Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
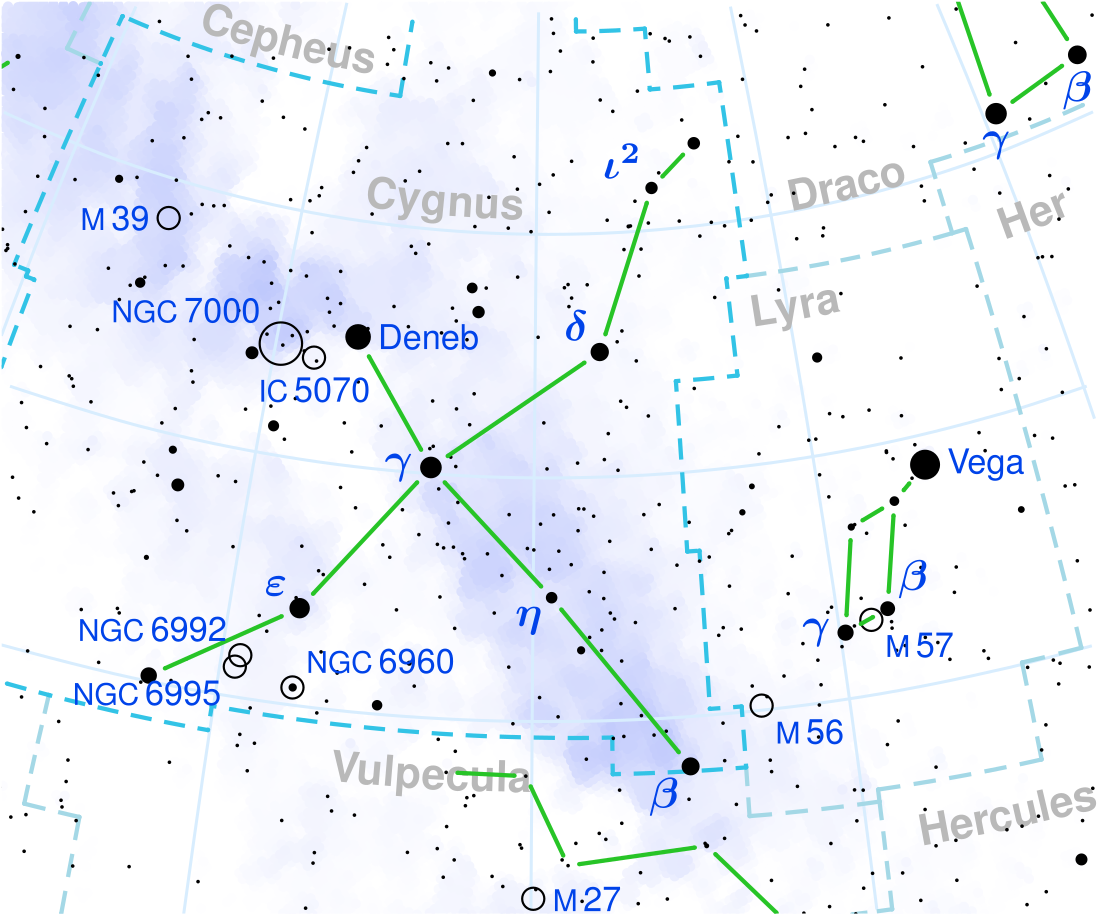
Delta Cygni
Third-magnitude star in the constellation Cygnus From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Delta Cygni is a binary star of a combined third-magnitude in the constellation of Cygnus. It is also part of the Northern Cross asterism whose brightest star is Deneb. Its name is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from δ Cygni, and abbreviated Delta Cyg or δ Cyg. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, Delta Cygni is located roughly 165 light-years (51 parsecs) distant from the Sun.[1]
Delta Cygni's two components are designated Delta Cygni A (officially named Fawaris /fəˈwɛərɪs/)[12] and B. More widely separated is a faint third component, a 12th magnitude star that is moving along with the others. Together they form a triple star system.[13]
Remove ads
Nomenclature
Summarize
Perspective
δ Cygni (Latinised to Delta Cygni) is the binary's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as Delta Cygni A and B derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).[14]
Traditionally, Delta Cygni had no proper name.[13] It belonged to the Arabic asterism al-Fawāris (الفوارس), meaning "the Riders" in indigenous Arabic,[15] together with Zeta, Epsilon, and Gamma Cygni, the transverse of the Northern Cross. In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[16] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN decided to attribute proper names to individual stars rather than entire multiple systems.[17] It approved the name Fawaris for the component Delta Cygni A on 1 June 2018 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[12]
In Chinese, 天津 (Tiān Jīn), meaning Celestial Ford, refers to an asterism consisting of Delta Cygni, Gamma Cygni, 30 Cygni, Alpha Cygni (Deneb) and Nu, Tau, Upsilon, Zeta and Epsilon Cygni.[18] Consequently, the Chinese name for Delta Cygni itself is 天津二 (Tiān Jīn èr, English: the Second Star of Celestial Ford).[19]
Remove ads
Properties
Summarize
Perspective
The primary, Delta Cygni A, is a blue-white giant star of spectral class B9,[4] with a temperature of 10,400 K.[11] It is nearing the end of its main-sequence life stage with a luminosity 155 times that of the Sun,[10] a radius of 4.81 solar radii,[11] and a mass approximately 2.93 solar masses. Like many hot stars, it spins rapidly, at least 135 kilometers per second at the equator, about 60 times that of the Sun.[10]
The close companion Delta Cygni B is a yellow-white F-type main-sequence star of the sixth magnitude (6.33) with a luminosity about 6 times that of the Sun, and a mass about 1.5 times the Sun's. The two stars orbit each other at an average distance of 157 AU and a period of 780 years.[13]
The much more distant third companion is an orange (class K) twelfth magnitude star, and only two thirds as massive.[13]
The two main stars together appear with a spectral type of A0 IV.[3] As seen from Earth, the entire triple star system of Delta Cygni shines at a combined apparent magnitude of 2.87.[2] Both δ Cygni A and B have been suspected to vary in brightness. δ Cygni A was reported in 1951 as varying between magnitudes 2.85 and 2.89, and δ Cygni B was reported in 1837 to vary between magnitudes 6.3 and 8.5. The variability of the stars has not been confirmed.[6]
Remove ads
Pole Star
Delta Cygni is a visible star located within 3° of the precessional path traced across the celestial sphere by the Earth's North pole. For at least four centuries around 11,250 AD it will probably be considered a pole star, a title currently held by Polaris which is just 0.5° off of the precessional path.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads