Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Deoxyribonuclease gamma
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
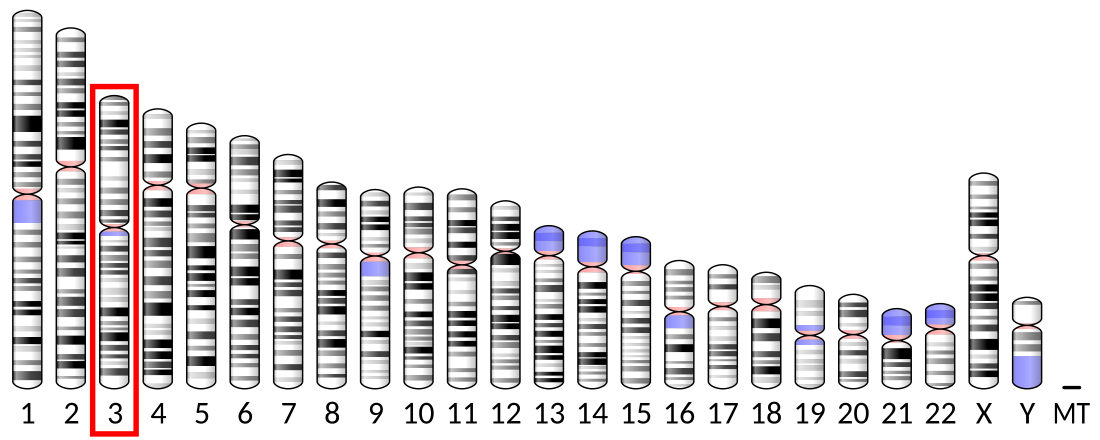
Deoxyribonuclease gamma (also termed DNase γ, deoxyribonuclease 1L3, DNASE1L3, of deoxyribonuclease I like 3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DNASE1L3 (also termed the deoxyribonuclease 1L3 or deoxyribonuclease 1 like 3) gene. This gene's is located on chromosome 3's "p arm", i.e., short arm, between region 1, band 4, sub-band 3 and region 2, band 1, sub-band 1 (this location's is abbreviation as 3p14.3-p21.1)[5][6]
Remove ads
Function
DNASE1L3 belongs to the family of deoxyribonuclease enzymes that are responsible for degrading DNA. Specifically, DNASE1L3 plays a key role in the breakdown of extracellular DNA, particularly DNA released from dying cells due to apoptosis or necrosis. This function is important for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing the accumulation of DNA debris, which could otherwise trigger widespread inflammatory autoimmune responses.[7]
Remove ads
Clinical significance
Summarize
Perspective
Role in autoimmune response
Humans with inactivating mutations in both of their DNASE1L3 genes have a greatly reduced ability fail to remove the extracellular DNA released by dead cell and therefore to eliminate these dead cells. This failure leads to the accumulation of DNA deposits and dead cells, which triggers autoimmune inflammation responses throughout the body.[8][9][10] These inflammatory responses cause the following types of inflammatory disorders.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a disorder in which an individua's immune system loses its tolerance for and therefore mounts inflammatory attacks on certain self-antigens in various tissues.[11] SLE most often develops in adults but in 10% to 20% of cases occurs in individuals less than 19 years old.[12][13] This childhood form of SLE, termed childhood-onset SLE, juvenile-onset SLE, juvenile SLE, or pediatric SLE,[14][15] is a more severe disorder than adult onset SLE in part because it more often involves lupus nephritis, kidney failure, and inflammation in the central nervous system.[16] A small percentage of pediatric SLE cases are caused by defects in both of an individual's DNASE1L3 genes.[9][10][16][17][18] These rare cases of pediatric SLE due to defective DNASE1L3 genes are classified as being one of the inborn error of immunity disorders.[8][14]
Other associated disorders
In extremely rare cases, inactivating mutations in the DNASE1L3 genes have also been associated with the development of pediatric rheumatoid arthritis[19][20][21][22] or the hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis syndrome (also known as McDuffie syndrome). Among 13 patients with this syndrome, four also had rheumatoid arthritis.[9][16][23] Individuals with DNASE1L3-deficient rheumatoid arthritis or hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis syndrome may concurrently present with additional inflammation-induced conditions such as alveolar hemorrhages, inflammatory bowel disease, uveitis, scleritis, inflammation of the gallbladder, or arthritis/arthralgia in multiple joints.[9][16]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads