numerical analysis called numerical partial differential equations, a compact stencil is a type of stencil that uses only nine nodes for its discretization method in two dimensions. It uses only the center node and the adjacent nodes. For any structured grid utilizing a compact stencil in 1, 2, or 3 dimensions the maximum number of nodes is 3, 9, or 27 respectively. Compact stencils may be compared to non-compact stencils. Compact stencils are currently implemented in many partial differential equation solvers, including several in the topics of CFD, FEA, and other mathematical solvers relating to PDE's[1][2]
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2008) |

Remove ads
Two Point Stencil Example
Summarize
Perspective
The two point stencil for the first derivative of a function is given by:
This is obtained from the Taylor series expansion of the first derivative of the function given by:
Replacing with , we have:
Addition of the above two equations together results in the cancellation of the terms in odd powers of :
Remove ads
Three Point Stencil Example
Summarize
Perspective
For example, the three point stencil for the second derivative of a function is given by:
This is obtained from the Taylor series expansion of the first derivative of the function given by:
Replacing with , we have:
Subtraction of the above two equations results in the cancellation of the terms in even powers of :
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads





![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}2f'(x_{0})&={\frac {f{\left(x_{0}{+}h\right)}-f(x_{0})}{h}}-{\frac {f{\left(x_{0}{-}h\right)}-f(x_{0})}{h}}-2{\frac {f^{(3)}(x_{0})}{3!}}h^{2}+\cdots \\[1ex]f'(x_{0})&={\frac {f{\left(x_{0}{+}h\right)}-f{\left(x_{0}{-}h\right)}}{2h}}-{\frac {f^{(3)}(x_{0})}{3!}}h^{2}+\cdots \\&={\frac {f{\left(x_{0}{+}h\right)}-f{\left(x_{0}{-}h\right)}}{2h}}+{\mathcal {O}}{\left(h^{2}\right)}.\end{aligned}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a855d52377de015dd20755ceaab94f4089530330)

![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}0&={\frac {f{\left(x_{0}{+}h\right)}-f(x_{0})}{h}}+{\frac {f{\left(x_{0}{-}h\right)}-f(x_{0})}{h}}-2{\frac {f^{(2)}(x_{0})}{2!}}h-2{\frac {f^{(4)}(x_{0})}{4!}}h^{3}+\cdots .\\[1ex]f^{(2)}(x_{0})&={\frac {f{\left(x_{0}{+}h\right)}+f{\left(x_{0}{-}h\right)}-2f(x_{0})}{h^{2}}}-2{\frac {f^{(4)}(x_{0})}{4!}}h^{2}+\cdots .\\[1ex]f^{(2)}(x_{0})&={\frac {f{\left(x_{0}{+}h\right)}+f{\left(x_{0}{-}h\right)}-2f(x_{0})}{h^{2}}}+{\mathcal {O}}{\left(h^{2}\right)}.\end{aligned}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4b14417c1fdddd0ed0cebee61933a6963a31052d)