Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
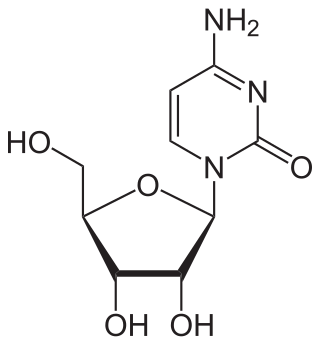
Cytidine
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Cytidine (symbol C or Cyd) is a nucleoside molecule that is formed when cytosine is attached to a ribose ring (also known as a ribofuranose) via a β-N1-glycosidic bond. Cytidine is a component of RNA. It is a white water-soluble solid[2] that is only slightly soluble in ethanol.[1]
Remove ads
Dietary sources
Dietary sources of cytidine include foods with high RNA (ribonucleic acid) content,[3] such as organ meats, brewer's yeast, as well as pyrimidine-rich foods such as beer. During digestion, RNA-rich foods are broken-down into ribosyl pyrimidines (cytidine and uridine), which are absorbed intact.[3] In humans, dietary cytidine is converted into uridine,[4] which is probably the compound behind cytidine's metabolic effects.
Remove ads
Cytidine analogues
A variety of cytidine analogues are known, some with potentially useful pharmacology. For example, KP-1461 is an anti-HIV agent that works as a viral mutagen,[5] and zebularine exists in E. coli and is being examined for chemotherapy. Low doses of azacitidine and its analog decitabine have shown results against cancer through epigenetic demethylation.[6]
Biological actions
In addition to its role as a pyrimidine component of RNA, cytidine has been found to control neuronal-glial glutamate cycling, with supplementation decreasing midfrontal/cerebral glutamate/glutamine levels.[7] As such, cytidine has generated interest as a potential glutamatergic antidepressant drug.[7]
Related compounds
- Deoxycytidine is cytosine attached to a deoxyribose.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads