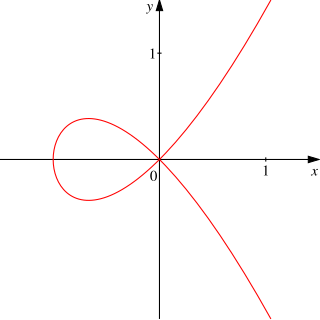Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Crunode
Point where a curve intersects itself at an angle From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In mathematics, a crunode[1] (archaic; from Latin crux "cross" + node[2]) or node of an algebraic curve is a type of singular point at which the curve intersects itself so that both branches of the curve have distinct tangent lines at the point of intersection. A crunode is also known as an ordinary double point.[3][4]
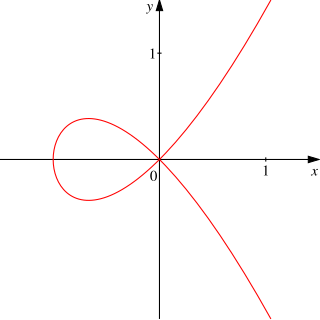
In the case of a smooth real plane curve f(x, y) = 0, a point is a crunode provided that both first partial derivatives vanish
and the Hessian determinant is negative:
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads