Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
E (musical note)
Also known as Mi From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
E is the third note and the fifth semitone of the C major scale, and mi in fixed-do solfège. It has enharmonic equivalents of F♭ [(F-flat) which is by definition a diatonic semitone above E♭] and D![]() (D-double sharp), amongst others.
(D-double sharp), amongst others.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2025) |
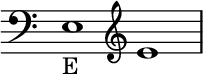
When calculated in equal temperament with a reference of A above middle C as 440 Hz, the frequency of Middle E (E4) is approximately 329.628 Hz.[1] See pitch (music) for a discussion of historical variations in frequency.
Remove ads
Designation by octave
Remove ads
Scales
Common scales in the key of E.
- E major: E F♯ G♯ A B C♯ D♯ E
- E natural minor: E F♯ G A B C D E
- E harmonic minor: E F♯ G A B C D♯ E
- E melodic minor ascending: E F♯ G A B C♯ D♯ E
- E melodic minor descending: E D C B A G F♯ E
E major modes (diatonic scales).
E melodic (Jazz) minor modes
- E ascending melodic minor: E F♯ G A B C♯ D♯ E
- E Dorian ♭2: E F G A B C♯ D E
- E Lydian augmented: E F♯ G♯ A♯ B♯ C♯ D♯ E
- E Lydian dominant: E F♯ G♯ A♯ B C♯ D E
- E Mixolydian ♭6: E F♯ G♯ A B C D E
- E Locrian ♮2: E F♯ G A B♭ C D E
- E altered: E F G A♭ B♭ C D E
E harmonic minor modes
E harmonic major modes
Remove ads
F-flat

F♭ is a common enharmonic equivalent of E, but is not regarded as the same note. F♭ is commonly found after E♭ in the same measure in pieces where E♭ is in the key signature, in order to represent a diatonic, rather than a chromatic semitone; writing an E♭ with a following E♮ is regarded as a chromatic alteration of one scale degree.
References
See also
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads