Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
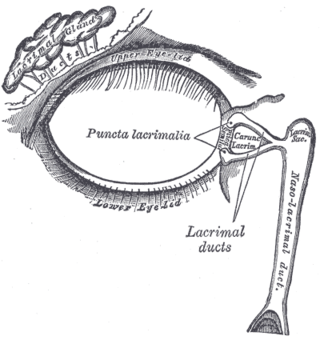
Dacryoadenitis
Medical condition From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Dacryoadenitis is inflammation of the lacrimal glands.[1]
Symptoms and signs
- Swelling of the outer portion of the upper lid, with possible redness and tenderness[citation needed]
- Pain in the area of swelling[citation needed]
- Excess tearing or discharge[citation needed]
- Swelling of lymph nodes in front of the ear[citation needed]
Complications
Swelling may be severe enough to put pressure on the eye and distort vision. Some patients first thought to have dacryoadenitis may turn out to have a malignancy of the lacrimal gland.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Causes
Acute dacryoadenitis is most commonly due to viral or bacterial infection. Common causes include mumps, Epstein-Barr virus, staphylococcus, and gonococcus.[citation needed]
Chronic dacryoadenitis is usually due to noninfectious inflammatory disorders. Examples include sarcoidosis, thyroid eye disease, and orbital pseudotumor.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
Dacryoadenitis can be diagnosed by examination of the eyes and lids. Special tests such as a CT scan may be required to search for the cause. Sometimes biopsy will be needed to be sure that a tumor of the lacrimal gland is not present.[citation needed]
Prevention
Mumps can be prevented by immunization. Gonococcus, bacteria can be avoided by the use of condoms. Most other causes cannot be prevented.[citation needed]
Treatment
If the cause of dacryoadenitis is a viral condition such as mumps, simple rest and warm compresses may be all that is needed. For other causes, the treatment is specific to the causative disease.[citation needed]
Prognosis
Most patients will fully recover from dacryoadenitis. For conditions with more serious causes, such as sarcoidosis, the prognosis is that of the underlying condition.[citation needed]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads