Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase
Mammalian protein found in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase, also known as DHCR7, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DHCR7 gene.[5][6][7]
Remove ads
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is an enzyme catalyzing the production of cholesterol from 7-dehydrocholesterol using NADPH.
The DHCR7 gene encodes delta-7-sterol reductase (EC 1.3.1.21), the ultimate enzyme of mammalian sterol biosynthesis that converts 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) to cholesterol. This enzyme removes the C(7-8) double bond introduced by the sterol delta8-delta7 isomerases. In addition, its role in drug-induced malformations is known: inhibitors of the last step of cholesterol biosynthesis such as AY9944 and BM15766 severely impair brain development.[5]
Remove ads
Pathology
A deficiency is associated with Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome.[8]
All house cats and dogs have higher-than-usual activity of this enzyme, causing an inability to synthesize vitamin D due to the lack of 7-dehydrocholesterol.[9]
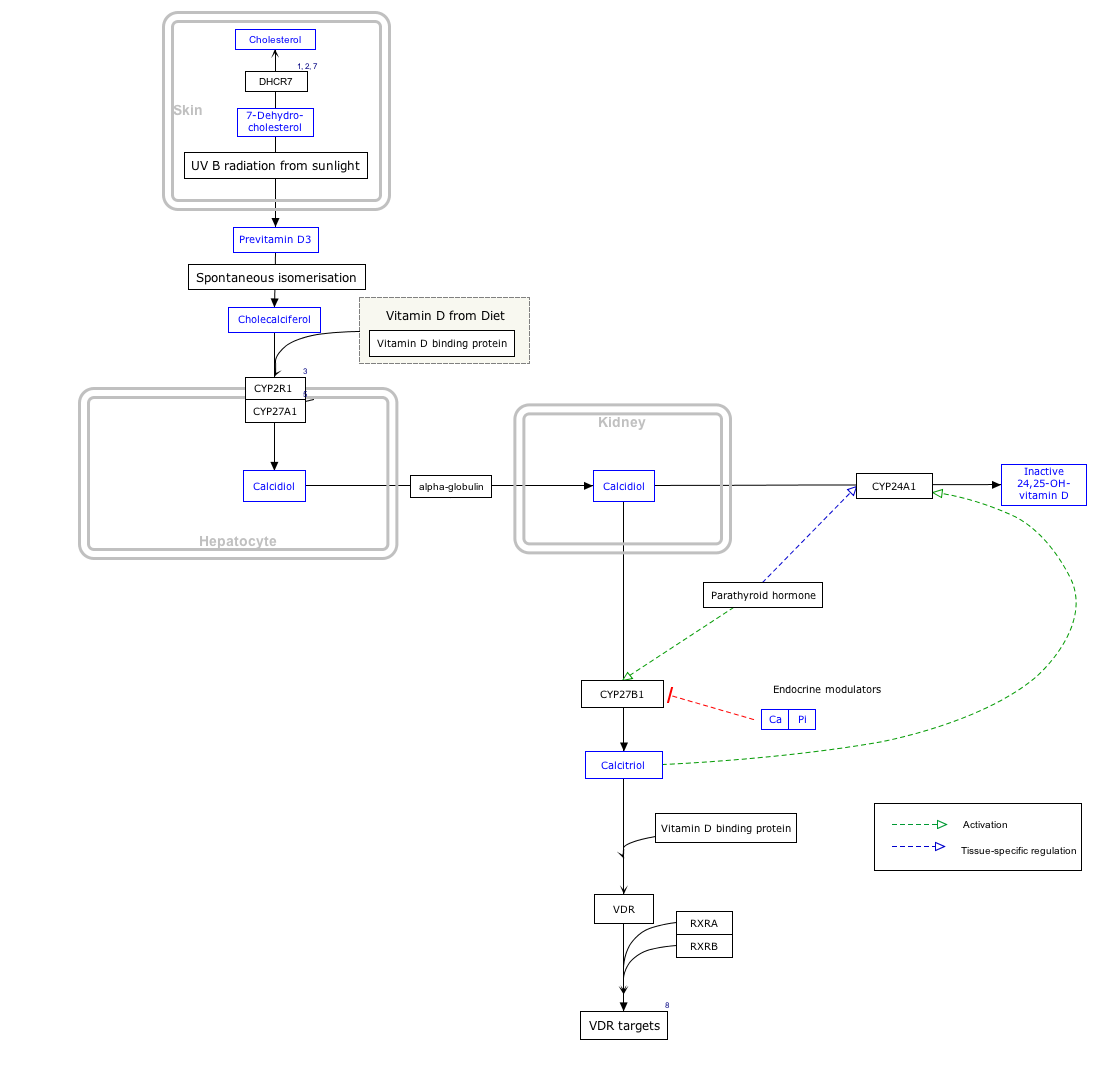
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads