Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Dipolar compound
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In organic chemistry, a dipolar compound or simply dipole is an electrically neutral molecule carrying a positive and a negative charge in at least one canonical description. In most dipolar compounds the charges are delocalized.[1] Unlike salts, dipolar compounds have charges on separate atoms, not on positive and negative ions that make up the compound. Dipolar compounds exhibit a dipole moment.
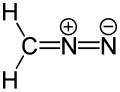
Example of a dipolar compound, represented by a resonance structure (isocyanide)
Dipolar compounds can be represented by a resonance structure. Contributing structures containing charged functional groups are denoted as zwitterions. Therefore, while all zwitterions are dipolar compounds, not all dipolar compounds are zwitterions because many polar molecules achieve their dipole moment through partial charges rather than full, discrete ionic functional groups.[2][3][4][5][6] Some dipolar compounds, e.g. amides, can have an uncharged canonical form.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Types of dipolar compounds
- 1,2-dipolar compounds have the opposite charges on adjacent atoms.
- 1,3-dipolar compounds have the charges separated over three atoms.[1] They are reactants in 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions.
- Also 1,4-dipolars,[4] 1,5-dipolars, and so on exist.
Examples
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
![{\displaystyle {[\mathrm {R} {-}{\overset {\oplus }{\mathrm {N} }}{\equiv }{\overset {\ominus }{\mathrm {C} }}{\text{:}}{}\mathrel {\longleftrightarrow } {}\mathrm {R} {-}{\ddot {N}}{=}\mathrm {C} {\text{:}}]}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5755177ecf83528cc710550d28d4727f06d6f8f0)