Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
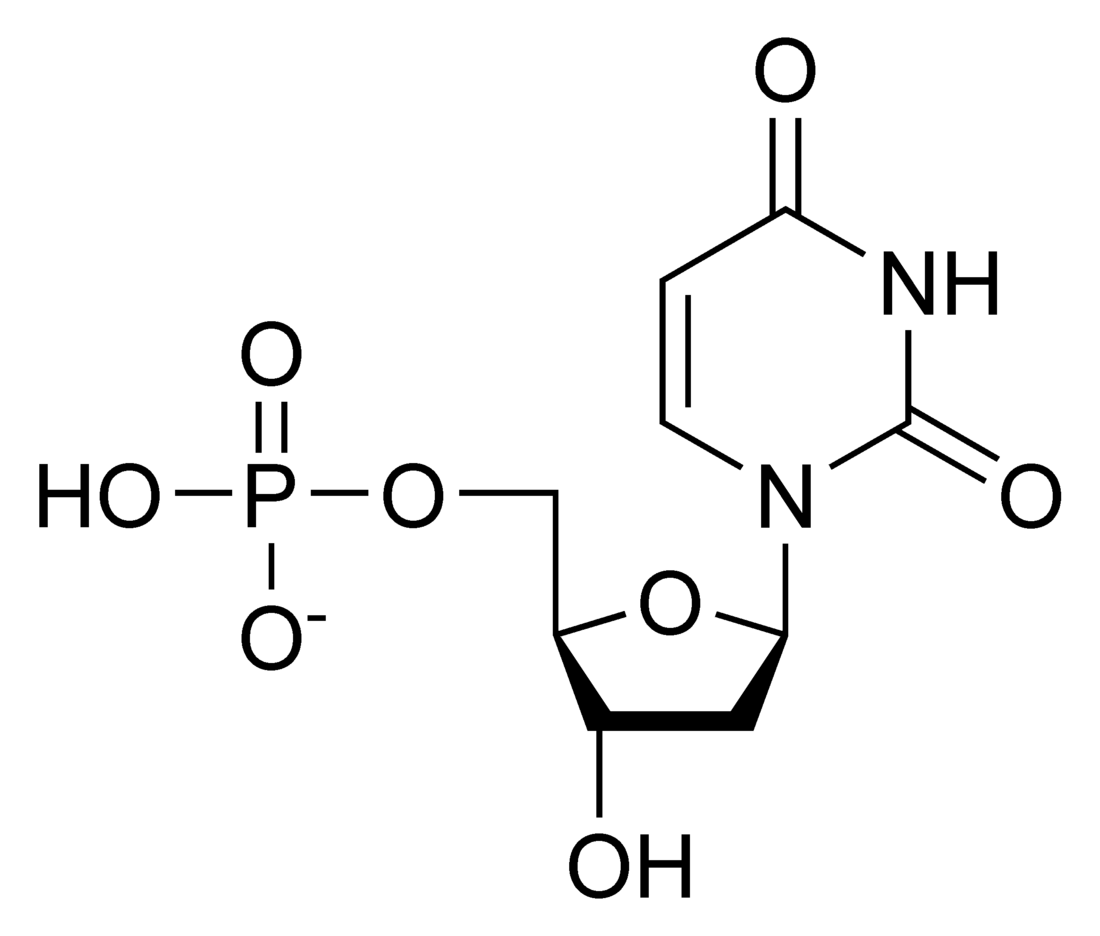
Deoxyuridine monophosphate
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP), also known as deoxyuridylic acid or deoxyuridylate in its conjugate acid and conjugate base forms, respectively, is a deoxynucleotide.
It is an intermediate in the metabolism of deoxyribonucleotides.
Remove ads
Biosynthesis
Deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) is the deoxygenated form of uridine monophosphate (UMP), and is the precursor to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP), a component of DNA nucleotide biosynthesis.[1] By replacing the hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon of ribose with a hydrogen, UMP becomes deoxygenated to dUMP.
The synthesis of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) is a multi-step process that begins with uridine monophosphate (UMP), the product of pyrimidine biosynthesis.[2] The enzyme nucleoside monophosphate kinase converts UMP and ATP to uridine diphosphate (UDP) and ADP.
In the presence of excess ATP, the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase initiates a chain reaction with UDP, which catalyzes the formation of deoxyuridine diphosphate (dUDP), which is then converted to deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP), then deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) via the addition or removal of phosphate groups.[3]
Remove ads
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.[§ 1]
Fluorouracil (5-FU) Activity edit
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "FluoropyrimidineActivity_WP1601".
Remove ads
See also
Notes
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads